Top 8 Risk Factors Associated with Early-Onset Dementia
This article explores eight key risk factors linked to early-onset dementia, affecting individuals under 65. These factors include lifestyle choices, medical history, genetics, and overall brain health. Understanding these risks can promote early detection and preventative measures to reduce the incidence of young-onset dementia, which impacts millions worldwide. The article provides insights into how habits and conditions like alcohol use, strokes, depression, and genetic predisposition play crucial roles in disease development.
Sponsored

Top 8 Risk Elements Linked to Early-Onset Dementia
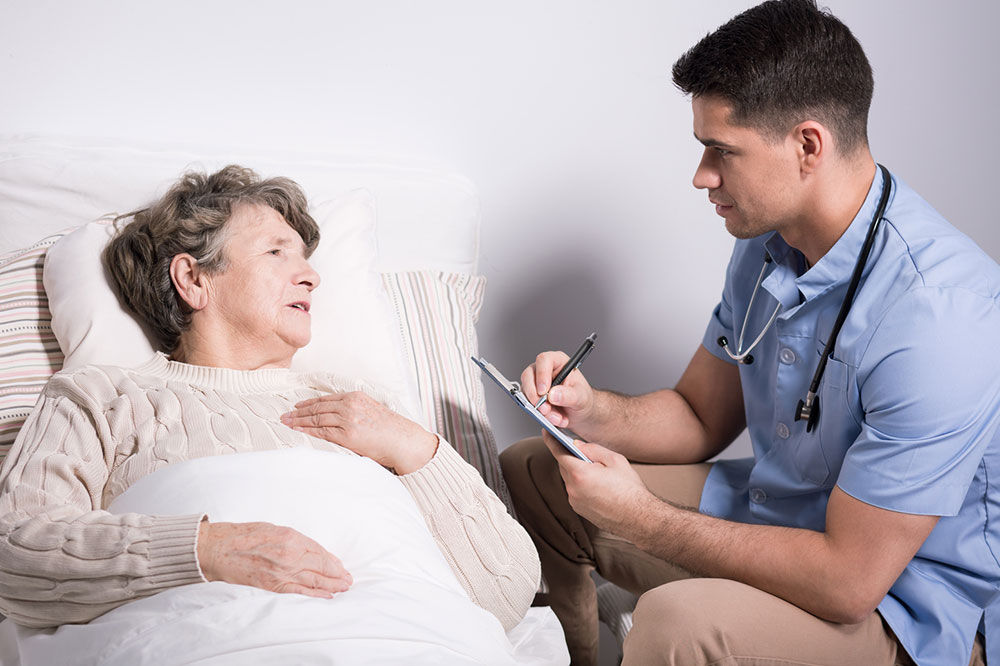
Early-onset dementia, also known as young-onset dementia (YOD), occurs before age 65 and affects approximately 35.6 million individuals globally. Around 4-10% of these cases are classified as YOD, typically affecting individuals as young as 30 to 35 years old. The disease develops due to plaque accumulation in the brain, often influenced by genetic mutations impacting plaque formation and processing. Eight major risk factors contribute to about 68% of early-onset dementia cases. Here are these factors ranked by significance:
Excessive alcohol consumption : Heavy alcohol intake is a leading risk factor for early-onset dementia. Excessive drinking is known to cause memory issues, hallucinations, and paranoia, increasing the risk of developing dementia at a younger age.
Previous stroke episodes : A stroke occurs when blood flow to parts of the brain is interrupted, impairing function. Such incidents raise the likelihood of early-onset dementia by damaging brain tissue and affecting cognition.
Use of antipsychotic drugs : Medications prescribed for depression or psychosis can influence brain health. While they help manage symptoms, long-term use may contribute to the development of early dementia.
Depressive disorders : Depression can diminish cognitive abilities, lead to social withdrawal, and cause mental fog. Prolonged depression adversely impacts brain function, heightening dementia risk.
Genetic predisposition : Family history of dementia, especially if a parent has been diagnosed, significantly increases the likelihood of early-onset cases due to inherited genetic factors.
Substance abuse : Use of illicit drugs can damage brain tissue and impair memory. Chronic drug abuse is a prominent risk factor for developing dementia at an earlier age.
Baseline cognitive abilities : Lower cognitive functioning at a young age signals vulnerability to early cognitive decline and dementia later in life.
Blood pressure and body weight issues : Both hypertension and abnormal body weight can disrupt brain health, increasing susceptibility to early dementia.