Comprehensive Overview of Five Eczema Types
Discover the key types of eczema, their symptoms, and triggers in this comprehensive guide. Learn how to identify atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, stasis dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Recognize symptoms early to seek proper treatment and improve skin health. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized care and appropriate medication options for each type of eczema.
Sponsored

Eczema is a prevalent skin disorder characterized by itchiness, inflammation, and redness. In the U.S., nearly 30 million individuals are affected by this non-contagious condition. Different eczema variants display unique symptoms and triggers, making accurate diagnosis essential for effective treatment. This article explores five notable types of eczema, highlighting their key features and visual references for better understanding. Whether it’s atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, stasis dermatitis, or seborrheic dermatitis, recognizing the signs helps in seeking appropriate medical care.
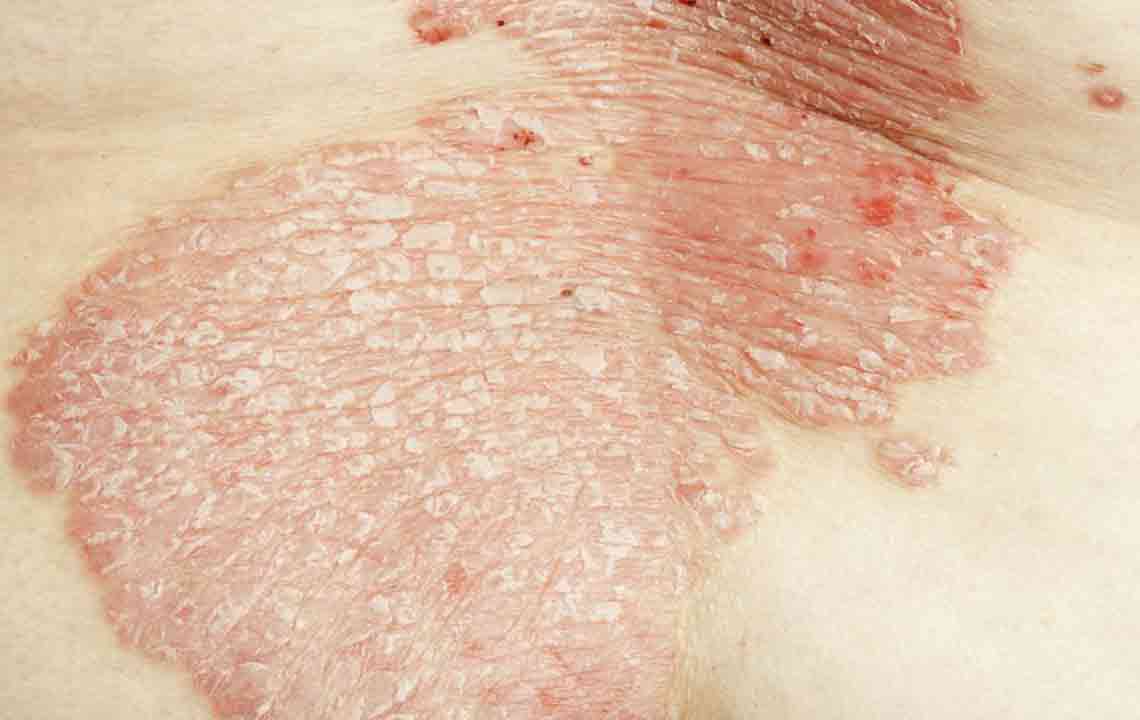
Atopic Dermatitis frequently begins in childhood, often improving or diminishing in severity by adulthood. It is part of the atopic triad, which includes hay fever and asthma, and presents with:
Dry, scaly skin
Intense itching
Redness
Rashes on limbs and cheeks
Crusted or weeping sores
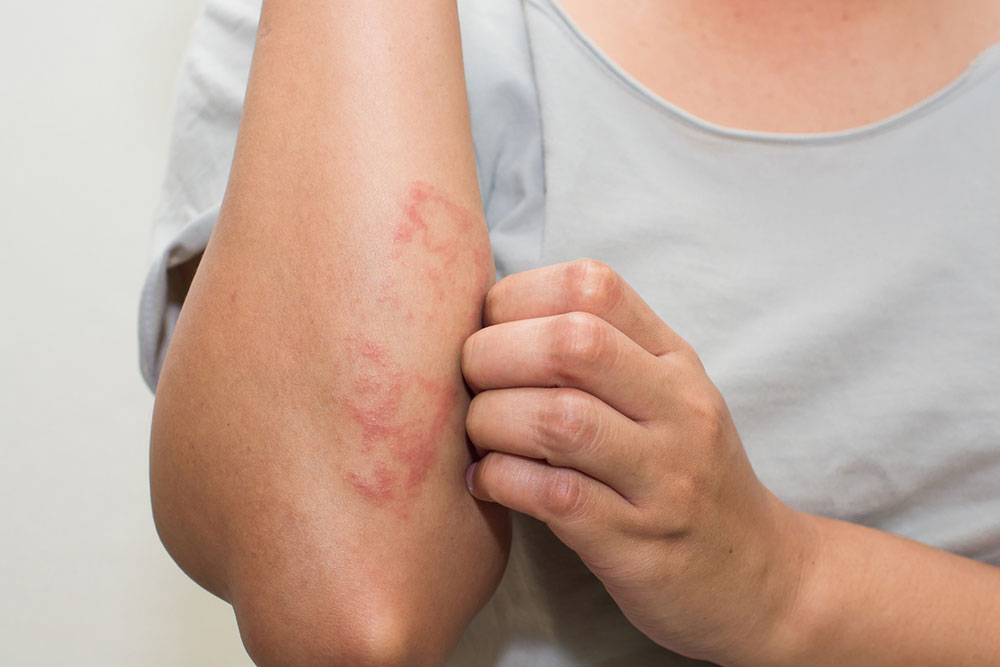
Contact Dermatitis occurs after skin contact with allergens or irritating substances, leading to symptoms such as:
Red, itchy, and burning skin
Hives or bumps
Thickening or scaly patches
Blisters that crust or weep
Dyshidrotic Eczema predominantly affects adults under 40, especially women. It manifests as itchy, small blisters on fingers, toes, palms, and soles, which may enlarge or fill with fluid, accompanied by cracking and flaking skin. Symptoms include:
Cracked, flaky, and scaly skin
Itchy or painful blisters
Stasis Dermatitis, also called venous or gravitational dermatitis, mainly targets lower legs. Typical signs include:
Swollen legs
Crusty patches
Dry, cracked skin
Itching and hot, blister-like spots
Seborrheic Dermatitis develops in oily skin areas, leading to itchy, flaky, and red patches that may be swollen or raised. Frequently affected regions include the scalp, face, ears, eyebrows, genitals, armpits, and upper back. White or yellow crusts often form on the surface. Always consult a healthcare professional before using treatments to ensure proper care.