Top 5 Lifestyle Habits That Increase Gout Risk
Gout, a form of arthritis, affects millions and is influenced by lifestyle choices. Key risk factors include crash dieting, dehydration, excess weight, diet, and alcohol. Avoiding these habits can lower gout risk and promote joint health. Understanding these factors helps in managing and preventing gout flare-ups effectively.
Sponsored

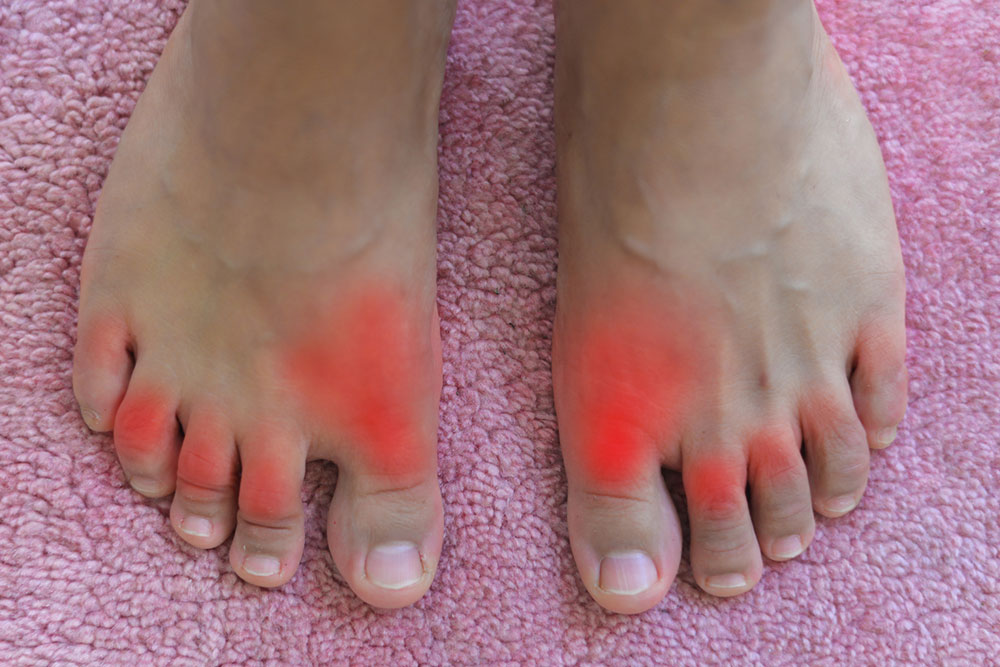
Gout is a prevalent form of arthritis affecting approximately 8.3 million Americans, characterized by sudden and intense joint pain. It primarily impacts the big toe, leading to swelling, stiffness, and discomfort. Flare-ups can occur unexpectedly, with pain lasting days, damaging joint tissues over time. Elevated uric acid levels cause uric acid crystals to deposit in joints, triggering inflammation. Besides genetics and medications, certain lifestyle choices significantly raise the risk of gout, including dietary and behavioral habits.
Several habits contribute to higher uric acid levels, leading to gout attacks. These include extreme dieting, dehydration, excess weight, poor dietary choices, and alcohol intake.
Extreme dieting and fasting - Severe calorie restrictions or prolonged fasting can cause the body to break down tissues, increasing purines and uric acid production, thus elevating gout risk.
Dehydration - Insufficient water intake results in concentrated uric acid in the blood, making crystal deposit formation more likely and triggering gout episodes.
Overweight - Excess body weight enhances uric acid synthesis and hampers its elimination, making obese individuals more susceptible to gout.
Dietary habits - Consuming foods high in purines such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood increases uric acid levels, promoting gout formation.
Alcohol consumption - Alcohol impairs kidney function, reducing uric acid clearance and raising the likelihood of gout attacks.