Understanding Normal Blood Cell Levels and Their Significance
This article provides a comprehensive overview of normal blood cell levels, including white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. It explains their vital roles, normal ranges, and the importance of regular blood testing to detect and prevent health issues such as anemia, infections, and clotting disorders. Understanding these levels can help individuals maintain optimal health through timely monitoring and medical consultation.
Sponsored
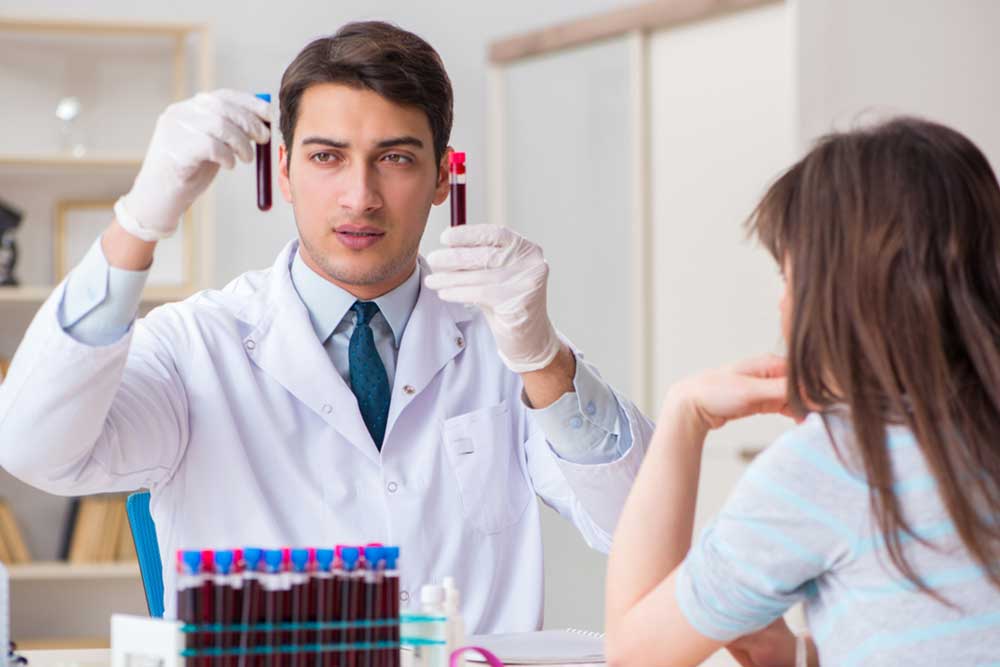

Maintaining proper levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets is vital for overall health. Doctors often order a complete blood count (CBC) test to evaluate these levels, diagnosing conditions like anemia, infections, or blood disorders. White blood cells are essential for immunity; a high count indicates infection or inflammation, while a low count raises infection risk. Red blood cells carry oxygen and remove CO2; low levels may lead to anemia. Platelets are key for blood clotting. Regular testing helps monitor these components and ensures health is maintained.
White blood cells – Vital for immune defense, their levels can indicate infection or inflammation. The normal range is 4,500 to 10,000 per microliter. High levels suggest infection; low levels increase susceptibility to illness.
Red blood cells – Responsible for oxygen transport, normal counts are 5–6 million per microliter in men and 4–5 million in women. Low counts can cause anemia and fatigue.
Platelets – Crucial for clotting, normal levels are 140,000 to 450,000 per microliter. Imbalances can lead to bleeding or clotting issues.
Regular blood testing helps detect abnormalities early. Maintaining balanced levels of blood components is essential for health, immune function, and wound healing. An annual CBC is recommended to monitor and manage your blood health effectively.