Comprehensive Guide to Blood Conditions and Management
This comprehensive guide explains blood disorders, covering symptoms, types, causes, and treatment options. It highlights how blood component problems impact health and discusses common conditions like anemia, leukemia, and hemophilia. Learn about causes, genetic factors, and therapies used to manage these conditions effectively, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans for better outcomes.
Sponsored
An In-Depth Overview of Blood Disorders
Blood disorders encompass a range of conditions affecting blood components or bone marrow function. Bone marrow, located within bones, produces white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. When abnormalities occur in these cells or plasma clotting factors, it results in various blood health issues. In this article, we explore the symptoms, types, causes, and treatment options for these conditions.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms depend on which blood element is impacted. Generally, these disorders lead to reduced cell counts or impaired function.
For example:
Red blood cell issues cause tiredness, breathlessness, muscle weakness, dizziness, and rapid heartbeat due to decreased oxygen supply.
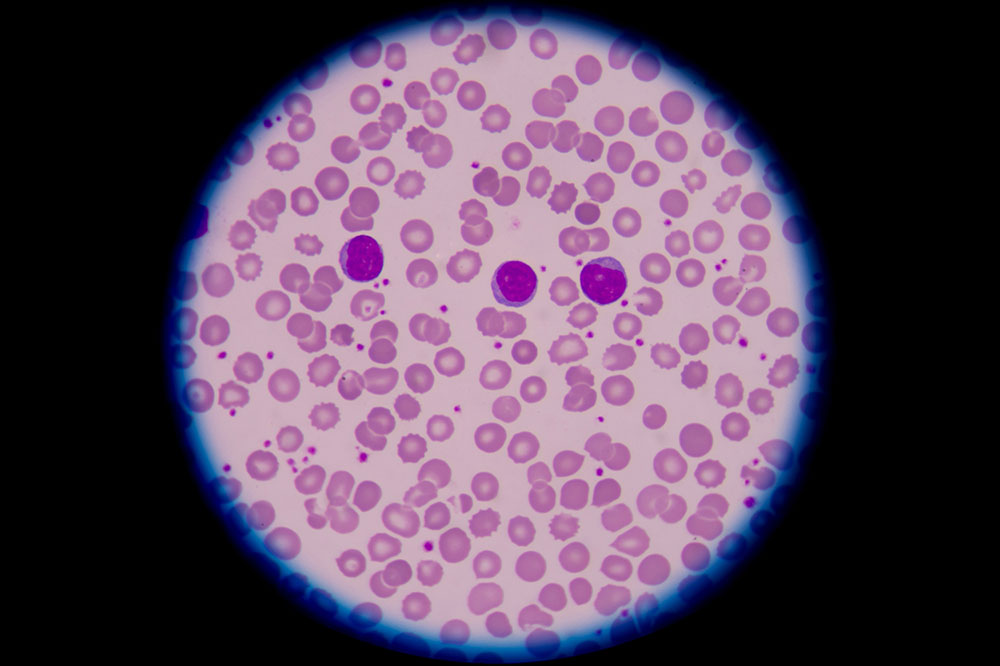
White blood cell problems often result in persistent infections, unexplained weight loss, and prolonged wound healing.
Platelet or clotting problems can make stopping bleeding difficult, cause easy bruising, nosebleeds, gum bleeding, and wounds that resist healing or reopen.
Categories and Origins
Most blood disorders are inherited but can also develop due to infections, exposure to toxins, medication side effects, or nutritional deficiencies like iron, vitamin K, or B12. Key types include:
Red blood cell disorders: These interfere with oxygen transport, leading to anemia, thalassemia, or polycythemia vera.
White blood cell disorders: These affect immune defense and include leukemia, lymphoma, and myelodysplastic syndromes.
Platelet disorders: Abnormal platelet levels or functions cause bleeding issues; examples include hemophilia and von Willebrand disease.
Plasma cell issues: These involve abnormal plasma cells, with plasma cell myeloma being a common blood cancer.
Therapies
Treatment options depend on the specific disorder, patient's age, and overall health. Some conditions require no immediate intervention but need management if symptoms worsen. For example, iron supplementation treats anemia caused by iron deficiency, while hemophilia may be managed with replacement therapy involving clotting factors or plasma infusions.