Understanding Acid Reflux: Causes, Symptoms, and Dietary Tips
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for acid reflux. It highlights common triggers, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes to reduce discomfort and prevent complications. Understanding these factors can help individuals control acid reflux naturally and improve quality of life.
Sponsored
Have you experienced a burning sensation in your chest after meals? This common condition is known as acid reflux or heartburn, which results from stomach acid traveling back into the esophagus.
Triggers of Acid Reflux
When the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) fails to close properly after eating, stomach acid can escape into the esophagus, causing discomfort. Factors that contribute to acid reflux include:
Excess weight
Large meal portions
Lying down immediately after eating
Snacking before bedtime
Foods like citrus, tomatoes, chocolates, mint, garlic, onions, spicy, and fatty dishes
Alcohol, sodas, tea, and coffee
Smoking
Pregnancy
Medications such as blood pressure drugs, muscle relaxants, aspirin, and NSAIDs
If symptoms occur more than twice weekly, it might be indicative of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), requiring further evaluation.
Recognizing Acid Reflux Symptoms
Knowing the signs of acid reflux is crucial. Common symptoms include:
Burning chest pain, discomfort in the stomach, throat, or chest
Regurgitation of sour or bitter fluids
Bloating and frequent belching
Blood in vomit or stools
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Persistent hiccups, nausea, or unexplained weight loss
Wheezing, dry cough, hoarseness, or sore throat
Persistent symptoms should prompt medical evaluation. Diagnostic procedures may include barium swallow, endoscopy, or pH monitoring to assess esophageal function and acid levels.
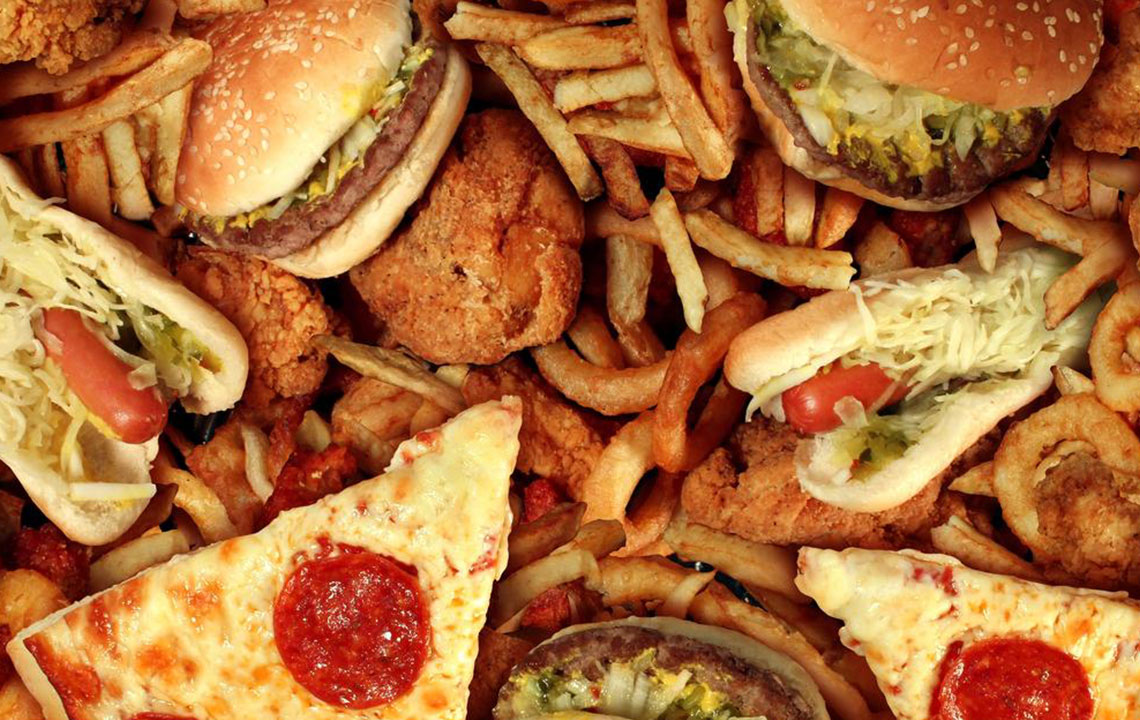
Foods and Habits to Limit or Avoid
Adjusting your diet plays a vital role in managing acid reflux. Foods to steer clear of include:
Fried and greasy meats, fast foods like chicken nuggets and wings
High-fat dairy, sweets such as chocolates, donuts, and ice cream
Citrus fruits, tomatoes, and acidic juices
Sodas, alcohol, caffeine, and processed grains like pasta with heavy sauces
Raw onions, mashed potatoes with butter, and fried snack foods
Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can significantly reduce symptoms.
Managing Acid Reflux
Long-term relief involves lifestyle modifications such as:
Monitoring and avoiding trigger foods
Maintaining a healthy weight
Eating smaller, more frequent meals
Waiting 2-3 hours before lying down after eating
Sleeping with elevated head using pillows or blocks
Wearing loose clothing
Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption
Consulting healthcare providers for medication options like acid reducers or antacids
In some cases, medications such as proton pump inhibitors or antacids are prescribed to control acid production. Severe cases may require surgical intervention, but lifestyle changes are often effective for management.
Remember, adopting healthier habits and dietary choices can help alleviate symptoms naturally. Regular check-ups and following medical advice are essential for effective treatment.