Top 5 Factors to Prevent Gout Attacks
Prevent gout attacks by understanding key triggers like medication effects, obesity, diet, dehydration, and improper footwear. Managing these factors can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve joint health.
Sponsored

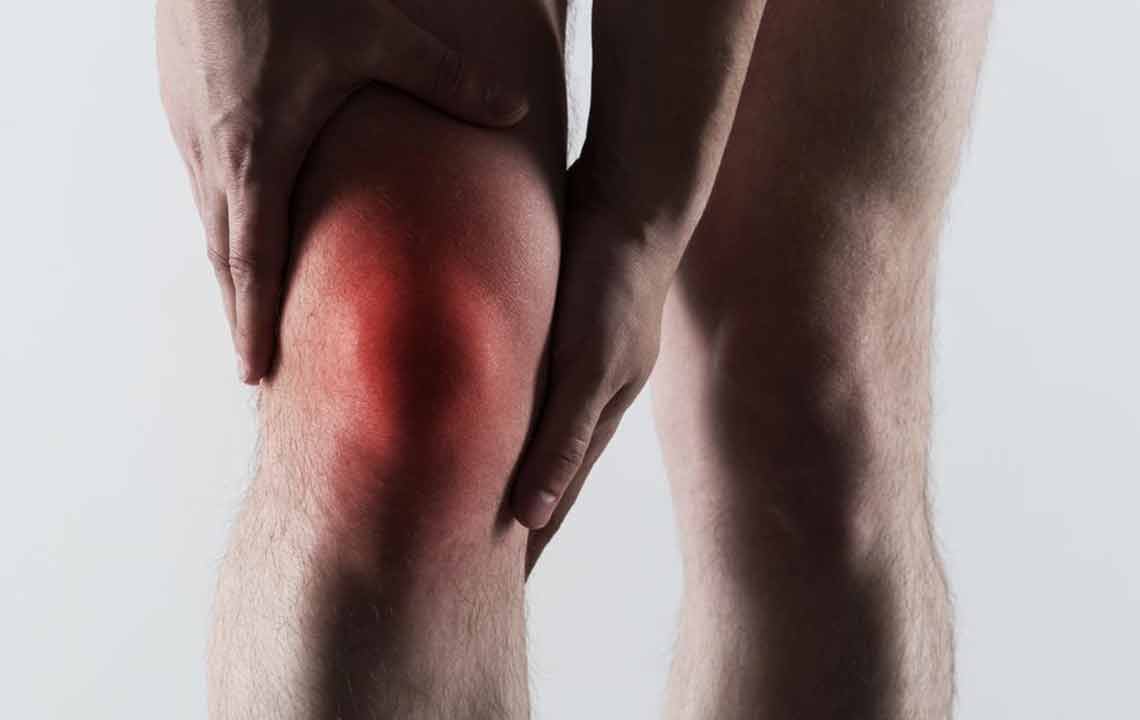
Gout is a painful form of arthritis that targets joints, causing intense discomfort. The pain is so severe that even gentle touches can feel unbearable. While movement is a major trigger, other factors also contribute significantly to gout flare-ups.
Medications and substances
Understanding what causes gout helps in managing triggers. Gout results from uric acid buildup in the blood.
Uric acid forms when purines—found in many foods—break down. Normally excreted via urine, excess uric acid can deposit in joints, forming sharp crystals that cause pain and swelling.
Interestingly, some medications, like aspirin, can increase uric acid levels. Even low-dose aspirin may trigger gout, especially in women. Diuretics such as hydrochlorothiazide, metolazone, and chlorothiazide can also impair the kidneys’ ability to eliminate uric acid, raising the risk of gout. Other drugs like cyclosporine, ACE inhibitors, and certain chemotherapy treatments may contribute as well.
Excess weight
Obesity heightens the chances of developing gout. Additional body fat increases uric acid levels, and insulin resistance may elevate uric acid production. Fat deposits and impaired kidney function in overweight individuals hinder uric acid elimination.
Foods high in purines
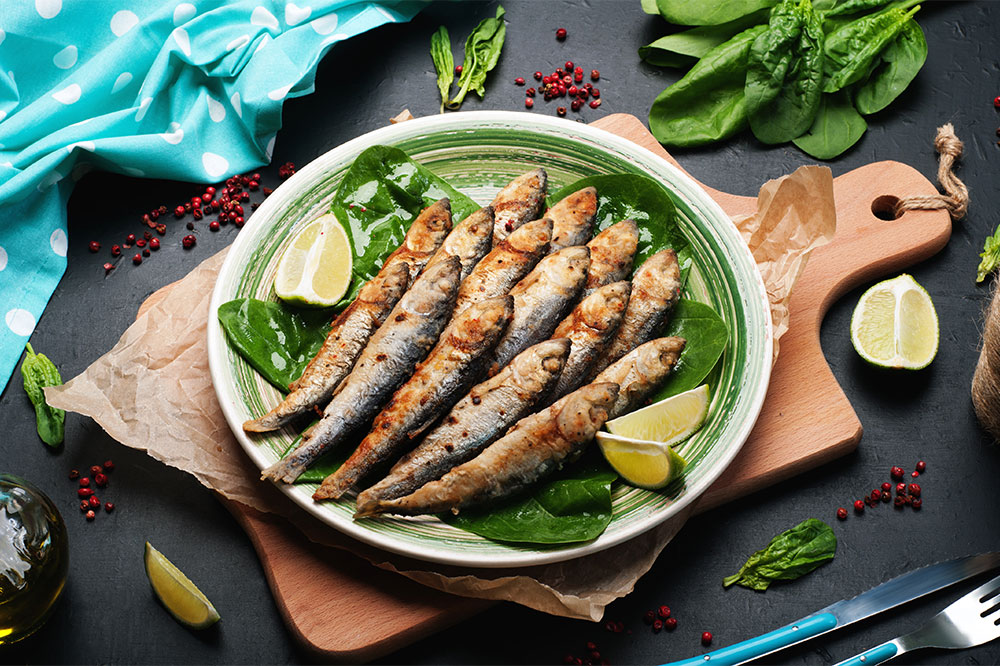
Consuming foods rich in purines can lead to increased uric acid. Limit intake of organ meats, high-fat fish like salmon and sardines, bacon, mutton, and turkey. Sugary drinks and alcohol, which are also high in purines, should be consumed minimally.
Dehydration
Dehydration can cause blood uric acid levels to rise, making it harder for kidneys to expel uric acid. Staying well-hydrated by drinking six to eight ounces of water daily is vital to prevent gout attacks.
Inappropriate footwear
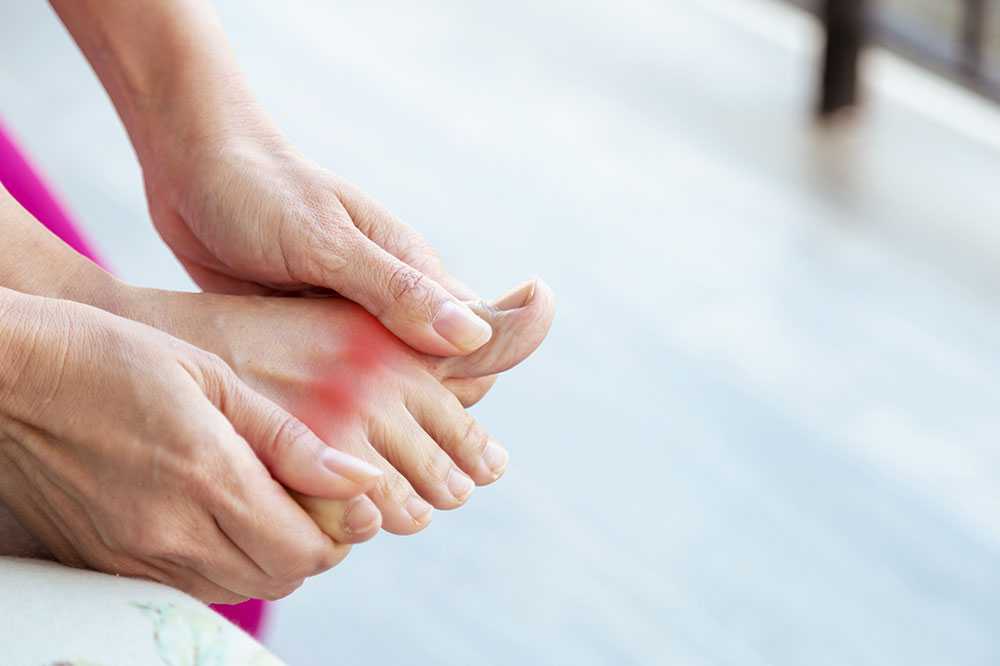
The big toe is often affected by gout. Wearing proper shoes that don't cause pressure or friction is essential. Avoid tight-fitting shoes, and women should choose lower-heeled options to reduce stress on the toe joint.