Top Strategies for Managing Diabetic Foot Health
Learn effective strategies for managing diabetic foot health, including prevention, common problems, and when to seek medical help. Proper foot care is essential for diabetics to avoid severe complications like infections and amputations. This guide covers foot hygiene, footwear choices, and active circulation techniques to maintain healthy feet and prevent long-term issues.
Sponsored
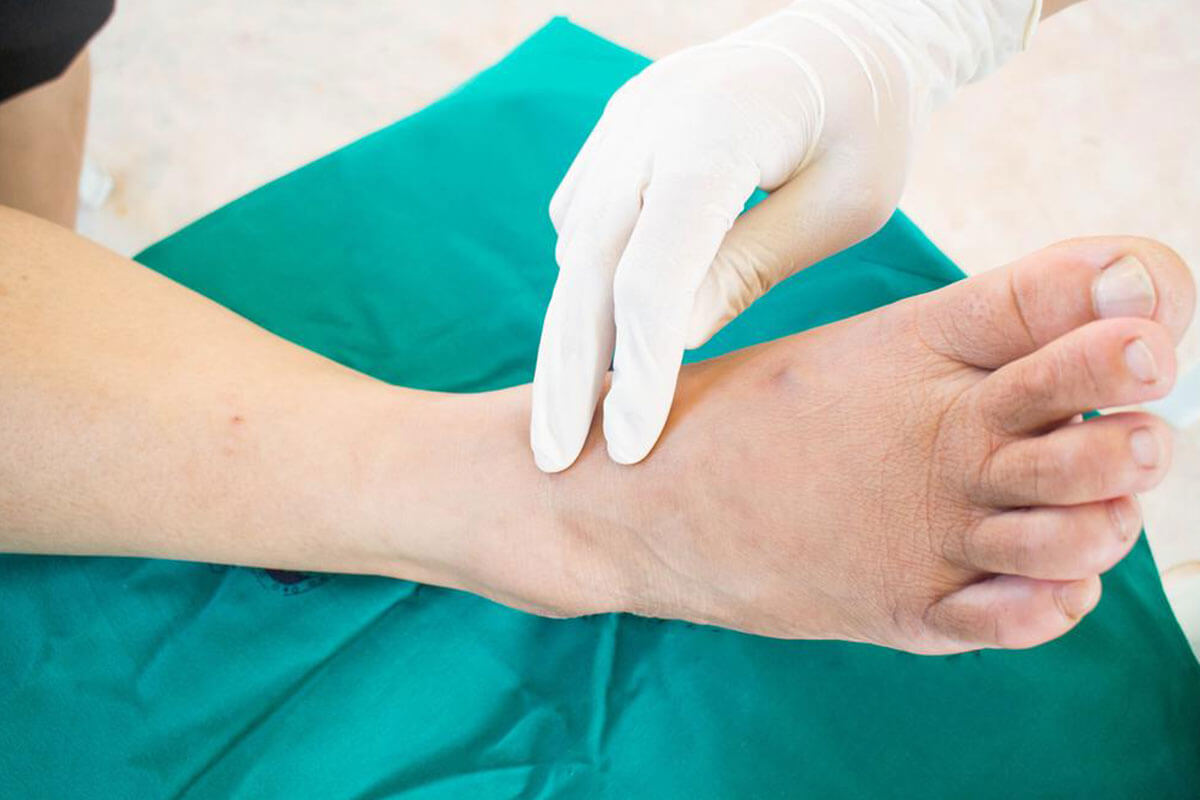
Diabetic foot complications stem from diabetes, a condition characterized by inadequate insulin production. Insulin is essential for converting food into energy; without it, blood glucose levels rise, leading to various health issues including foot problems. High blood sugar can cause nerve damage and poor circulation, increasing the risk of injuries, infections, and deformities. Proper foot care, injury prevention, and regular monitoring are crucial to avoid severe consequences like amputations. Being proactive can significantly improve foot health in diabetic individuals.
Two main causes of diabetic foot issues are reduced oxygen and nutrient supply due to poor blood flow, and peripheral neuropathy, which diminishes sensation, raising injury risks.
Common Diabetic Foot Problems:
Toenail Fungal Infections: Bacterial infections can cause redness, discoloration (yellowing), pain, and crumbling toenails. If unmanaged, infection can spread, leading to further tissue damage and difficulty walking.
Muscular and Joint Issues: Nerve damage can result in muscle weakness, joint pain, and numbness, affecting balance and mobility over time.
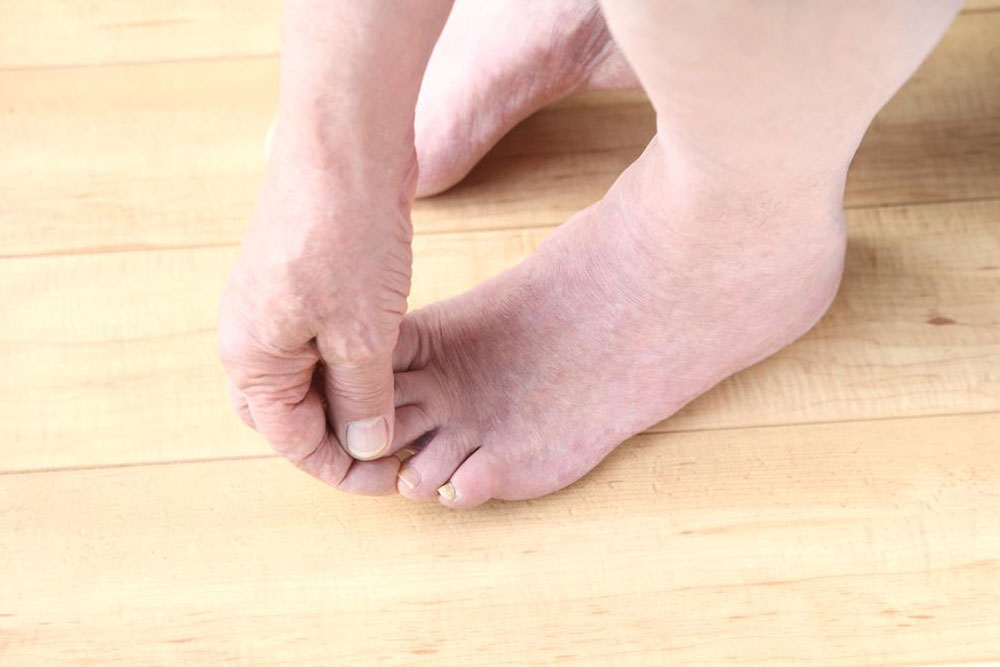
Calluses and Corns: Hard skin patches develop due to uneven pressure or friction from footwear, leading to foot deformities but manageable with proper care.
Bunions: Misalignment of the big toe causes swelling, redness, and irritation, often worsened by ill-fitting shoes. Certain cases may require surgical correction.
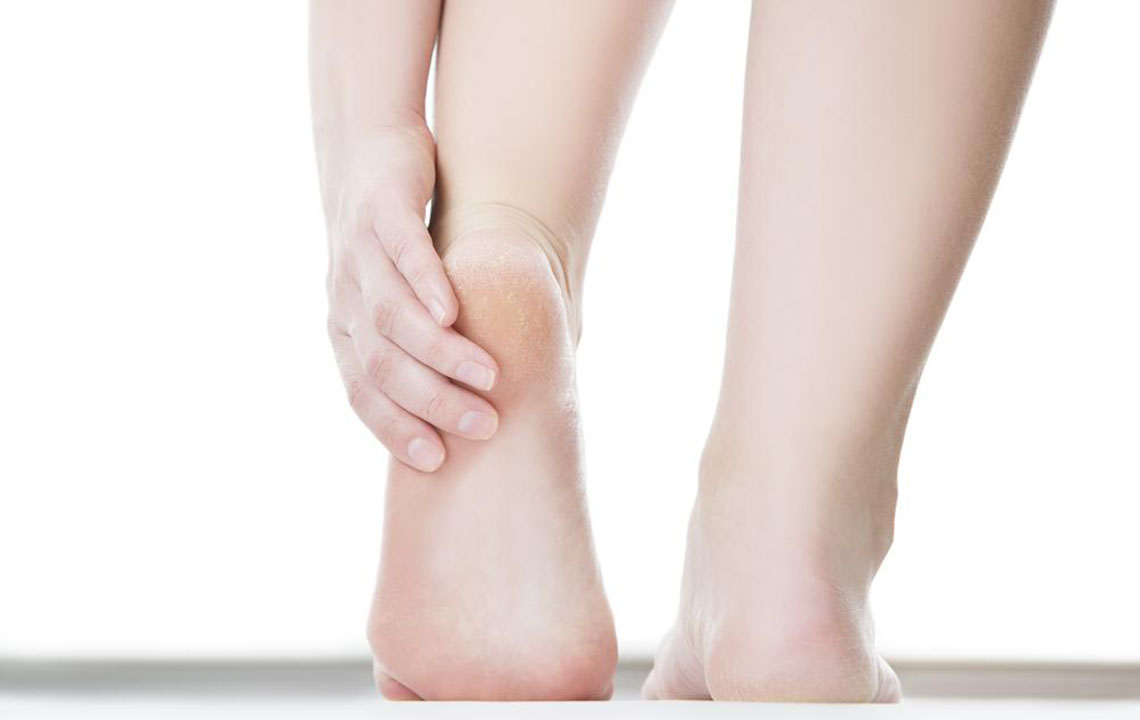
Dry Skin: Cracked, dry skin increases infection risk, especially around heels. Regular moisturizing helps maintain healthy skin and prevents germ entry.
Preventive Tips for Diabetic Foot Care:
Moisturize Regularly: Keeps skin healthy and prevents cracks.
Daily Foot Hygiene: Washing with warm water and applying powder can eliminate germs and keep feet dry.
Manage Calluses and Corns: Gently file with a pumice stone to prevent discomfort.
Wear Proper Footwear: Well-fitted shoes and socks protect against injuries and infections.
Active circulation is vital; simple toe wiggles and movement throughout the day enhance blood flow. If foot problems worsen, seek medical attention promptly. Regular foot care can prevent severe complications, ensuring a healthier life with diabetes.