Top 7 Medical Applications of Botox Injections
Discover how Botox injections transcend cosmetic use, offering therapeutic solutions for conditions like migraines, depression, bladder issues, and more. FDA-approved and increasingly studied, Botox proves to be a versatile medical tool with significant benefits across multiple health concerns.
Sponsored
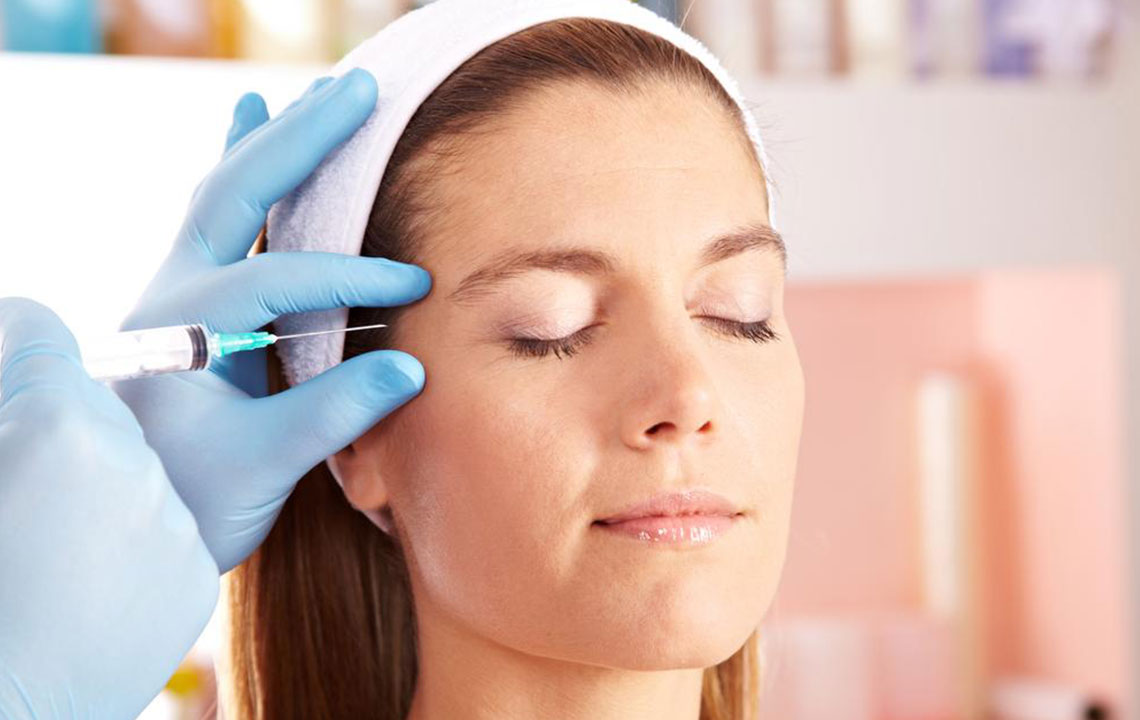

Top 7 Medical Benefits of Botox Injections
Botox, a well-known cosmetic treatment, has gained recognition for more than just improving appearance. Derived from the botulinum toxin, produced by the Clostridium botulinum bacteria found in soil and water, Botox operates by blocking the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, causing temporary muscle paralysis. While primarily used for smoothing wrinkles, it is also FDA-approved to treat various health conditions. Its versatility has surprised doctors, offering solutions for ailments such as depression, urinary issues, and migraines. Here are seven notable medical uses of Botox.
Depression: Emerging studies suggest Botox may help relieve depression symptoms, possibly via the facial feedback hypothesis, which links facial expressions to mood. Initial trials show promising results, prompting further research.
Early Ejaculation: Though not yet FDA-approved, Botox is being explored as a treatment for premature ejaculation by injecting it into the penile muscles to delay climax. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate its effectiveness.
Irregular Heartbeat: Post-surgery arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation are being examined for Botox treatment, aiming to understand its safety and potential to stabilize abnormal heart rhythms.
Overactive Bladder: FDA-approved Botox injections effectively reduce urinary leaks in overactive bladder patients. However, rare side effects include excessive bladder shutdown, making careful evaluation essential.
Neck Spasms: Botox is approved for cervical dystonia, providing relief from painful neck spasms by relaxing overly tense muscles.
Chronic Migraines: FDA-approved for migraine management, Botox injections into the head and neck have been shown to decrease attack frequency, with effects lasting 2-3 months.
Excessive Underarm Sweating: Approved by the FDA in 2004, Botox reduces severe sweating in the underarms, as well as in palms and feet, improving quality of life for sufferers.
Cleft Lip Scars: Injected into scar tissue, Botox can ease muscle tension, aiding in scar reduction and healing, especially in infants. Though promising, this use is not yet FDA-approved.