Essential Insights into Gum Disease Prevention and Treatment
Gum disease affects many adults but is preventable through proper dental care and lifestyle choices. Recognizing early signs like bleeding gums and inflammation enables prompt treatment, which can save you from costly procedures later. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco and sugar, and visiting the dentist regularly are effective strategies to keep gums healthy. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and types of gum disease empowers individuals to take charge of their oral health and prevent serious complications. Proactive care leads to healthier smiles and overall well-being.
Sponsored
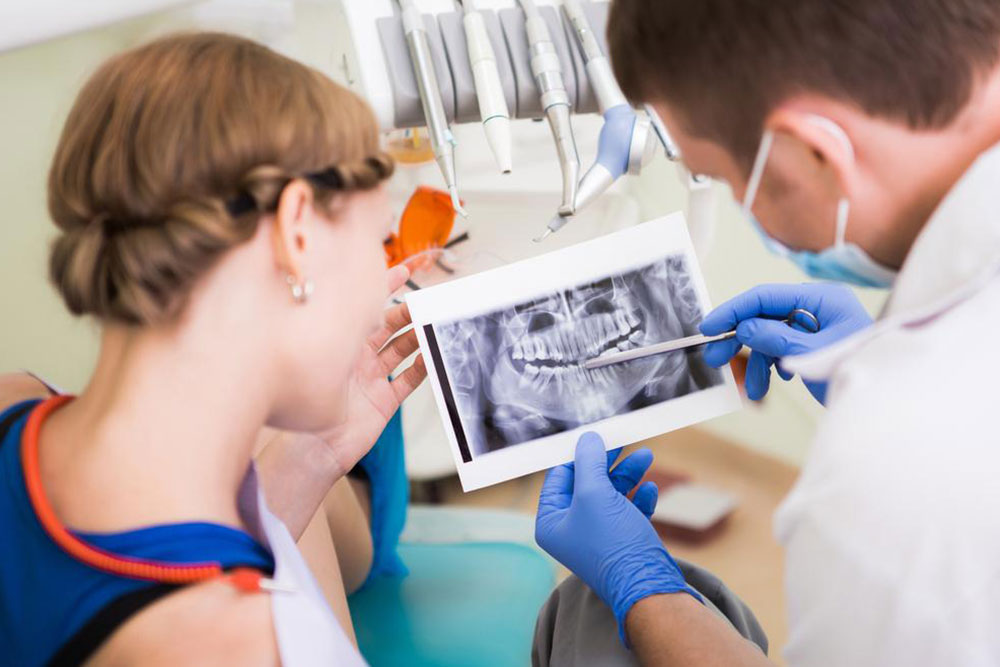
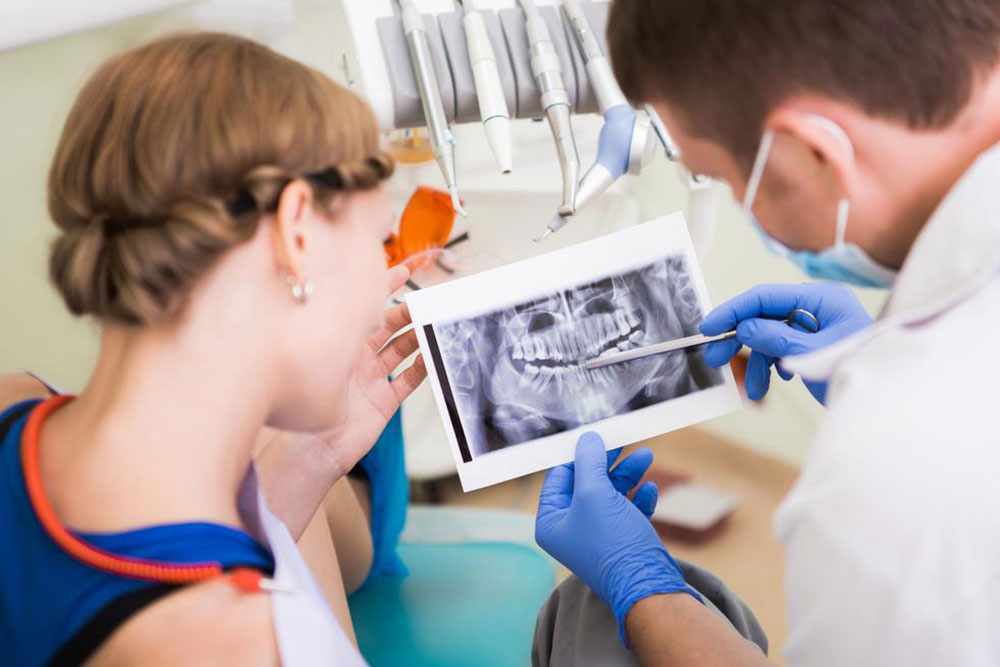
Gum disease is a widespread dental issue that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. According to the CDC, approximately 50% of adults in the United States experience some form of gum disease, with higher prevalence among seniors aged 65 and older. Fortunately, simple preventive measures such as proper oral hygiene, healthy diet, and routine dental check-ups can significantly reduce risks. Recognizing early signs like bleeding gums, inflammation, and receding teeth allows for timely intervention. Awareness and proactive care are key to maintaining healthy gums and overall oral health.
Causes of gum disease
Bacterial buildup in dental plaque primarily causes gum disease.
The bacteria consume sugars from dietary sources, releasing toxins that irritate the gums, leading to swelling and bleeding. If plaque isn't removed, it hardens into tartar, causing gum recession and potential bone loss. Factors elevating risk include poor oral hygiene, excessive sugar intake, smoking, genetic predisposition, and immune system weakness. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help strengthen gum health.
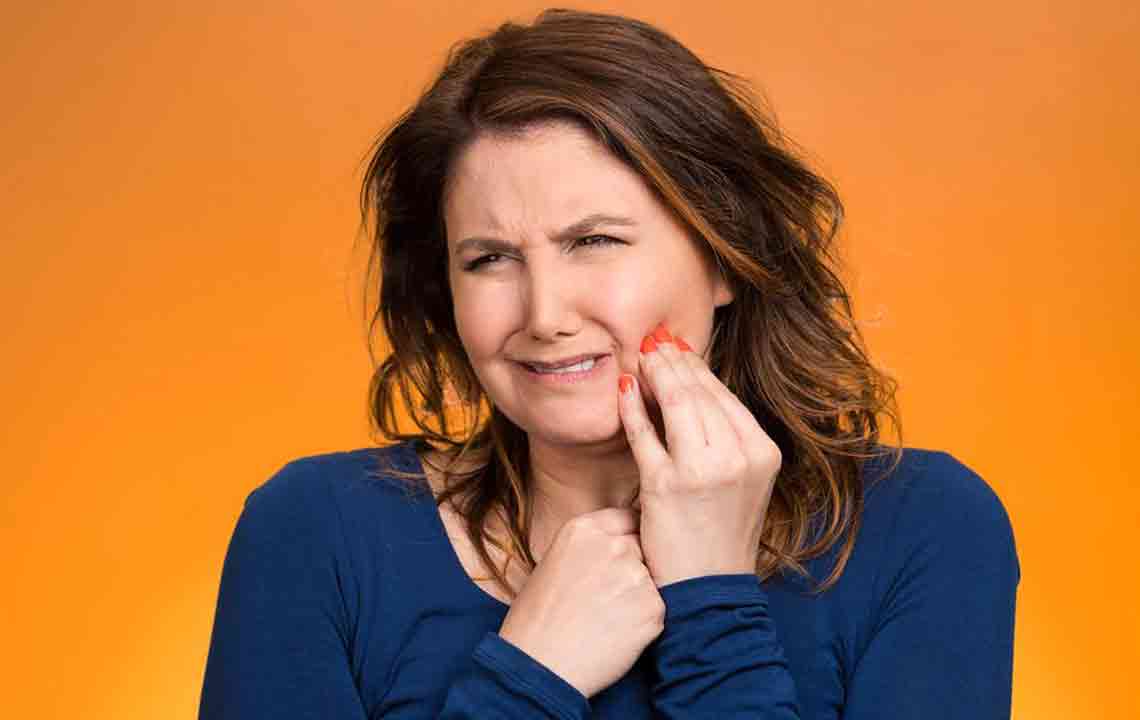
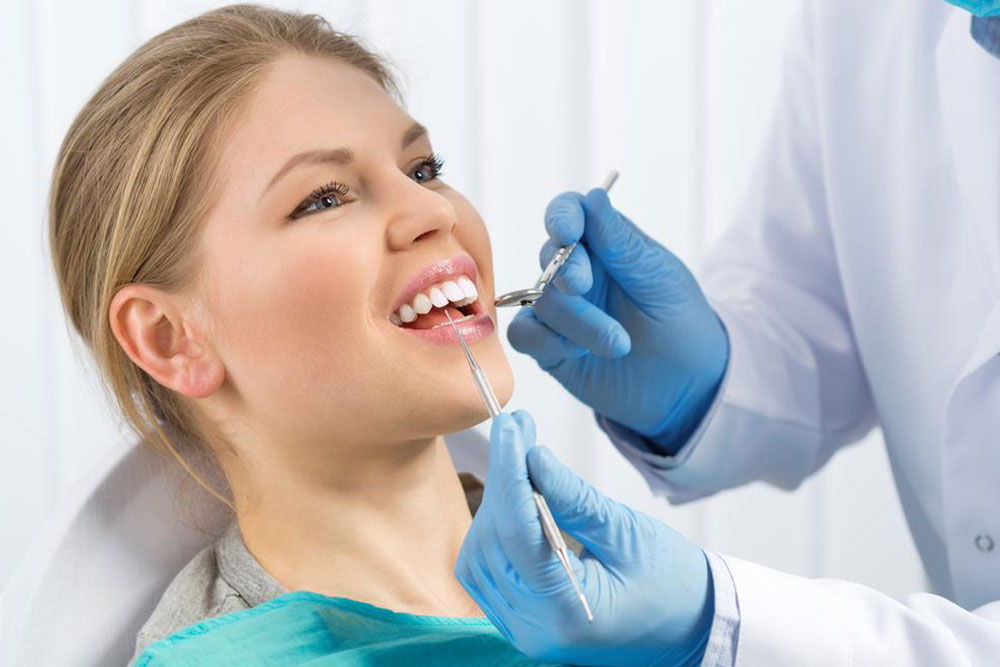
Signs to watch for include bleeding while brushing or flossing, gum inflammation, sensitivity, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath. Gum disease manifests mainly as gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis causes gums to become inflamed and bleed easily, often linked to stress, smoking, and hormonal changes. Over time, untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, damaging the supporting structures and causing tooth loss.
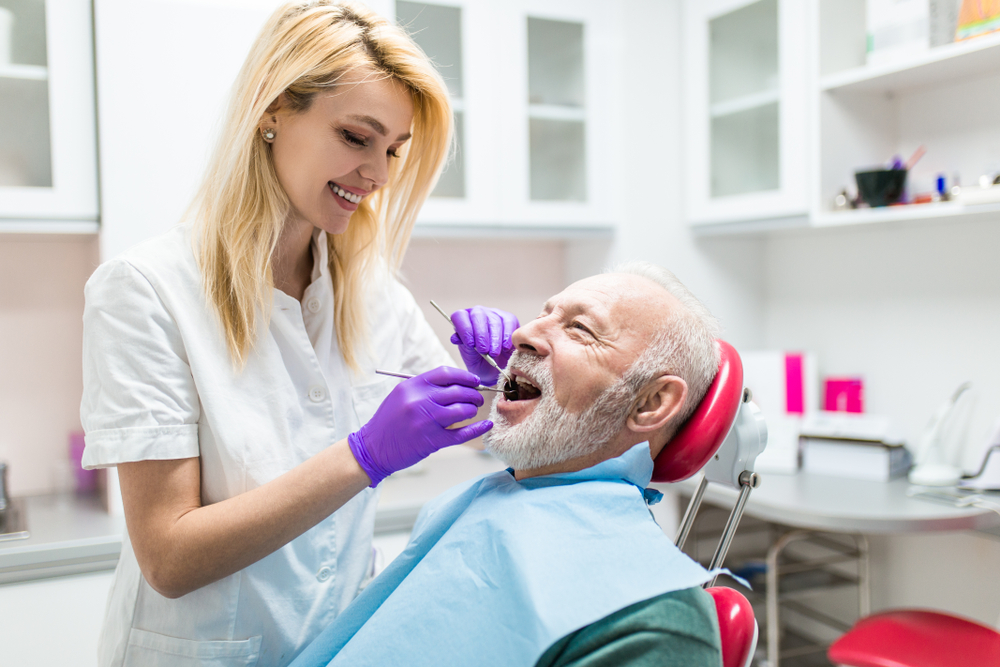
Effective prevention involves maintaining proper oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco and excess sugars, and scheduling regular dental visits for cleaning and evaluation. Early treatment of gum issues can prevent costly procedures like implants or surgeries. Adopting good habits ensures healthier gums and reduces the risk of severe dental problems. Staying informed and vigilant is essential for lasting oral health.