Diet Guidelines for Managing Crohn's Disease: Foods to Embrace and Avoid
Managing Crohn's disease involves a strategic diet that minimizes flare-ups. This article outlines foods to include and avoid, emphasizing the importance of easy-to-digest options like rice and cooked vegetables. Personalized dietary planning can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Sponsored

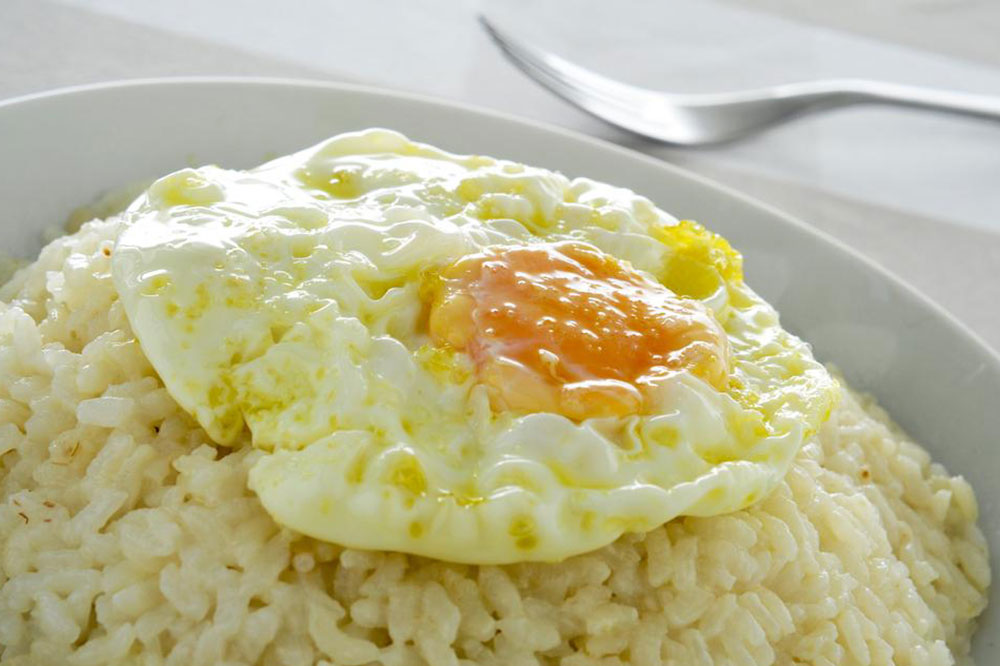
Crohn's disease is a prevalent inflammatory bowel disorder characterized by symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal discomfort, bloating, and gastritis. As a long-term condition with no known cure, managing Crohn's primarily involves lifestyle changes, particularly diet. While medications offer symptom relief, dietary adjustments can significantly impact disease progression. Identifying trigger foods is essential since they can worsen symptoms. Common culprits include high-fiber foods, certain fruits with seeds, caffeine, acidic items, nuts, and gluten-containing grains. A tailored, low-residue diet focusing on easily digestible foods like rice, well-cooked vegetables, and lean proteins is often recommended to reduce flare-ups and promote comfort.
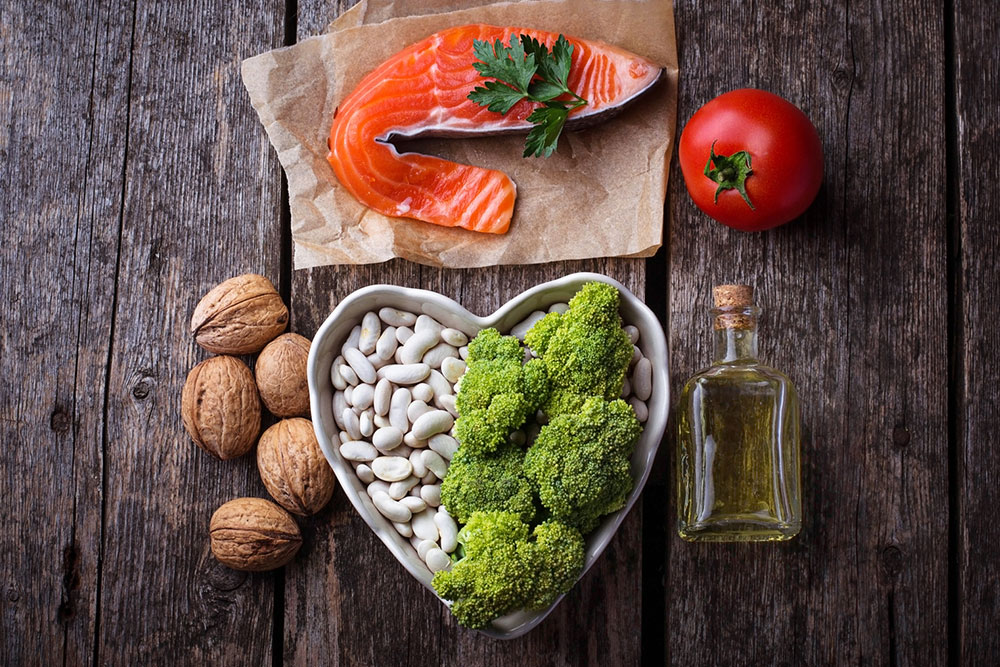
Incorporating gentle, nutrient-rich options such as steamed carrots, bananas, papayas, and oatmeal can support digestion. Some oily fish like tuna may also aid symptom management, though responses vary among individuals. Avoiding carbonated drinks, alcohol, fatty meats, and spicy foods can help prevent aggravations. Consulting with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary plans is advisable to ensure nutritional adequacy while minimizing discomfort.