Essential Tips for Managing Foot Health in Diabetic Patients
Learn vital strategies for maintaining foot health in diabetics, including routine inspections, proper hygiene, appropriate footwear, and blood sugar control. Early intervention and consistent care can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications like ulcers and amputations, ensuring better quality of life for diabetic patients.
Sponsored
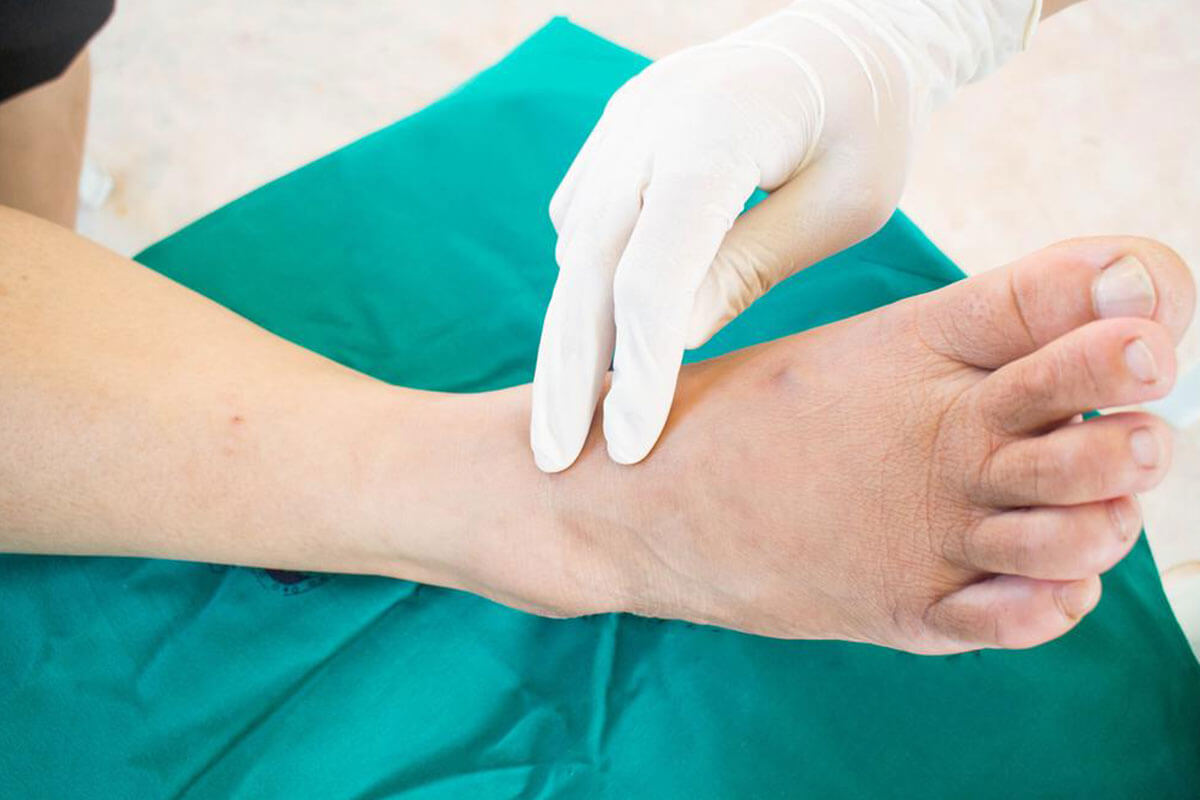
Diabetes, also called diabetes mellitus, is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to irregular insulin production or utilization. Over time, this disease can impact various organs, including the heart, kidneys, and limbs. How does diabetes affect foot health? Elevated blood sugar damages nerves and impairs circulation, increasing the risk of foot problems. Regular foot inspections and care are crucial for diabetics—neglect can lead to severe complications like infections, ulcers, or even amputation. Active management of blood sugar and routine foot care are vital steps to prevent serious outcomes.
Proper foot hygiene and periodic evaluations help avoid infections and complications. Unchecked foot issues in diabetics can rapidly worsen, leading to tissue damage or limb loss. Common problems include nerve damage (neuropathy), ulcers, and gangrene. Prolonged high blood sugar levels cause nerve impairment, reducing sensation, which makes injuries go unnoticed—and untreated wounds can turn severe. Poor blood flow hampers healing, risking tissue death and infections. Smoking and ill-fitting shoes further increase risks. Adherence to foot care routines, wearing comfortable footwear, and controlling blood sugar levels are fundamental to maintaining foot health in diabetics. Seek medical attention promptly for any foot abnormalities or wounds to ensure proper treatment and prevent severe consequences.