Understanding Gout-Related Foot Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Discover comprehensive insights into gout foot pain, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods, and effective treatment strategies. Early intervention is key to managing this common yet painful condition and preventing long-term joint damage.
Sponsored
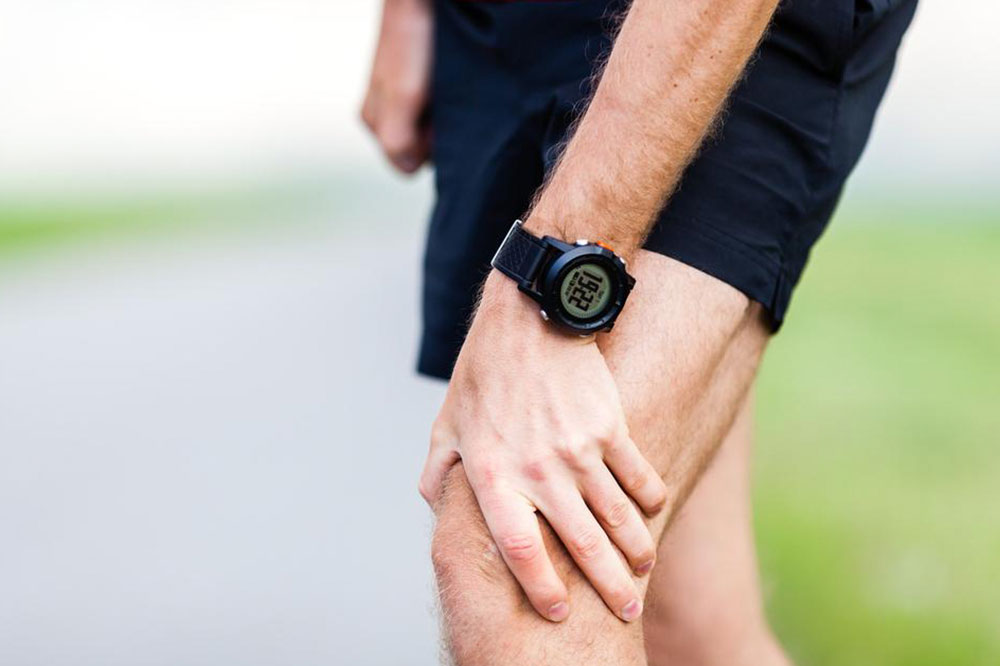
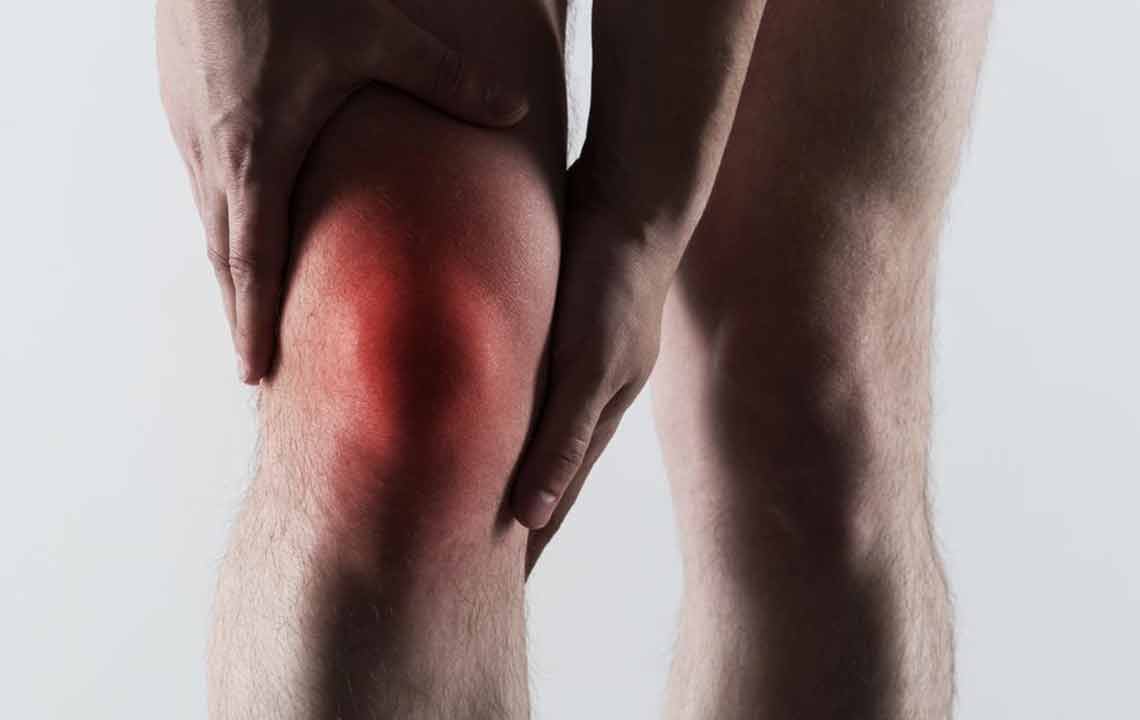
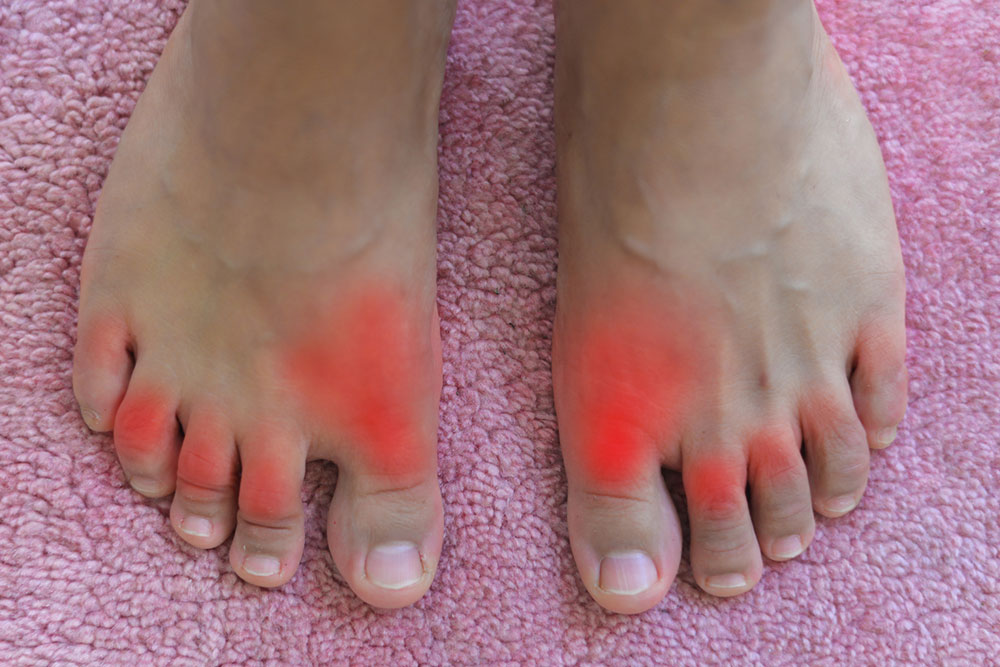
Gout is a prevalent form of arthritis characterized by sudden, intense burning pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joint. It most commonly targets the big toe but can also affect the ankles and knees. If left untreated, gout may cause joint damage and tissue inflammation. Men are more frequently affected than women. Effective management and prompt treatment are essential to prevent complications and alleviate discomfort.
What leads to gout?
Factors such as obesity, excessive alcohol intake, and high-purine foods like red meat and certain fish increase the risk of developing gout. Medications can also trigger gout episodes in some cases.
Recognizing the symptoms
Gout attacks often cause sudden swelling, redness, tenderness, and sharp pain, primarily affecting the big toe. The pain may extend to the ankles, knees, or other joints. Episodes can last from a few days to weeks. Some individuals experience infrequent gout attacks, while others may go months or years without symptoms.
Diagnosing gout
If you experience unexplained foot pain, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Diagnosing gout involves physical examinations, joint fluid analysis for uric acid crystals, and blood tests to measure uric acid levels. Accurate diagnosis ensures proper treatment planning.
Approaches to treatment
Effective management involves medications tailored to reduce pain and lower uric acid levels. Initial high-dose drugs can mitigate symptoms quickly, followed by dosage reduction as symptoms improve. Rest and avoiding stress on the affected joint are vital. Anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed for severe pain. The primary goal is to control uric acid buildup and prevent future attacks, making prompt treatment crucial.