Effective Strategies for Preventing and Controlling Atopic Skin Conditions
Explore comprehensive strategies to prevent and manage atopic dermatitis. The article covers effective treatments, lifestyle modifications, trigger avoidance, and supportive therapies to control eczema symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Learn how moisturizing, avoiding irritants, and medical options like phototherapy and biologics can enhance skin health. Understanding these measures empowers individuals to better manage chronic skin conditions and improve their quality of life.
Sponsored
Strategies for Preventing and Managing Eczema
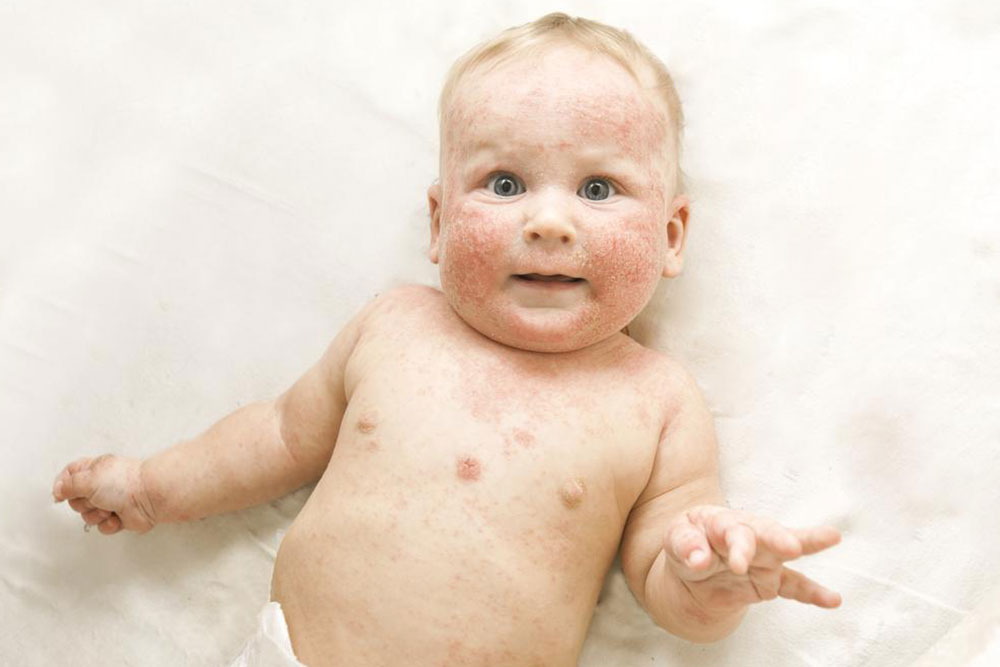
Experiencing redness and itching of the skin may indicate atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema. While prevalent among children, it can occur at any age. Over 31 million individuals in the country are affected by eczema in some form. This chronic skin issue tends to flare multiple times annually. Though a permanent cure remains unavailable, proper management is possible.
Treatment options for eczema
Symptoms can persist for years despite treatments, with flare-ups reappearing even after successful management. Here are some approaches to treating atopic dermatitis:
Creams and Topical Agents
Doctors often recommend corticosteroid creams or ointments to reduce itching and promote healing. Calcineurin inhibitors are prescribed for children over two, while antibiotic creams address bacterial infections or open sores. Applying these after moisturizing, as directed, is crucial, but awareness of side effects such as skin thinning is necessary.
Oral Medications
Oral antibiotics are used for infections like Staph, while antihistamines alleviate allergy symptoms. For severe cases, short-term corticosteroids may be prescribed, but prolonged use can cause adverse effects.
Injectable Biological Therapies
Recently, FDA-approved injectable biologics are available for severe cases when other treatments fail. Though costly, they are effective and considered safe when used appropriately.
Phototherapy
Light therapy benefits patients unresponsive to topical treatments or experiencing frequent flare-ups. This includes natural sunlight exposure or artificial UV light, such as UVA or narrowband UVB, often combined with other therapies.
Additional Supportive Therapies
Addressing emotional well-being through therapy or counseling can help manage the psychological impact. Techniques like relaxation, biofeedback, and behavior modification can reduce scratching and improve quality of life.
Preventive Measures
Keep Skin Moisturized
Regularly applying creams, lotions, or ointments seals moisture, preventing dryness. Petroleum jelly is a good option, especially for babies at risk.
Avoid Triggers
Factors like harsh soaps, detergents, pollen, dust, and sweat can provoke flare-ups. Certain foods like milk, soy, eggs, and wheat may also trigger reactions in children. Maintaining a food and symptom diary helps identify and avoid these triggers. Consulting a doctor for allergy testing is recommended.
Limit Bath Duration and Temperature
Prolonged hot baths can worsen symptoms. Using lukewarm water for a maximum of 15 minutes is advisable. Adding a small amount of diluted household bleach to bathwater may help reduce bacteria, but always consult a doctor before use.
Use Gentle Soaps
Choose mild, fragrance-free soaps that do not strip natural oils. After bathing, gently pat the skin dry and apply moisturizer while the skin is still damp to lock in hydration.
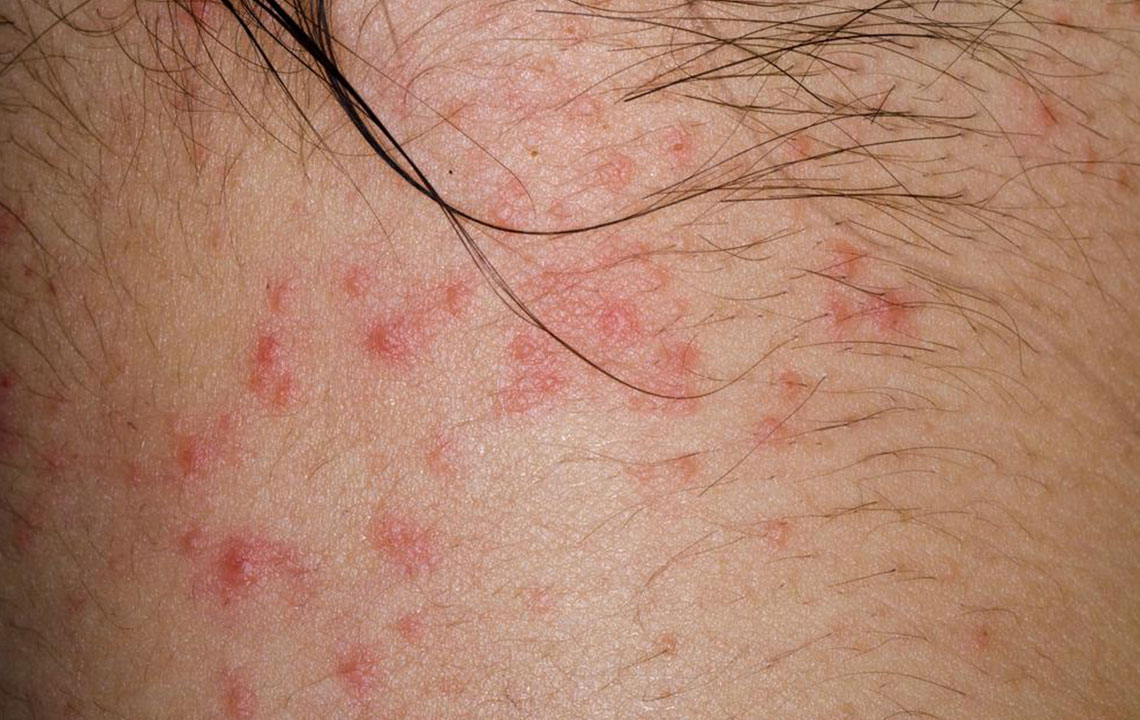
Perioral Dermatitis Management
This condition manifests as a rash around the mouth, possibly spreading to the nose and eyes. It is common in women aged 20-45, often caused by overuse of topical steroids, heavy moisturizers, sunscreens, or inhaler medications.
Treatment for Perioral Dermatitis
Doctors may prescribe immunosuppressive creams, topical or oral antibiotics, and recommend lifestyle adjustments such as reducing spicy and salty foods, minimizing cosmetic use, and frequently washing bedding and towels to prevent flare-ups.