Comprehensive Guide to Rotator Cuff Injury Management
This comprehensive guide covers rotator cuff injury management, highlighting causes, symptoms, treatment options, and surgical considerations. Modern medical techniques effectively treat both minor and severe injuries, restoring shoulder stability and function. Timely intervention and expert care are essential for optimal recovery, especially for active individuals. Preventive measures and proper post-treatment care help avoid long-term complications and improve quality of life.
Sponsored
Managing Rotator Cuff Injuries Effectively
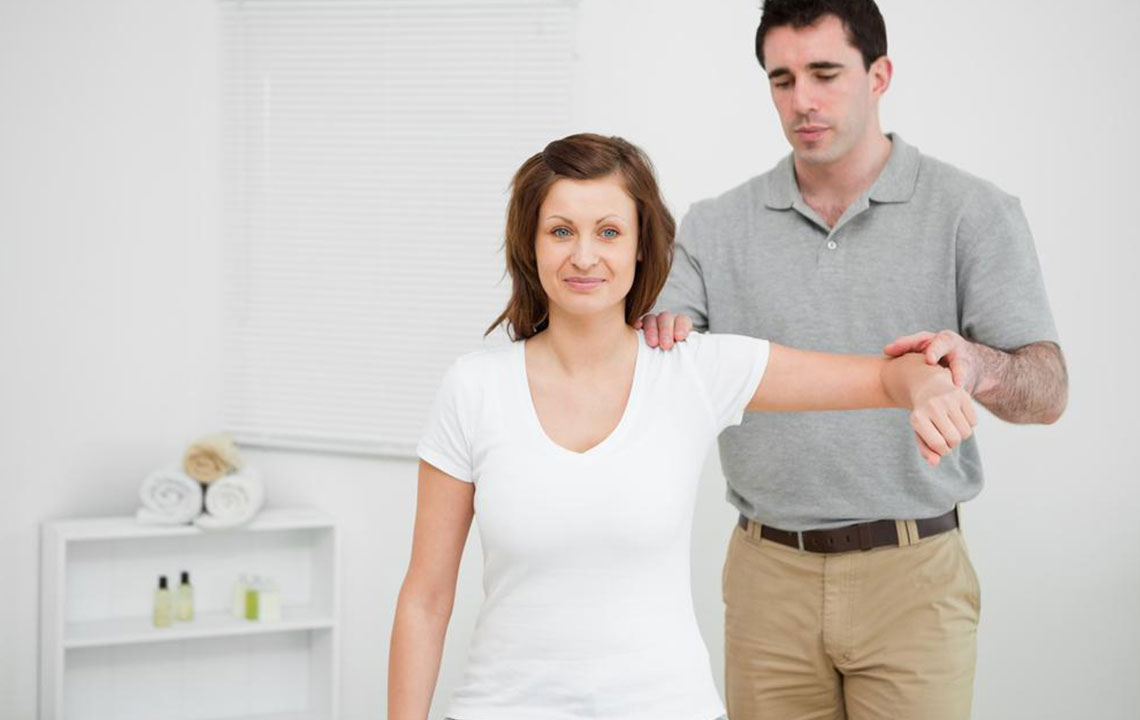
Individuals engaged in high-intensity activities or sports are prone to rotator cuff injuries, which affect the group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. These tendons connect the shoulder muscles to the humorous bone, providing joint stability. Damage to any of the four rotator cuff muscles may require surgical intervention. While mild injuries often heal with rest, severe cases might necessitate operation.
Injuries can happen suddenly or develop gradually. Tendonitis increases the risk of rotator cuff damage. Sportspersons like baseball players or painters frequently encounter overuse injuries, whereas falls or heavy lifting can cause acute injuries. Preventive measures are advisable, but if injury occurs, prompt treatment is essential to avoid long-term issues.
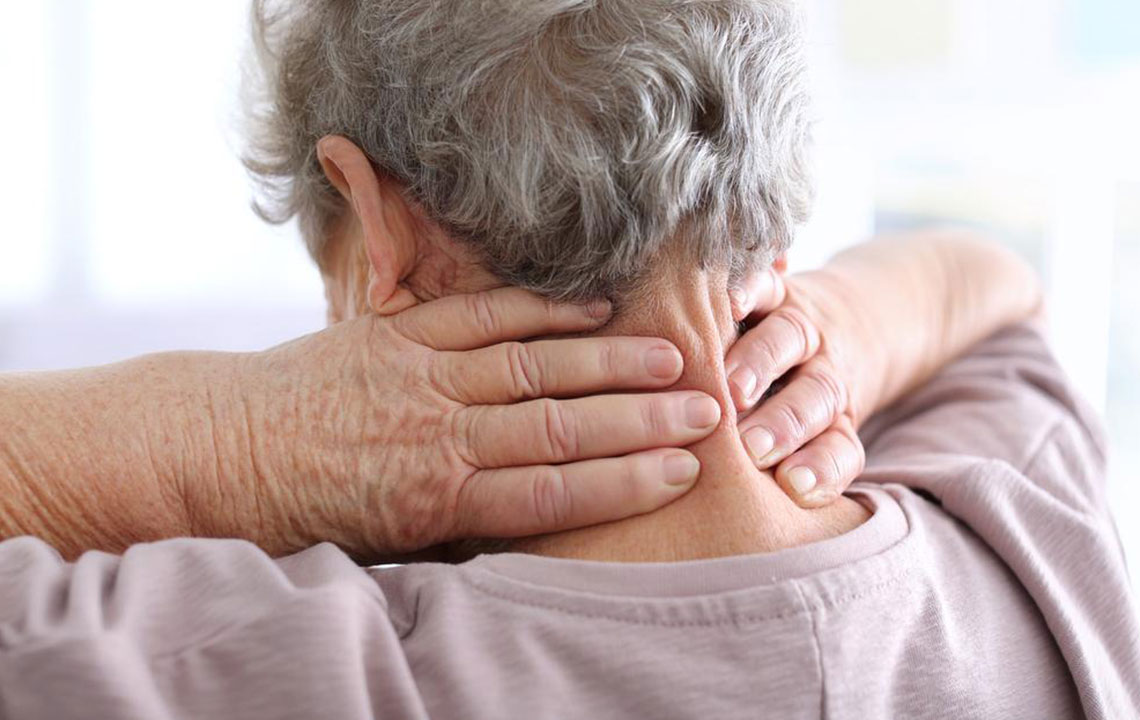
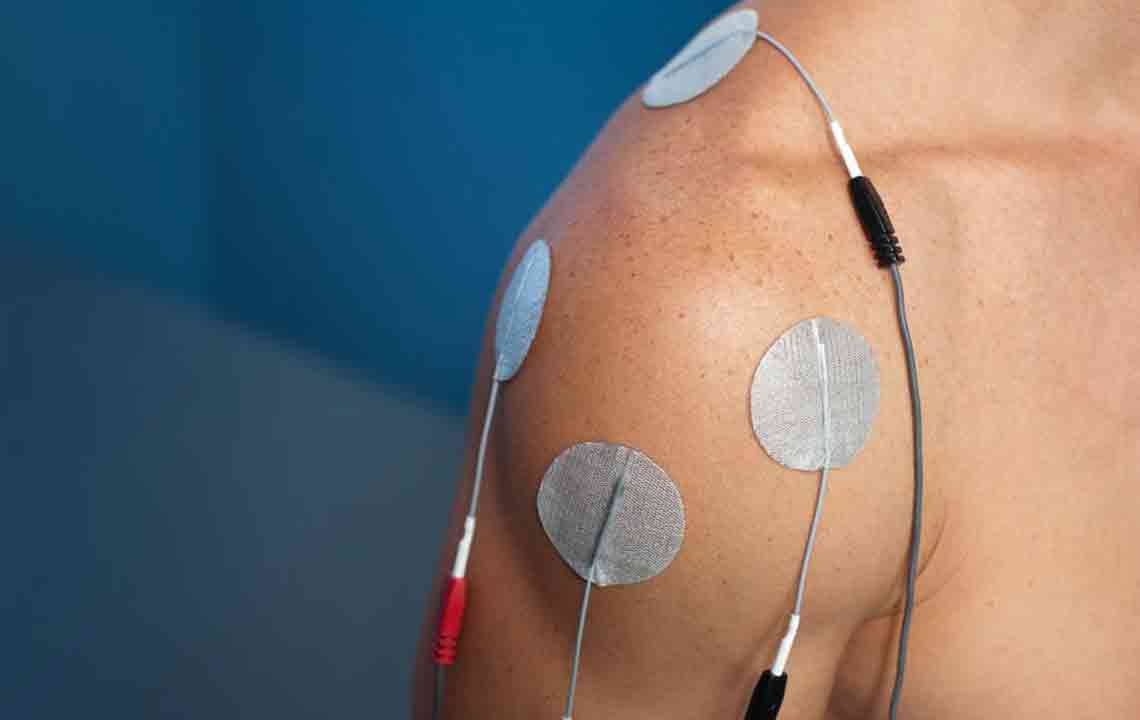
Symptoms include intense localized shoulder pain, stiffness, and limited movement, often impairing daily activities. Modern medical advancements have simplified treatment options, which range from non-invasive therapies to surgical repair. Rest, ice or heat application, and physiotherapy help restore shoulder function. Home exercises can effectively aid recovery.
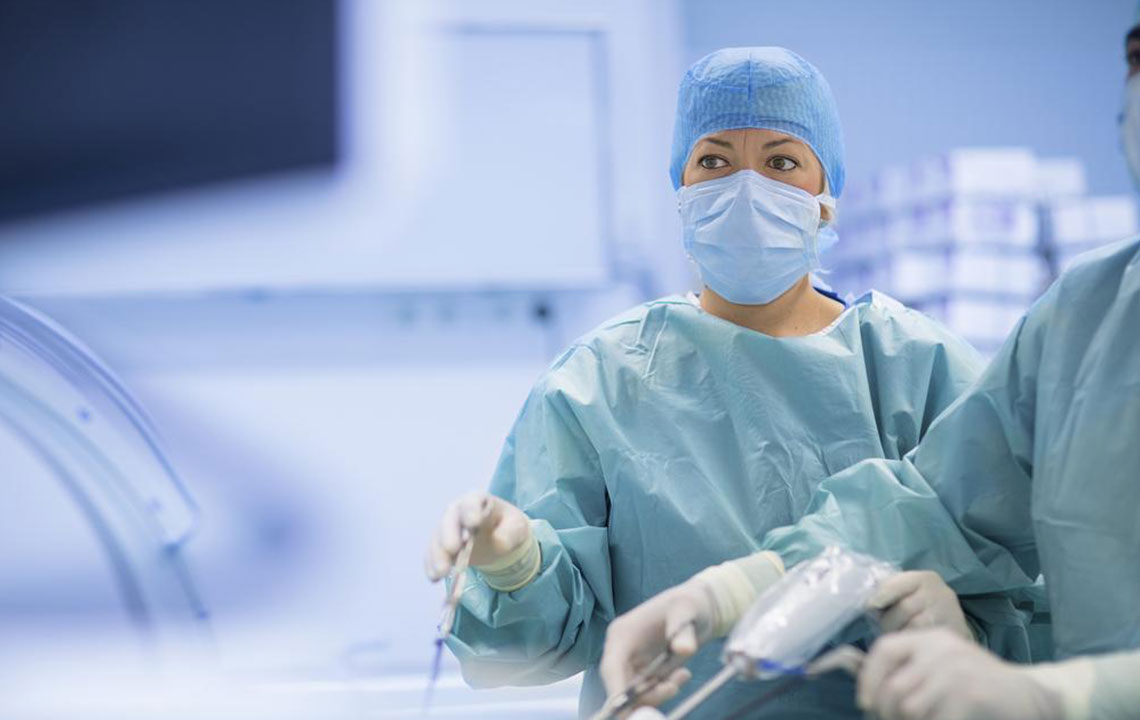
Surgical procedures involve re-attaching tendons to the bone using suture anchors, often made of dissolvable material. The process is minimally invasive, performed via arthroscopy, with video guidance. Post-surgery care is crucial to ensure proper healing.
Why opt for surgery? Persistent pain despite conservative care, active lifestyles, large tears, or recent injuries often require surgical repair. Minor tears may heal with rest and exercises. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, surgical intervention becomes necessary.
Every surgery carries risks like anesthesia reactions, bleeding, infections, or nerve injuries. Choosing an experienced specialist reduces complications. If pain persists for weeks despite non-surgical efforts, surgery can significantly improve shoulder function and quality of life.