Understanding Gum Disease: Causes and Effective Treatments
This article explores common causes of gum disease, including plaque buildup, medications, lifestyle habits, and nutritional deficiencies. It offers practical remedies like professional cleanings, proper flossing, a balanced diet, and lifestyle changes. Emphasizing the importance of early detection and professional consultation, the piece guides readers toward maintaining optimal oral health to prevent serious complications.
Sponsored
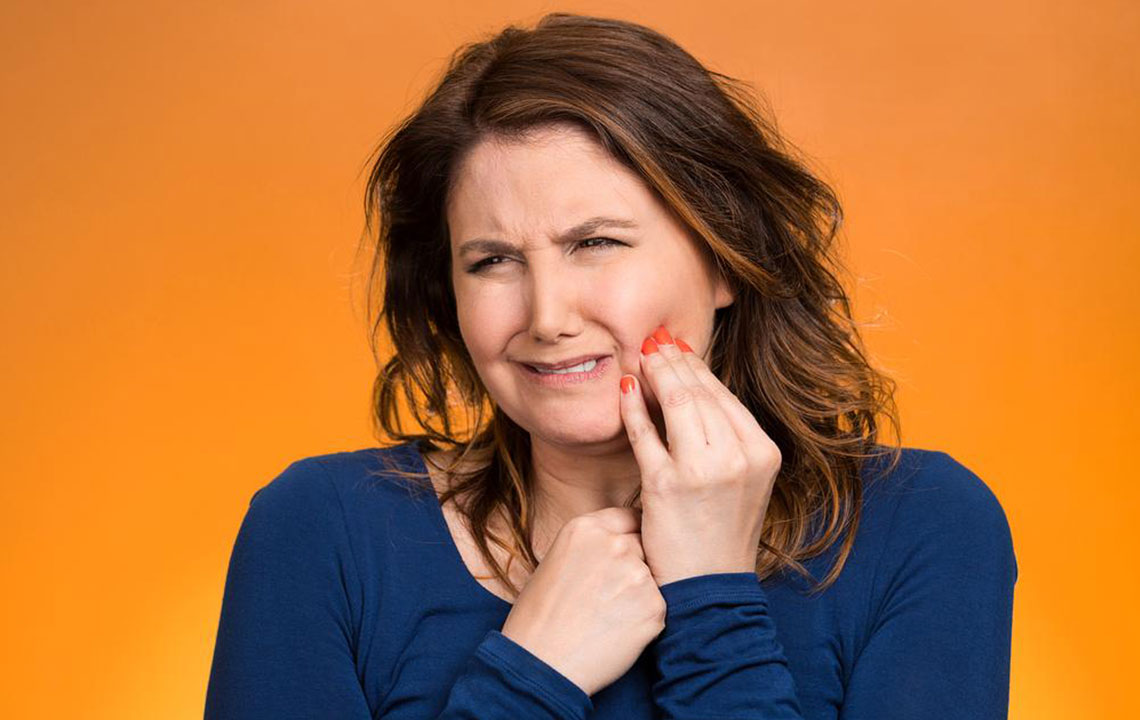

Maintaining good oral health is vital for overall well-being, as issues like cavities and gum infections can lead to serious health complications such as diabetes and breathing problems. Besides health concerns, these conditions can cause discomfort and inconvenience.
Common causes of gum disease and practical solutions include:
Plaque Buildup: A sticky, clear film filled with bacteria, plaque often leads to gum infections. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, which brushing alone cannot remove, requiring professional cleaning.
Dentists can perform simple procedures like cleaning to eliminate plaque.
Medications: Blood-thinning drugs frequently contribute to swollen and bleeding gums, according to the American Dental Association. Other medicines may also affect gum health. Consult your dentist for tailored advice.
Flossing Habits: Changing how often and how you floss can sometimes cause gum bleeding, especially if you’re new to flossing or adjusting routines. Proper technique and consistency are key to avoiding problems.
Nutritional Gaps: A diet high in sugars and carbs but low in vitamin C and water increases the risk of gum disease. Eating a balanced, nutritious diet is an effective preventive strategy.
Proper oral hygiene, such as regular mouth rinses and green tea consumption, can help manage early gum issues like gingivitis.
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy-induced hormonal fluctuations can make gums more vulnerable. Special care and increased attention to oral health during pregnancy can prevent disease progression.
Smoking: Tobacco use damages gum tissues and impairs healing, significantly raising the risk of infections.
Genetics: A family history of gum problems can predispose individuals. Your dentist can suggest personalized remedies to mitigate risks.
Understanding these causes allows for targeted prevention and treatment. Home remedies such as mouthwash, green tea, and good hygiene practices often help. Nonetheless, consulting a dentist is crucial to identify the root cause and receive appropriate care.