Comprehensive Guide to Managing Arthritis Discomfort
This comprehensive guide provides insights into arthritis symptoms, causes, and different types of pain. It discusses effective topical treatments such as NSAIDs and nerve-blocking patches, along with the biological process of pain transmission. Emphasizing lifestyle changes, the article aims to help readers manage symptoms better and seek appropriate interventions for lasting relief.
Sponsored

Understanding and Managing Arthritis Discomfort
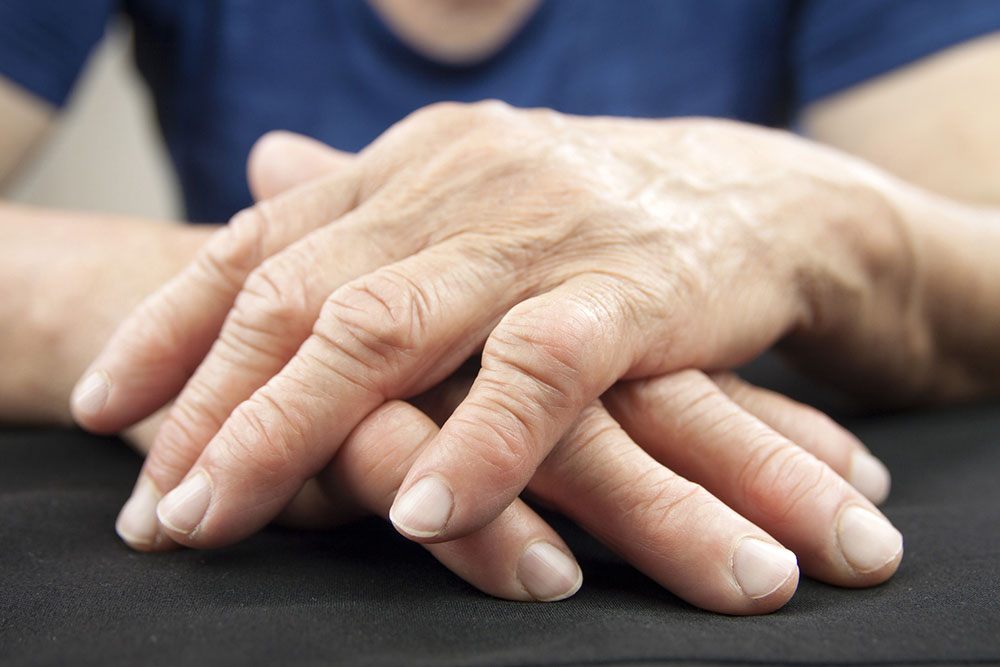
Understanding Arthritis and Its Impact Arthritis encompasses a range of degenerative and inflammatory joint conditions characterized by pain, stiffness, and swelling. It primarily affects joints such as the wrists, hips, knees, and fingers, but some types can also involve other connective tissues and skin. Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for proper management.
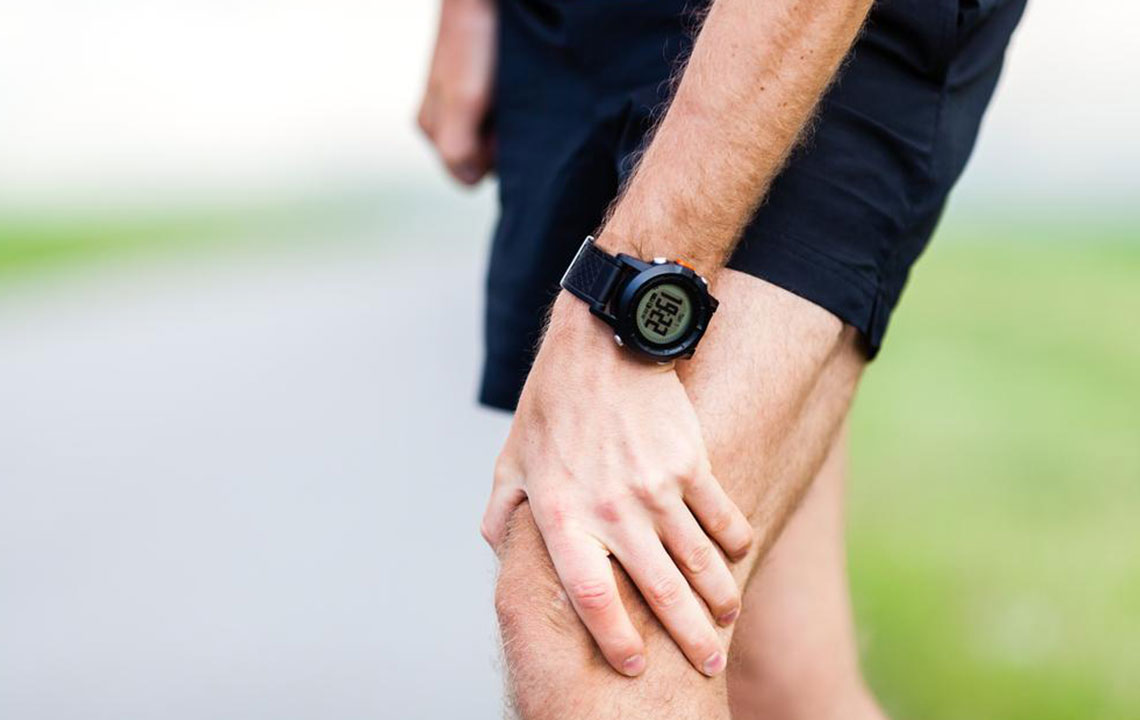
Signs of Knee Arthritis Pain
Persistent pain that may intensify gradually or appear suddenly.
The pain often occurs in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
Knee discomfort can worsen with climbing stairs, standing up, or bending.
Inflammation can lead to swelling from excess fluid or bone spurs.
Over time, muscles weaken, and the joint structure becomes unstable.
Stiffness, locking, or grinding sounds may also be experienced.
Movement may become painful, affecting daily activities.
Causes of Arthritis
Multiple factors contribute to joint inflammation, varying by type.
Previous joint injuries can accelerate degenerative changes.
Metabolic disorders like gout and pseudogout can cause arthritis.
Genetics play a role; having family members with arthritis increases risk.
Infections such as Lyme disease can trigger joint pain.
Immune system dysfunction, as seen in rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, is a common cause.
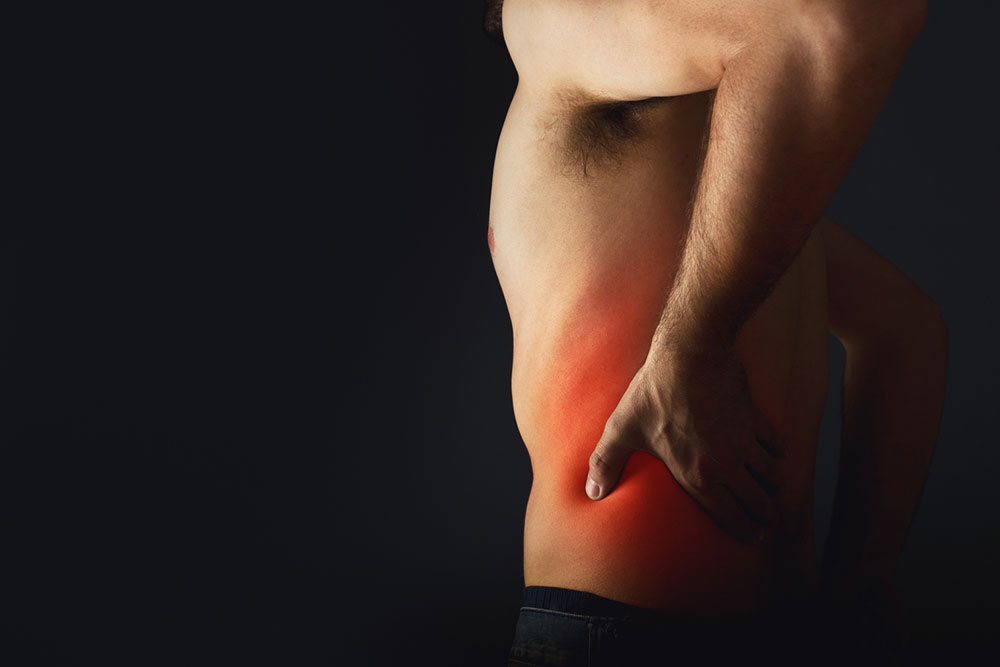
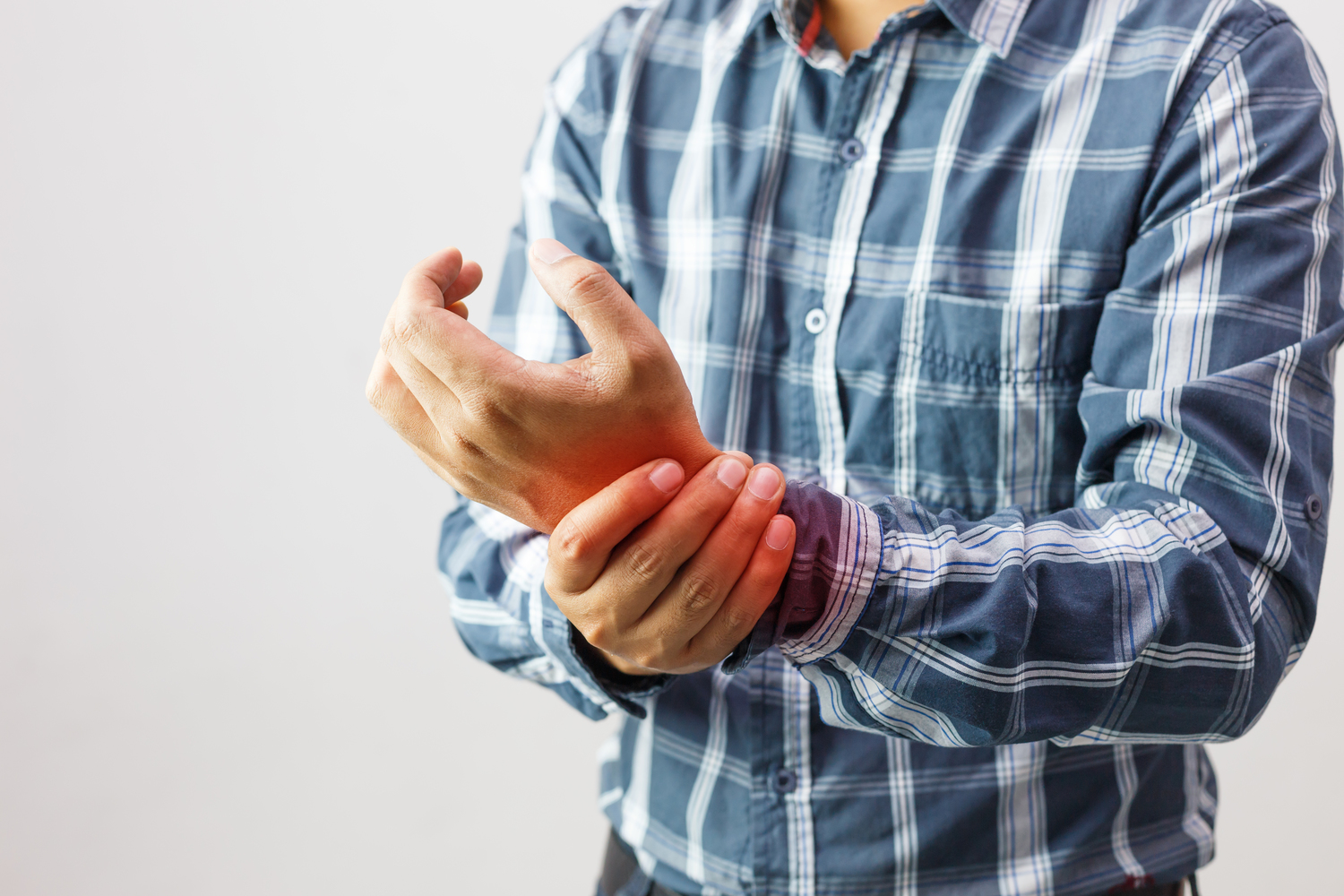
Types of Arthritis-Related Pain
Acute pain arises suddenly due to injury or inflammation and serves as a warning signal.
This pain can be temporary or persist until the issue is addressed, like a dental ache.
Some episodes resolve then recur; the pain may be sharp or dull.
If unresolved, acute pain can evolve into chronic discomfort, lasting months or years.
Chronic arthritic pain may include joint stiffness, nerve pain, or muscle soreness.
Long-term pain can become a condition itself, complicating treatment.
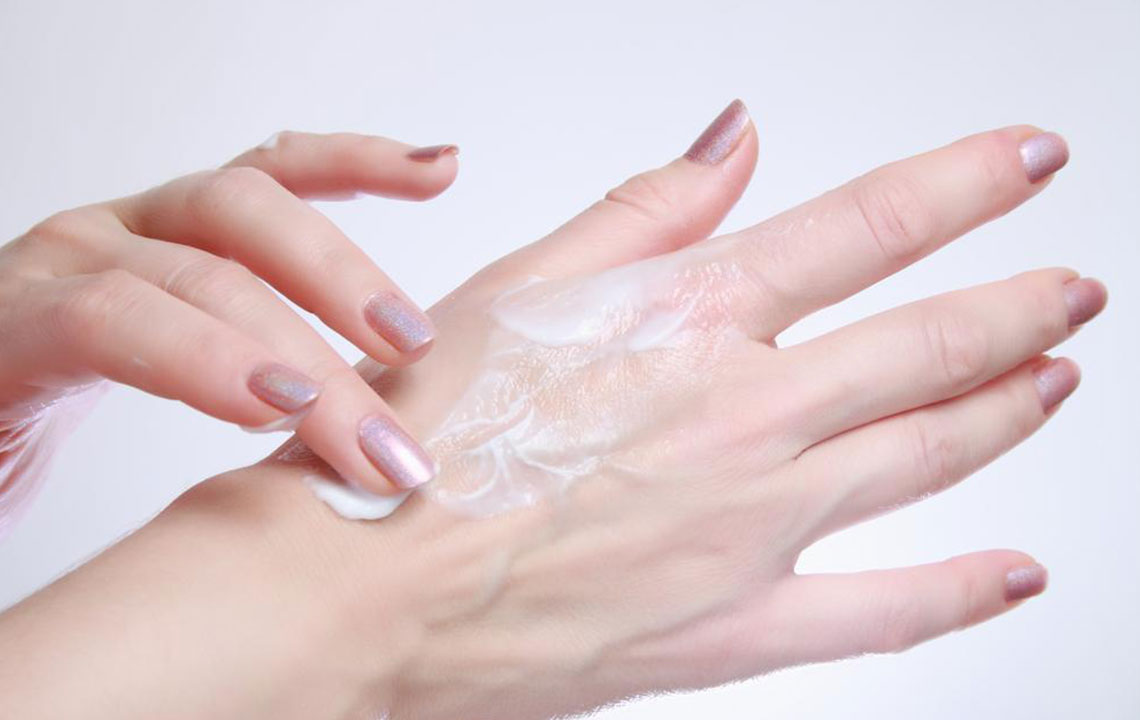
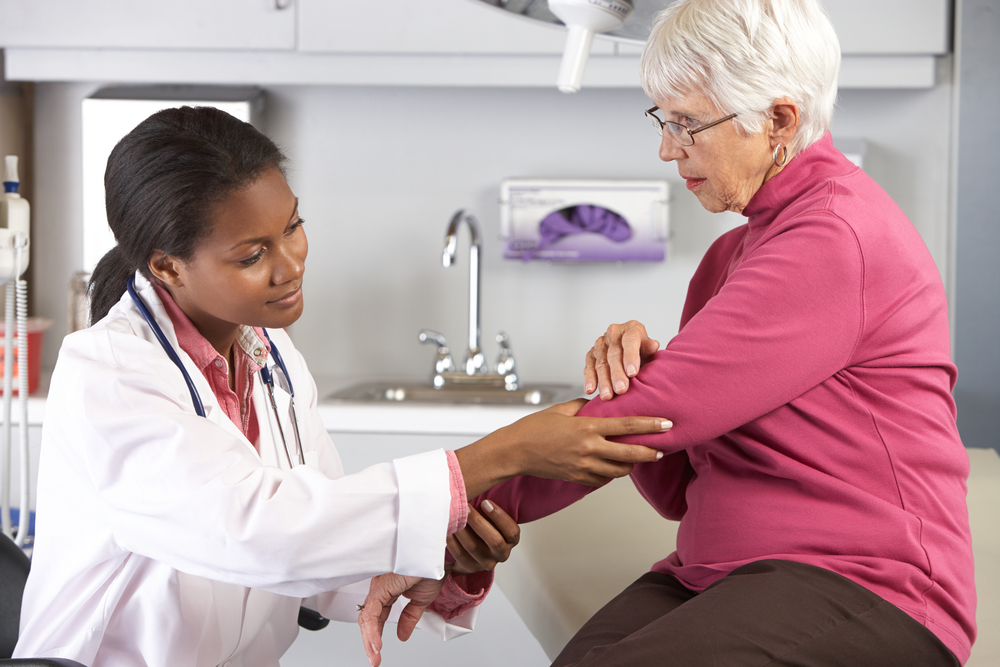
Topical Treatments for Arthritis Relief
Medications such as lidocaine or prilocaine patches and creams target nerve endings to reduce pain.
Topical NSAIDs decrease inflammation and soothe joint pain directly.
These treatments are particularly effective for localized symptoms and nerve-related discomfort.
How Pain Signals Are Processed
Inflammation or injury causes surrounding tissues to release chemicals that activate nerve endings.
Signals travel via nerves to the spinal cord and then to the brain.
The brain interprets these signals and prompts responses to manage pain or injury.
Pain management involves lifestyle adjustments and targeted treatments to improve quality of life.