Key Signs and Risks of Crohn’s Disease You Should Recognize
Discover the essential signs and risk factors of Crohn’s disease. This article highlights common symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, blood loss, and fatigue, alongside potential complications. Understanding these indicators can lead to early diagnosis and effective treatment, reducing health risks. Learn more about how genetics, immune response, and lifestyle influence this condition and why timely medical intervention is critical for managing Crohn’s disease effectively.
Sponsored

Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that impacts the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. It often causes symptoms like abdominal discomfort, persistent diarrhea, and weight loss. This disease varies in severity and can target different parts of the gastrointestinal system, mainly the cuối ileum and colon.
Typical Crohn’s Disease Symptoms
The symptoms usually develop gradually but can sometimes appear suddenly. Common signs include diarrhea, fatigue, fever, blood in stool, loss of appetite, and mouth ulcers. Severe cases may involve skin, joint, and eye inflammation, as well as liver issues. Children might show delayed growth as a symptom.
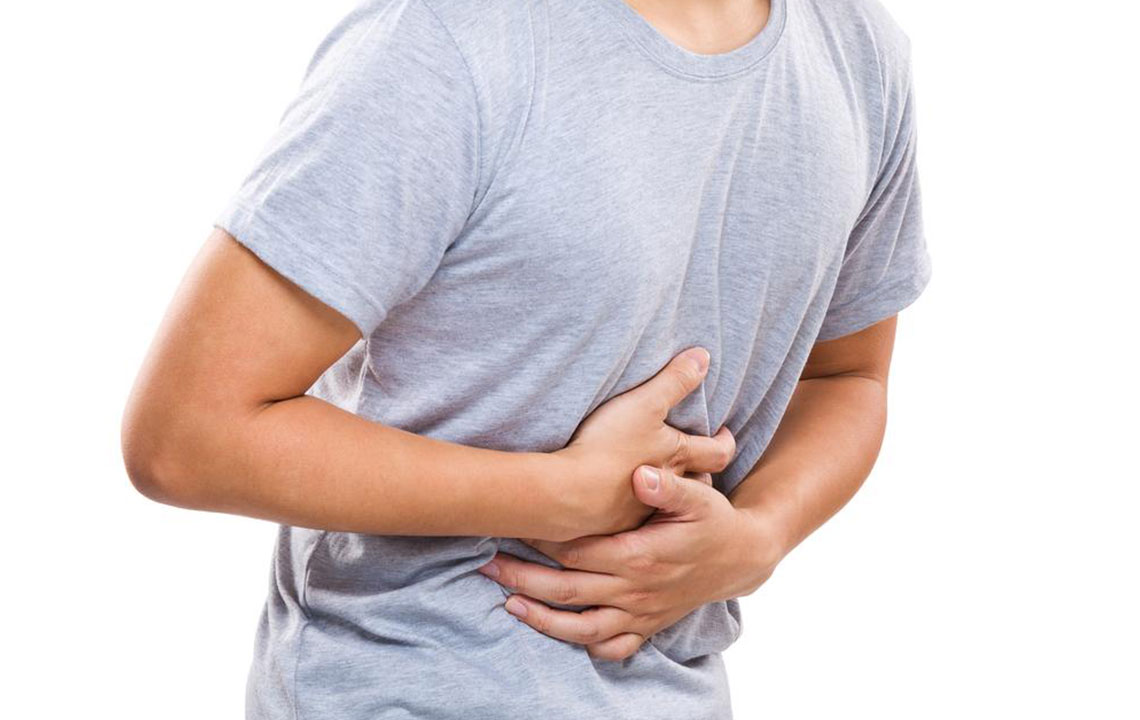
Abdominal Pain:
Patients often experience intermittent cramps, soreness, and eventually persistent ache in their abdomen, which can worsen over time.
Diarrhea and Blood:
Advanced stages often involve frequent diarrhea, sometimes accompanied by blood, occurring multiple times daily.
Appetite Suppression:
Loss of appetite leads to decreased food intake and weight loss.
Fever and Anemia:
Persistent high fever is common in some cases, and blood loss can cause anemia due to lowered iron levels.
Anal Fissures:
Small tears around the anus may develop, leading to discomfort. The immune system's role is central, and causes of Crohn’s remain unclear—though factors like genetics, infections, stress, and diet may contribute. Immune malfunction and hereditary predisposition are significant factors. Triggers such as bacteria or viruses can also initiate the disease.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase Crohn’s disease risk, including age (typically under 30), ethnicity (more common in some regions like Eastern Europe), family history, and medication use that may promote inflammation.
Potential Complications
Untreated Crohn’s can cause bowel obstructions, ulcers, fistulas, and anal fissures. It also raises the risk of colon cancer and related issues like anemia, arthritis, skin conditions, and liver diseases. Consulting a healthcare professional promptly when symptoms occur is vital for management and improved quality of life.