Complete Overview of Blood Disorders and Their Causes
This article provides a detailed overview of blood disorders, highlighting their types, symptoms, causes, and risk factors. It explains how imbalances in blood components can lead to various health problems, emphasizing the importance of understanding this condition. The piece covers symptoms like fatigue, bleeding, and abnormal clotting, along with factors that increase risk. Whether genetic or acquired, blood disorders require proper diagnosis and management, making this guide a valuable resource for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Sponsored

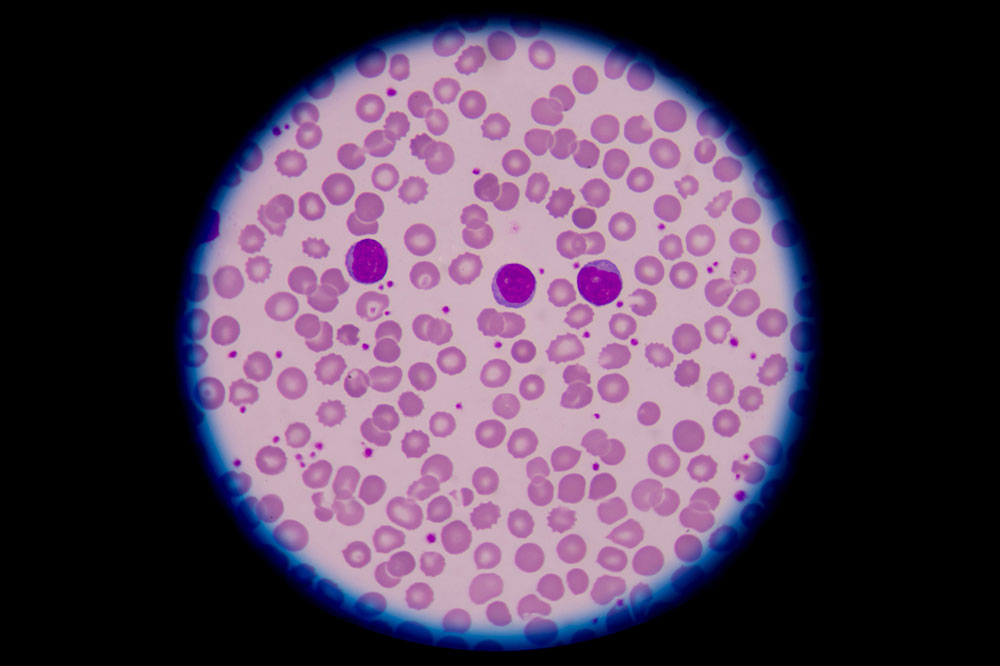
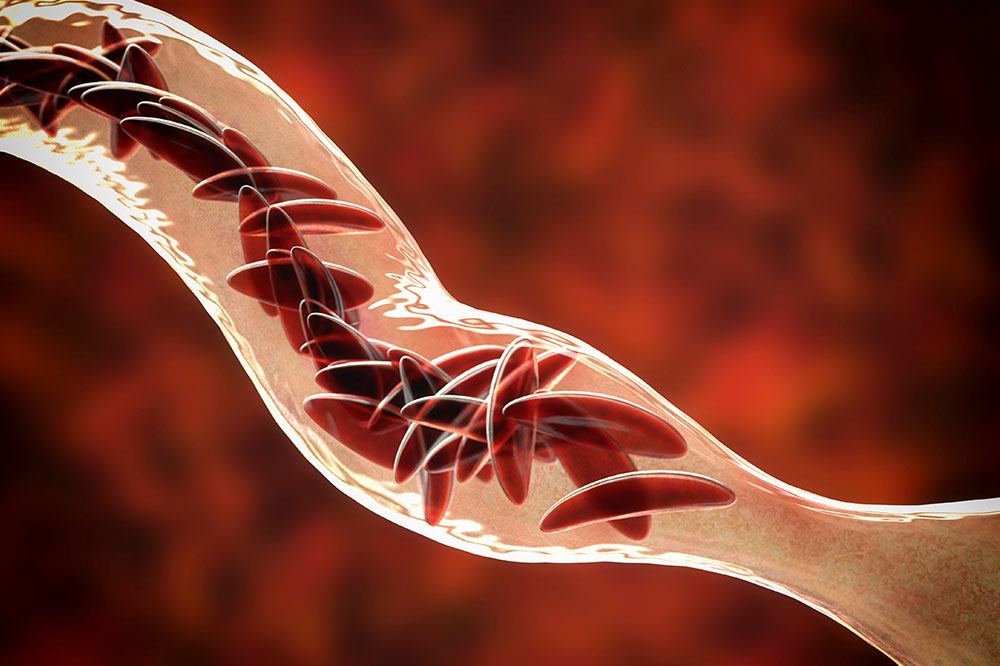
Blood disorders are conditions that disrupt the normal functions of blood components, affecting the flow and activity of blood in the body. These conditions can reduce vital cells, nutrients, or platelets, leading to various health issues. Types of blood disorders often named after the blood component they impact, such as anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia, involve decreased blood elements. Conversely, disorders like erythrocytosis, leukocytosis, and thrombocythemia involve elevated levels of specific blood components.
Common symptoms vary based on the specific disorder and affected body parts. For instance, low red blood cell count results in fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Reduced white blood cells cause frequent infections, and low platelets lead to unexplained bruising and bleeding. Conversely, high blood cell counts can cause blood thickening, headaches, skin redness, or abnormal clotting.
Signs such as clotting issues, redness and swelling in the legs, skin rash (petechiae), enlarged lymph nodes, pallor, and cravings for non-food items (Pica) indicate underlying blood issues. Risk factors include genetic predisposition, aging, liver or kidney diseases, poor diet, toxin exposure, pregnancy, and trauma or surgeries.