Essential Insights into Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Learn essential facts about rheumatoid arthritis, including symptoms, causes, stages, treatments, and dietary tips to manage this autoimmune condition effectively. Early diagnosis and lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference in long-term health outcomes.
Sponsored
Key Facts About Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
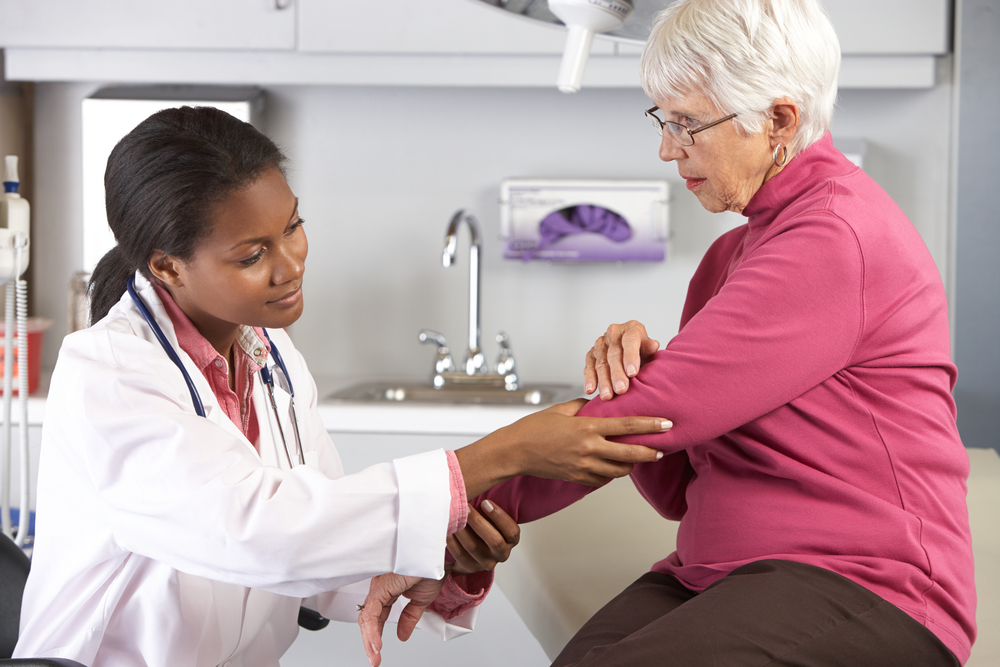
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues. This results in inflammation, swelling, and pain that affect joint function. If untreated, chronic inflammation can damage cartilage, compromise joint stability, and hinder mobility over time.
About 1.5 million individuals are affected by RA nationwide. Although men are at greater risk, women aged 30 to 60 should be extra cautious.
Possible Causes of RAWhile the exact cause remains unknown, factors like genetics, hormonal influences, and environmental triggers play roles.
Individuals with family history are more susceptible. The immune system's abnormal response is believed to be influenced by genetic mutations, hormonal shifts, and environmental exposures such as toxins, bacteria, or pollutants. Other risk factors include:
Exposure to infectious agents
Overweight or minor obesity
Physical or psychological trauma
Environmental toxins
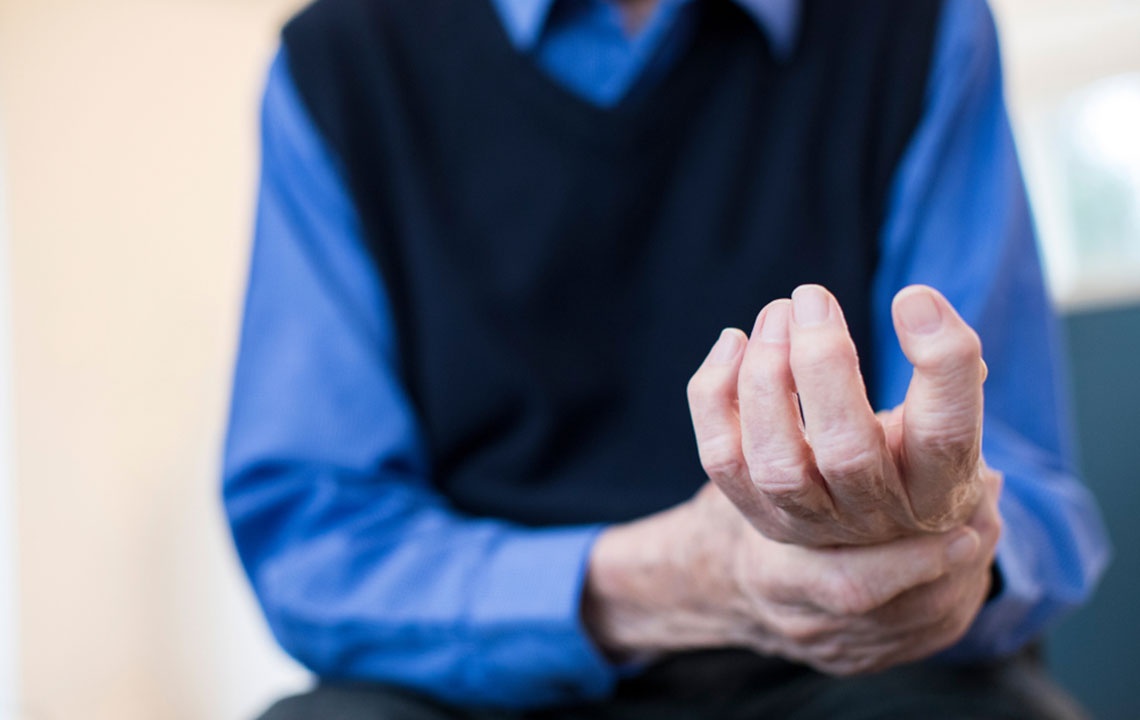
Common SymptomsRA primarily impacts joints, presenting with:
Morning stiffness
Multiple joint pain
Persistent tenderness and swelling
The disorder can also affect various organs and systems.
Symptoms vary based on inflammation severity and may include:
Light sensitivity, dryness, pain, redness, and vision issues
Subcutaneous lumps near bones
Breathing difficulties due to inflammation
Nerve damage and anemia from blood vessel inflammation
Stages of RA ProgressionIndicators of disease development are evident through different stages:
Stage 1: No bone damage, but joint pain, swelling, and stiffness are present.
Stage 2: Synovial inflammation may cause cartilage degradation.
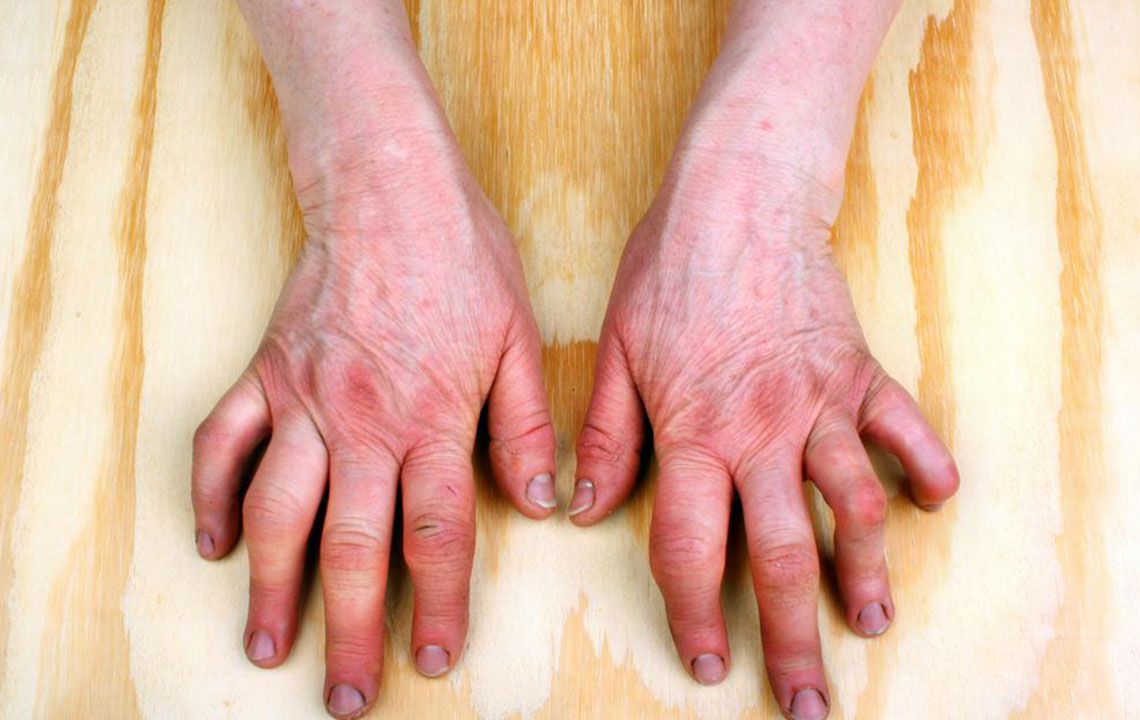
Stage 3: Cartilage and bone damage with severe symptoms, swelling, and reduced mobility.
Stage 4: Joint destruction and loss of function, with possible bone fusion (ankylosis).
Treatment StrategiesInitial treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, alleviating symptoms, preventing joint and organ damage, and enhancing physical ability.
Medications play a vital role, including:
NSAIDs for pain relief
Corticosteroids for short-term inflammation control
DMARDs and biologics for slowing disease progression
When joints are severely damaged, surgery like joint replacement may be necessary to restore mobility. Common surgical options include hip and knee replacements, as well as procedures for shoulders, elbows, and wrists.
Dietary Tips for Managing RAAdopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in antioxidants can help control RA symptoms. Consider including:
Omega-3 Rich Fish: Salmon, sardines, and tuna help reduce inflammation.
Colorful Fruits and Vegetables: Blueberries, strawberries, spinach, and broccoli are packed with antioxidants.
Nuts: Walnuts, almonds, and pistachios contain healthy fats and protein beneficial for inflammation management.
Legumes: Beans such as black, kidney, and garbanzo are rich in anti-inflammatory compounds and nutrients.
Avoid processed, salty, fatty, and sugary foods, and monitor sodium intake. Always consult healthcare professionals for tailored medical advice.
This information is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical guidance. Please consult your healthcare provider for personal medical advice.