Essential Overview of Common Blood Conditions
Explore the essential types of blood disorders, including anemia, leukemia, lymphoma, and clotting issues. This overview highlights symptoms, causes, and implications for overall health. Early awareness and diagnosis are vital for effective management of these conditions, which can significantly impact quality of life.
Sponsored
Key Blood Disorders Everyone Should Know
Blood disorders are health issues that disrupt the normal functions of blood components such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are produced in the bone marrow and play vital roles in oxygen transport, immune defense, and blood clotting. Symptoms vary but often include unexplained fatigue and weight fluctuations. Understanding different blood conditions is crucial for early detection and management. Here’s a detailed look at the main blood disorder categories affecting overall well-being:
Red Blood Cell Anemias
This category involves problems with red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
Types of red blood cell issues include:
Anemia
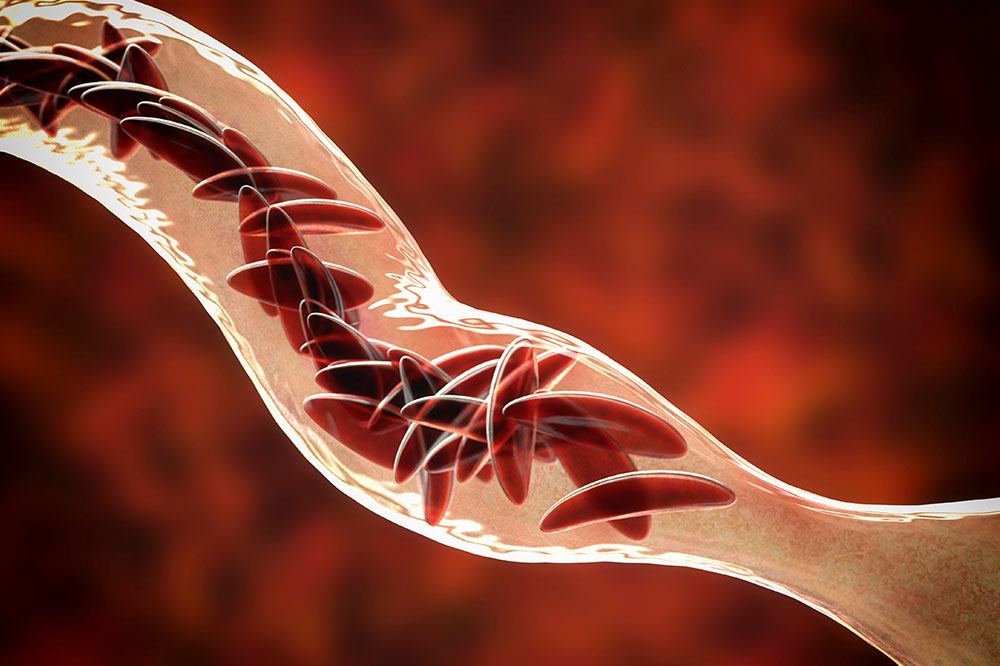
Anemia results from iron deficiency and other factors, such as vitamin shortages or genetic conditions. Variants include iron deficiency anemia, pernicious anemia, aplastic anemia, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and sickle cell disease.
Thalassemia
Thalassemia is an inherited disorder affecting hemoglobin production. It leads to reduced oxygen delivery, causing fatigue and other health issues.
Polycythemia Vera
This rare blood cancer causes bone marrow to produce too many red blood cells, thickening the blood and impairing flow. Risks include blood clots, stroke, and heart attack.
White Blood Cell Disorders
White blood cells defend against infections. Disorders like lymphoma, leukemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes impair immune function and can cause serious health complications.
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a blood cancer affecting the lymphatic system, resulting in abnormal cell growth. Types include Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Leukemia
Leukemia causes excess white blood cell growth in the bone marrow, either rapidly (acute) or gradually (chronic).
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
MDS involves abnormal development of immature blood cells and can progress to leukemia, affecting blood cell production and immune health.
Platelet Disorders
Platelet issues disrupt clot formation, leading to bleeding or clotting problems. Conditions include:
Von Willebrand Disease
This inherited disorder results from low von Willebrand factor, impairing normal clotting.
Hemophilia
A genetic disorder where blood doesn’t clot properly, causing prolonged bleeding episodes.
Plasma Cell Disorders
Plasma cells produce antibodies to fight disease; disorders like plasma cell myeloma involve malignant growths in these cells, leading to bone marrow damage and weakened immunity.