Effective Techniques for Measuring Body Temperature
Learn about various effective methods to measure body temperature accurately, including rectal, oral, armpit, and ear techniques. Proper technique ensures precise readings, essential for timely health assessment in children and adults.
Sponsored

Monitoring body temperature is a common practice, especially in children, as a fever can indicate an immune response to infection. A high temperature helps the body fight off bacteria and viruses naturally. While most fevers resolve with proper care, persistent or unusual fever warrants medical attention. Doctors often review temperature charts to assess illness. There are multiple ways to measure body temperature accurately, each suitable for different situations and age groups.
One critical aspect is to avoid mercury thermometers due to breakage risks. The main methods include rectal, oral, armpit, and ear measurements, each with specific steps and precautions.
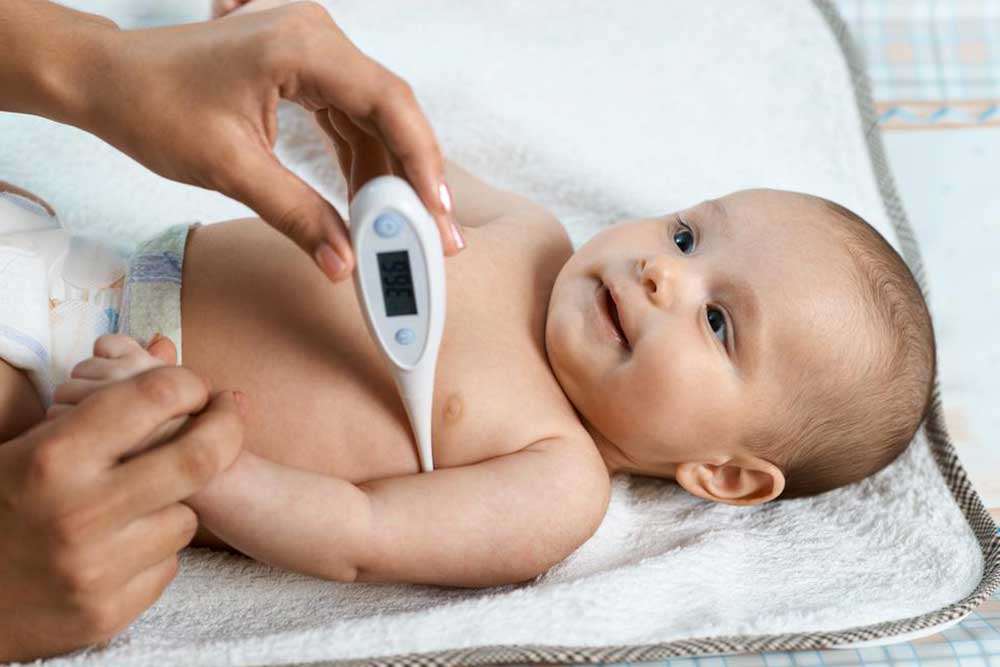
Rectal Method: Considered the most reliable for infants and young children. Clean the thermometer, apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly, gently insert about 2.5 cm into the anus, and wait for about a minute until it beep. Record the reading, clean the thermometer, and store safely.
Oral Method: Suitable for children above 5 years. Place the cleaned thermometer under the tongue, keep it there for a minute, then record the temperature. Avoid this method for younger children who cannot hold the thermometer properly.
Armpit Method: Less accurate, often used as a quick measure. Place the thermometer under the arm, ensure good contact, and wait for the reading. If a baby feels warm but the reading is normal, consider a rectal check for accuracy.
Ear Method: Not very precise; results may vary even with proper use. Typically not recommended for critical assessment.
Tips for accurate temperature measurement include using digital thermometers, avoiding the use of fever strips, and measuring at regular intervals for better tracking.