Guide to Recognizing and Managing Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
This comprehensive guide highlights the early signs of rheumatoid arthritis and emphasizes the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, and swelling can lead to early intervention, which is crucial in preventing long-term joint damage and other health complications. The article covers diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and distinguishes RA from similar conditions like fibromyalgia. Early medical consultation can significantly enhance management outcomes and improve overall well-being.
Sponsored

Understanding the Initial Symptoms and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Key insights into early detection and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
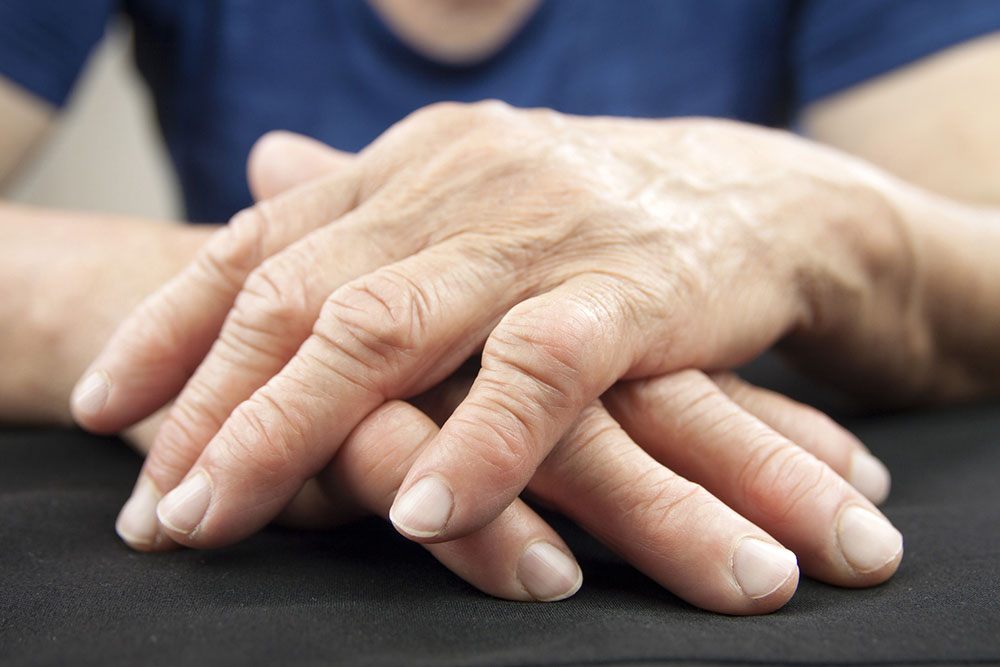
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition causing persistent joint inflammation, primarily affecting the knees, hands, feet, and fingers. Recognizing early signs and seeking prompt medical care are crucial for effective management. RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and joint damage. In the U.S., approximately 1.5 million individuals experience RA symptoms.
This condition can impact any gender and age, though women between 30 and 60 are most commonly affected. Both sides of the body are typically involved, especially the hands, wrists, and knees. Early intervention can prevent severe health complications linked to prolonged inflammation, such as damage to blood vessels, lungs, eyes, mouth, and skin.
Vascular issues: Inflamed blood vessels may result in nerve, skin, and organ damage.
Lung problems: Inflammation can cause breathing difficulties.
Eye symptoms: Dryness, redness, pain, light sensitivity, and vision issues
Mouth and skin: Dryness, gum irritation, or small lumps under the skin
Early signs of RA include:
Fatigue
Stiffness in the morning
Joint stiffness and pain
Minor swelling
Fever
Numbness and tingling
Reduced movement range
While RA shares some symptoms with fibromyalgia, they are distinct conditions. RA is an autoimmune disease targeting joints; fibromyalgia causes musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and mood issues. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Other RA symptoms may include trouble sleeping, chest pain during breathing, appetite loss, fatigue, dry mouth, itchy eyes, eye discharge, and weight loss. If you experience these, visit a doctor promptly.
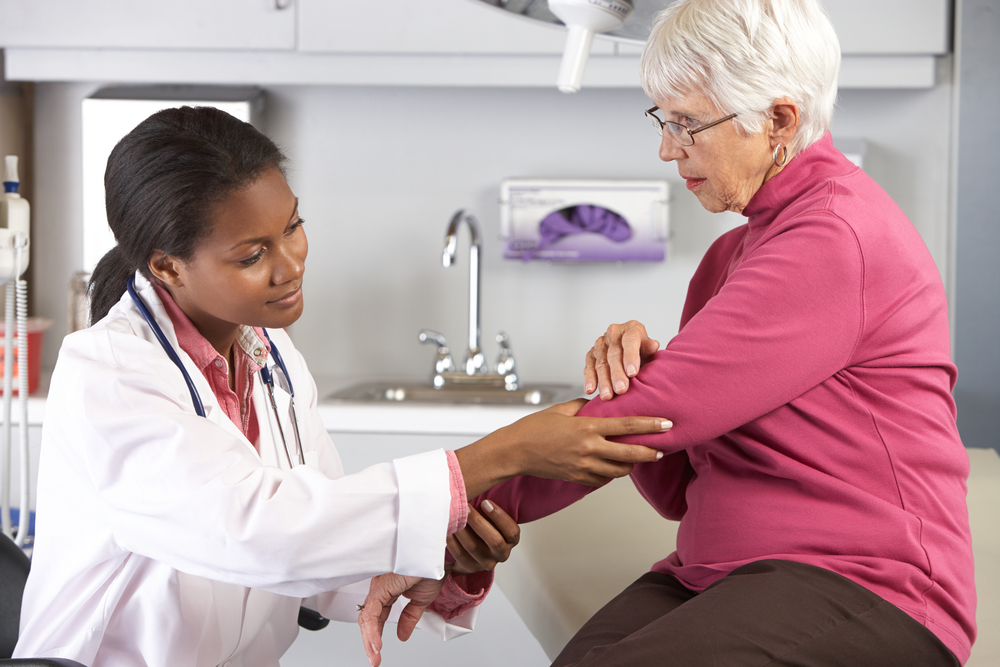
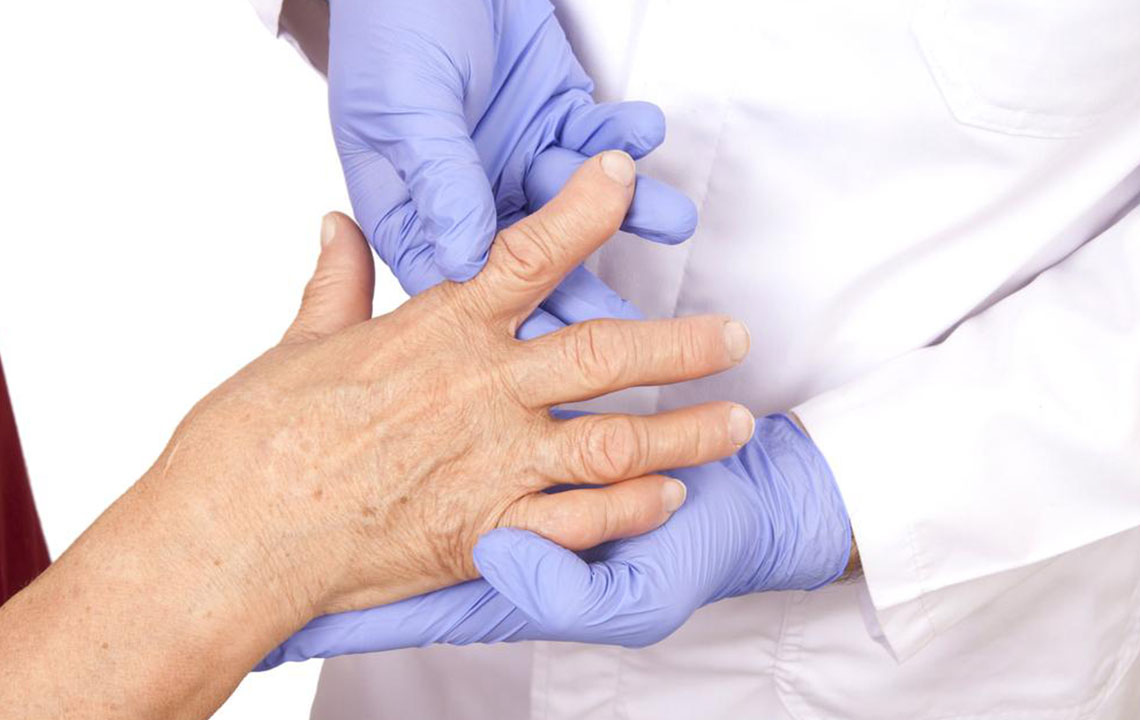
Diagnosis involves multiple tests, as no single test confirms RA. Your doctor will review medical history, perform physical exams, and may order blood tests for inflammation markers and auto-antibodies. Imaging tests like ultrasound can reveal joint damage. Treatments include pain relievers such as acetaminophen, NSAIDs like ibuprofen, and, if necessary, surgery — typically a last resort. Early treatment is vital to prevent severe health issues and improve quality of life.