Critical Blood Disorders That Might Be Life-Threatening If Not Addressed
Discover five severe blood disorders that can threaten life if left untreated. From anemia to thalassemia, learn about their symptoms, causes, and importance of early diagnosis to prevent serious health consequences. This overview emphasizes vigilance in blood health for overall well-being.
Sponsored

Critical Blood Conditions That Could Be Deadly Without Proper Treatment
The human body faces constant threats from harmful agents that can invade and disrupt its normal functions, often leading to severe health issues. All organs and tissues, including blood, are vulnerable. Blood disorders are quite common, affecting about 20% of people in the United States. These conditions arise when blood components—red cells, white cells, or platelets—are impaired. If not diagnosed and treated timely, they can cause serious health complications.
The blood's liquid part, plasma, is also susceptible to diseases. Recognizing the risks associated with blood disorders is essential. Here are some of the most serious conditions that could impact anyone:
Anemia: A disorder impacting red blood cells, which are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body. Iron deficiency is often the culprit, essential for hemoglobin production. Low hemoglobin levels hinder oxygen delivery, causing fatigue and weakness.
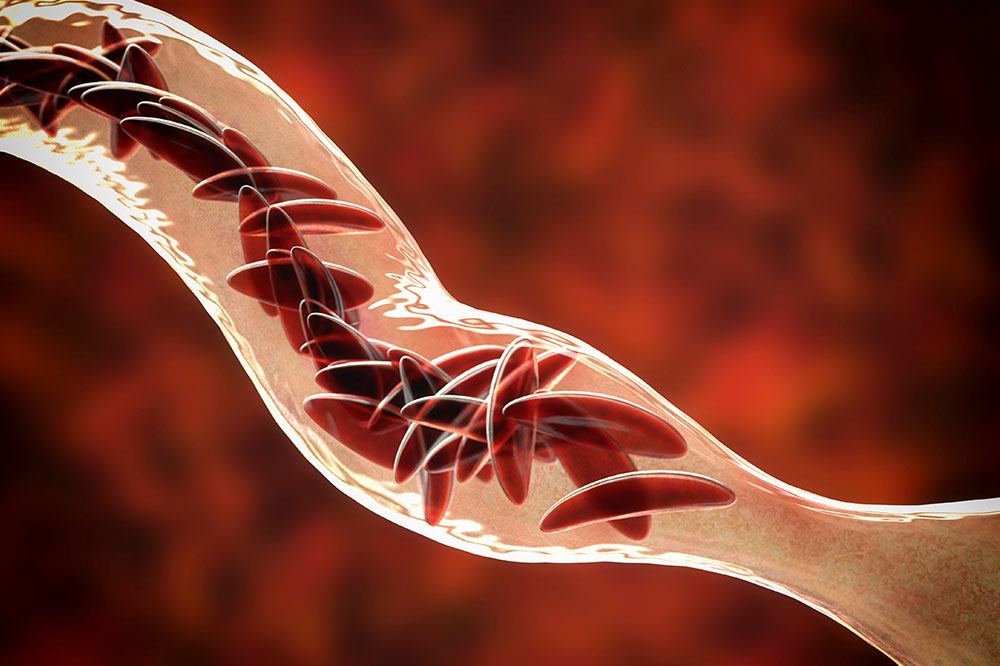
Sickle Cell Disease: A genetic condition where red blood cells are sickle-shaped, impairing their ability to carry oxygen efficiently. This abnormal shape can cause blockages in blood flow and pain. Treatment options like stem cell therapy may be necessary for management.
Lymphoma: A type of blood cancer affecting lymphocytes, the white blood cells. It leads to uncontrolled growth of these cells, which can be either Hodgkin’s or Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, posing significant health risks.
Hemophilia: A hereditary disorder where platelets, which help blood clot, are deficient or dysfunctional. Individuals with hemophilia tend to bleed excessively, both internally and externally, due to impaired clot formation.
Thalassemia: An inherited condition impacting red blood cells' ability to transport oxygen, leading to complications such as heart issues, bone deformities, enlarged spleen, and developmental delays, especially in children.