Effective Strategies for Managing Atopic Dermatitis in Children
Discover essential strategies to effectively manage atopic dermatitis in children. This guide covers skin hydration, avoiding irritants, medication use, and environmental controls to reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life for young patients.
Sponsored
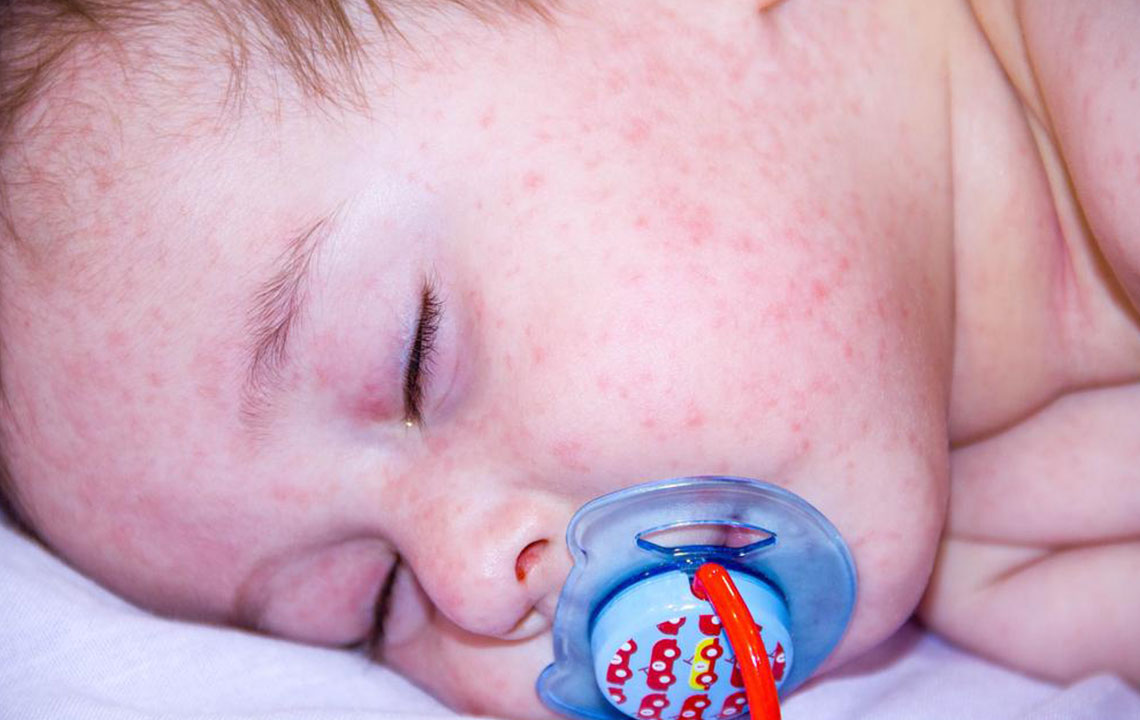
Top Strategies to Manage Atopic Dermatitis in Children
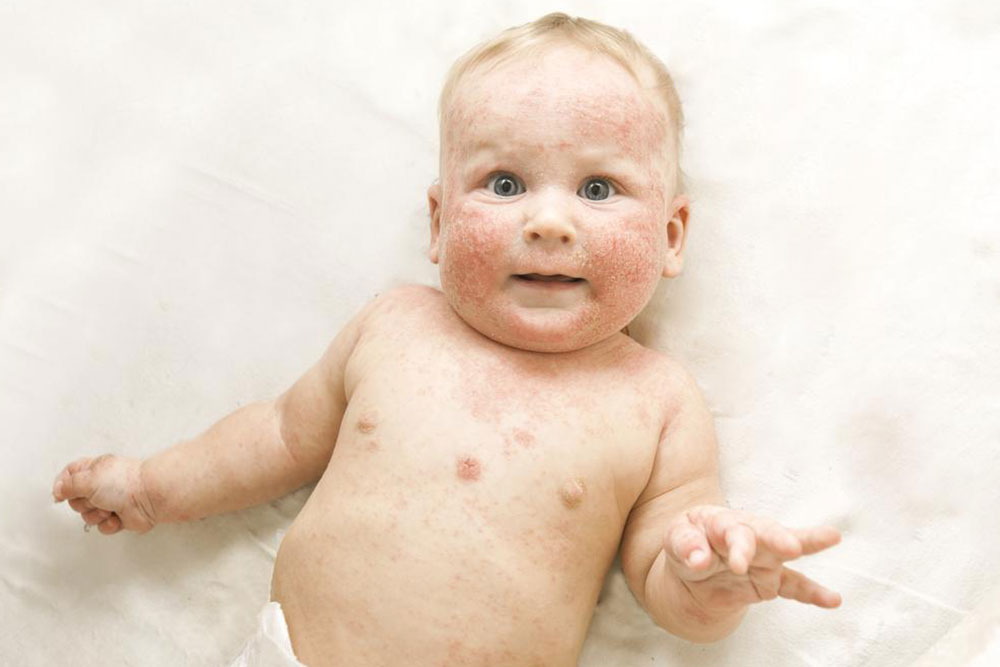
Atopic dermatitis is a prevalent form of eczema affecting infants and young children under two, often linked to genetic and immune factors. It presents with symptoms ranging from dry, itchy red patches to oozing blisters, with episodes of flare-ups and remission. The condition typically improves with age, sometimes clearing before puberty. Managing atopic dermatitis involves a comprehensive care plan focusing on skin hydration, inflammation reduction, and quality of life improvement. Various measures can help control symptoms and minimize flare-ups.
The key to effective treatment includes maintaining skin moisture, avoiding irritants, and using targeted therapies. Regular skincare routines and avoiding common triggers are essential for long-term management.
Consistently keep the child's skin moisturized using emollients to create a protective barrier and prevent dryness. This helps reduce triggers for flare-ups and maintains skin health. Applying an emollient immediately after bathing ensures optimal hydration.
Use lukewarm water during baths, as hot water can dry out the skin. Choose gentle, fragrance-free soaps with a neutral pH. After bathing, gently pat the skin dry and apply a moisturizer without rubbing.
Administer antihistamines at bedtime to alleviate itching and redness, promoting better sleep.
Identify and avoid environmental factors such as dust mites, which can worsen symptoms. Dress children in natural fabrics like pure cotton and steer clear of synthetic materials.
Apply topical corticosteroids during flare-ups in small quantities to targeted areas, reducing inflammation effectively.
In cases of secondary infection, healthcare providers may recommend topical or oral antibiotics for quick recovery.
Incorporating mild bleach baths for 5-10 minutes weekly can help prevent skin thickening and pigmentation changes.
For severe cases, treatments like psoralen combined with ultraviolet light therapy may be suggested.
Schedule regular follow-ups to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and adjust medications as needed. Prompt consultation with your pediatrician during frequent flare-ups is crucial for optimal care.