Essential Strategies for Treating Rotator Cuff Injuries Effectively
This guide provides effective treatment options for rotator cuff injuries, including initial care, physical therapy, injections, and surgical procedures for severe cases. Early diagnosis and professional consultation are essential for proper recovery.
Sponsored
Effective Approaches to Managing Rotator Cuff Injuries
What is a rotator cuff injury?
A rotator cuff injury involves inflammation or damage to the shoulder muscles and tendons that help stabilize and move the shoulder joint. The group of four muscles forming the rotator cuff can experience issues due to tears or impingement caused by overuse, injury, or aging.
Symptoms often include shoulder pain, swelling, stiffness, weakness, and difficulty lifting objects. You might also hear clicking sounds when raising your arm, alongside discomfort during movement.
To address rotator cuff injuries, initial treatment may involve:
Rest and RICE Technique: Rest to prevent further strain, and RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) to reduce swelling and pain. Applying ice for 10-15 minutes multiple times daily can be highly effective.
Compression and Elevation: Using a bandage loosely to minimize swelling, and elevating the shoulder while resting can enhance recovery.
Persistent pain or severe injuries might require advanced options such as:
Injections: Steroid injections can help decrease inflammation, especially if pain interferes with daily activities. However, they should be used cautiously as they may weaken tendons.
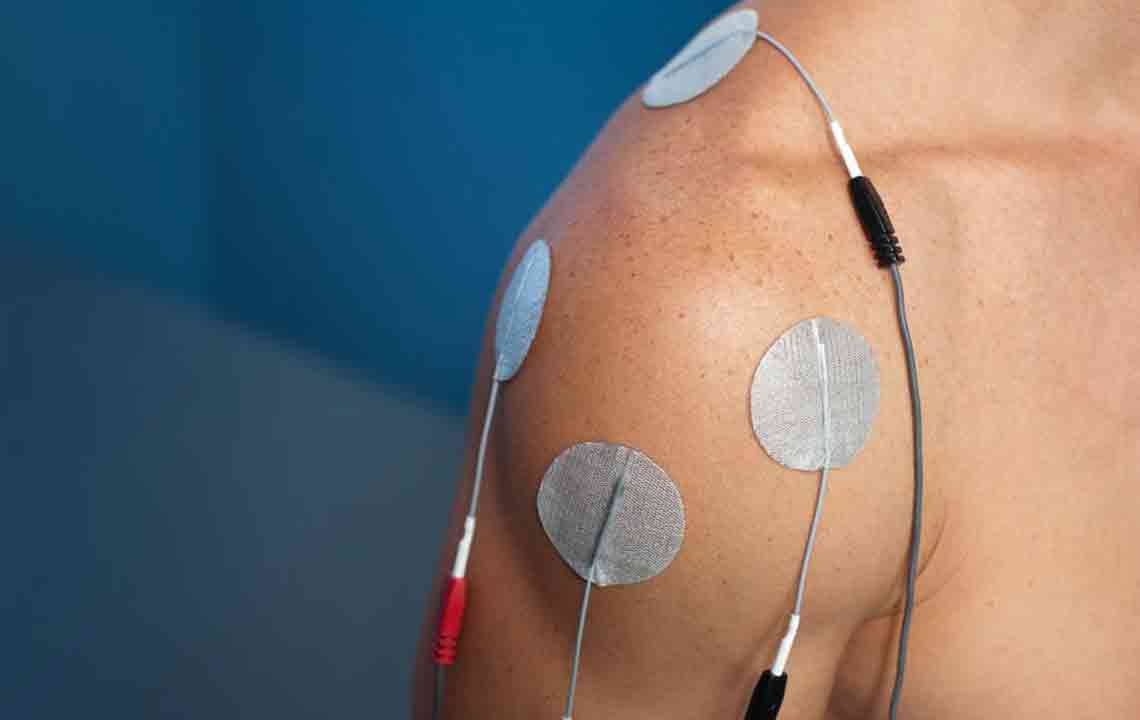
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises, including shoulder stretches, pendulum swings, wall stretches, and arm reaches, can rebuild strength and flexibility in the shoulder joint.
When non-invasive methods fail, surgical solutions may be necessary:
Arthroscopic Tendon Repair: Minimally invasive procedure using a small camera to reattach torn tendons with precision.
Open Tendon Repair: A more extensive surgery involving a larger incision to reattach tendons, often used for complex injuries.
Tendon Transfer and Shoulder Replacement: Replacing severely damaged tendons or the entire shoulder joint with artificial components when necessary.
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: A newer technique reversing the normal joint structure for certain severe cases.
Consult a healthcare professional immediately if you suspect a rotator cuff injury to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.