Top Strategies for Managing Persistent Pain Effectively
Discover effective strategies to manage persistent pain, including dietary changes, hydration, stress relief, and proper posture. These lifestyle adjustments can improve quality of life and alleviate discomfort caused by chronic conditions.
Sponsored

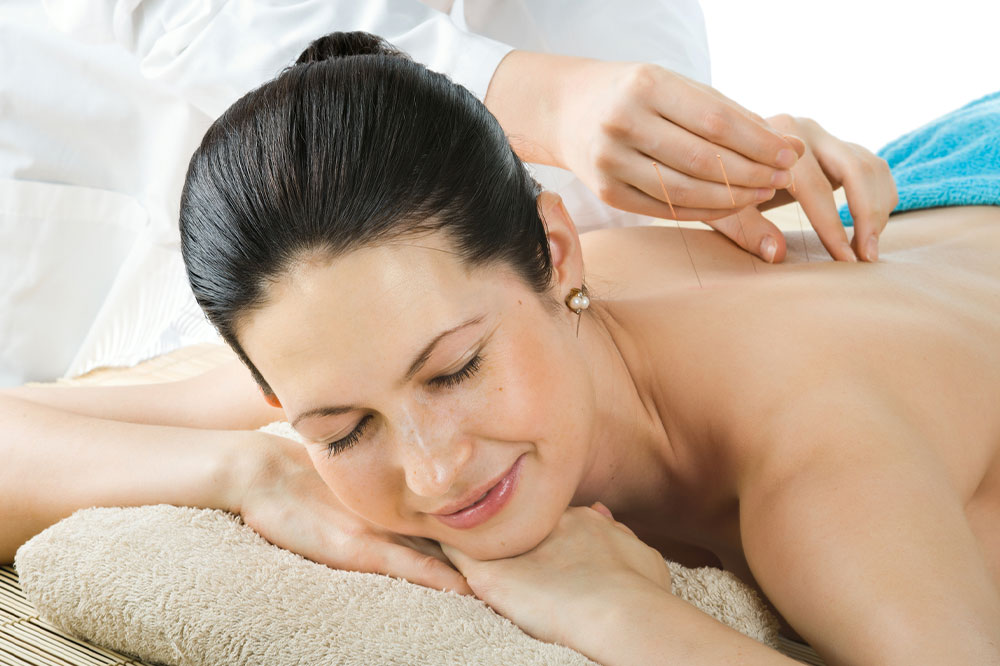
Persistent pain refers to discomfort that persists beyond three to six months and may last much longer. When pain endures for at least 12 weeks in a specific body part, it is classified as chronic. Approximately 100 million individuals in the country suffer from chronic pain. Sedentary lifestyles, poor diets, and high stress levels contribute to the rising number of chronic pain cases. Initially, pain may be temporary and intermittent, but if neglected, it can evolve into long-term suffering. Managing this pain is challenging but essential for maintaining quality of life.
Causes of chronic pain include injuries such as strains or ligament tears, excess weight, surgeries, and nerve damage. Other common reasons include inflammatory bowel disease, fibromyalgia, sciatica, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. These conditions often have physical origins but can also cause psychological effects, leading to emotional stress. Effective management involves lifestyle adjustments and treatments to alleviate symptoms and support a normal life.
Nutrition-rich diet: Incorporate foods that fight inflammation, such as omega-3 fatty acids, leafy greens, turmeric, ginger, and soy products. Reduce intake of processed foods, high-fat dairy, eggs, wheat products, red meat, oranges, lemons, tomatoes, and caffeinated drinks, as they can worsen pain.
Stay well-hydrated: Drinking enough water is vital for reducing the severity of back pain and headaches caused by dehydration. Aim for about eight glasses of water daily; avoid substituting with caffeinated or sugary beverages.
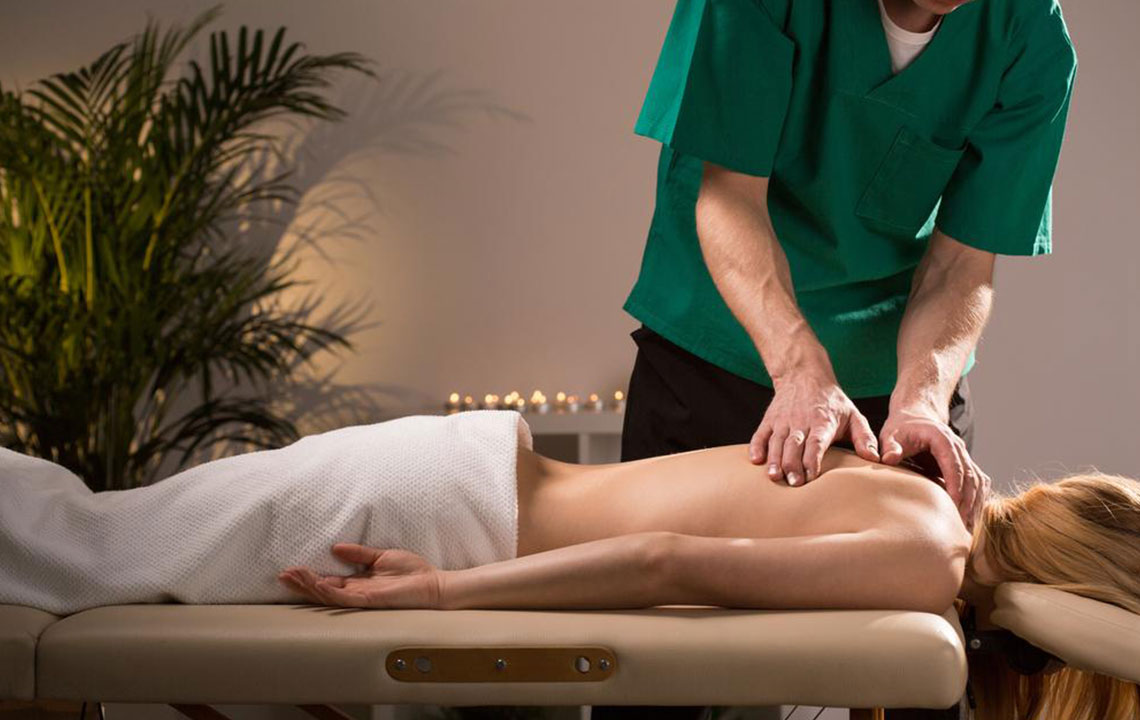
Stress management: Lower stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing, listening to relaxing music, yoga, tai chi, or massage therapy. Managing anxiety, anger, and depression can significantly decrease pain aggravation.
Exercise regularly: Even with pain, gentle and tailored physical activity can reduce weight, improve joint mobility, and boost mood through endorphin release. Consult a specialist to develop a suitable routine.
Avoid alcohol and smoking: Alcohol can disrupt sleep and heighten pain, while nicotine impairs circulation and immune health. Eliminating these substances promotes better pain management and overall well-being.
Correct posture: Maintaining proper sitting and standing posture minimizes pressure on the spine and neck, reducing the risk and severity of chronic pain, especially during long periods of sitting.