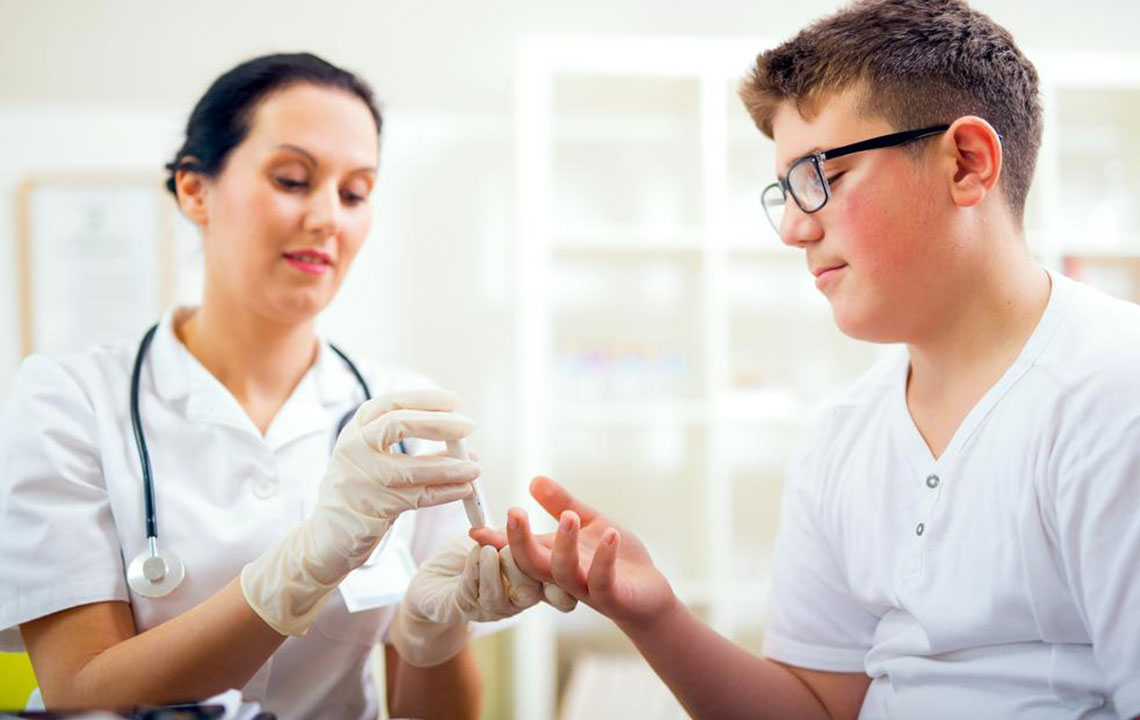
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Glucose Monitoring
This comprehensive guide covers the importance, timing, methods, and target ranges for blood glucose testing. Regular monitoring helps diabetic individuals manage their condition effectively by understanding their blood sugar fluctuations and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. Proper testing techniques and consultation with healthcare professionals ensure safe and accurate results, aiding in preventing complications and maintaining overall health.
Sponsored
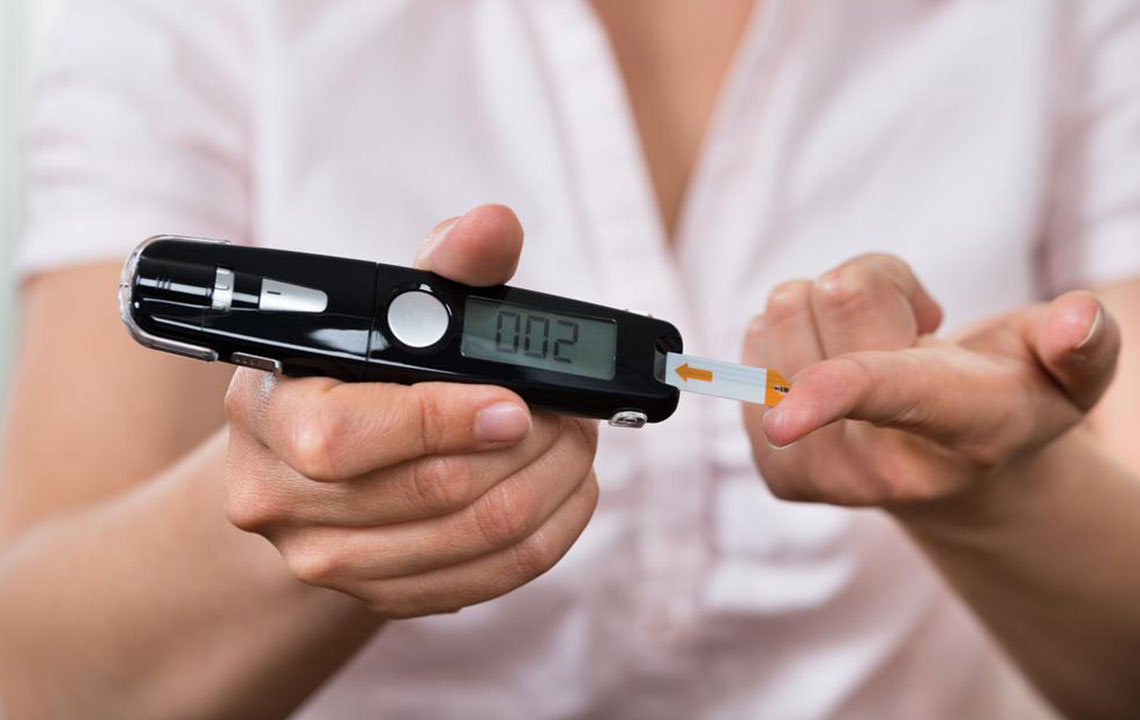
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for individuals managing diabetes, especially when levels become critical. Self-testing provides valuable insights for tailoring treatment plans and maintaining optimal health.
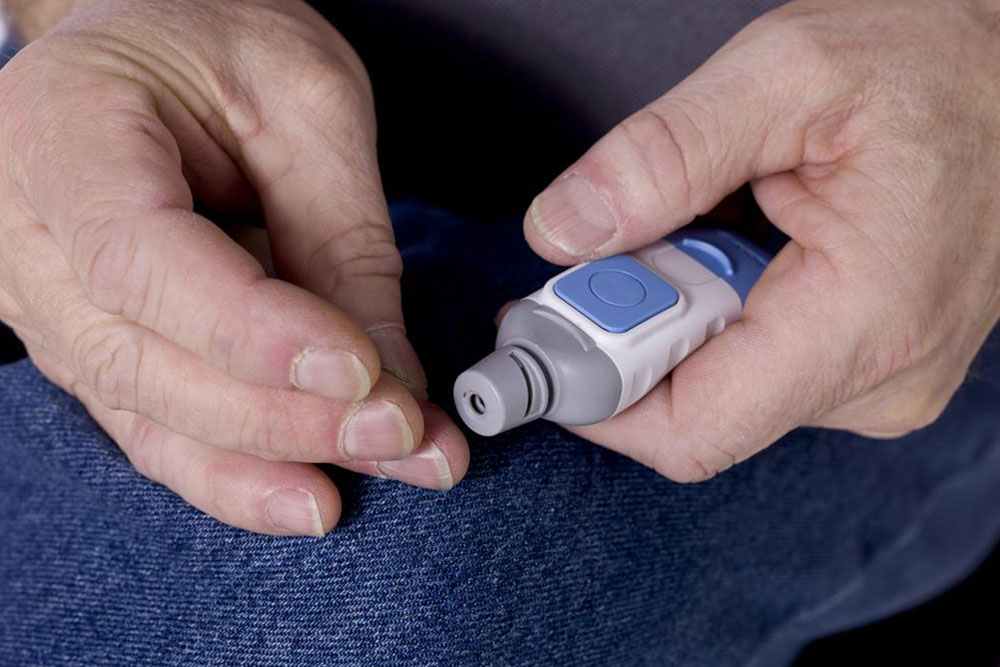
Home-based blood sugar measurement is simple with a small glucose meter that accurately tracks levels.
Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular testing helps diabetic patients assess treatment effectiveness and adjust lifestyle choices. It also aids in understanding how diet, exercise, and illness influence blood glucose levels, including fluctuations during high or low sugar episodes.
Consistent blood glucose testing allows individuals to evaluate their response to medication and lifestyle changes. It also helps detect dangerous spikes or drops in sugar levels, facilitating prompt medical intervention when necessary.
Timing for Blood Glucose Testing
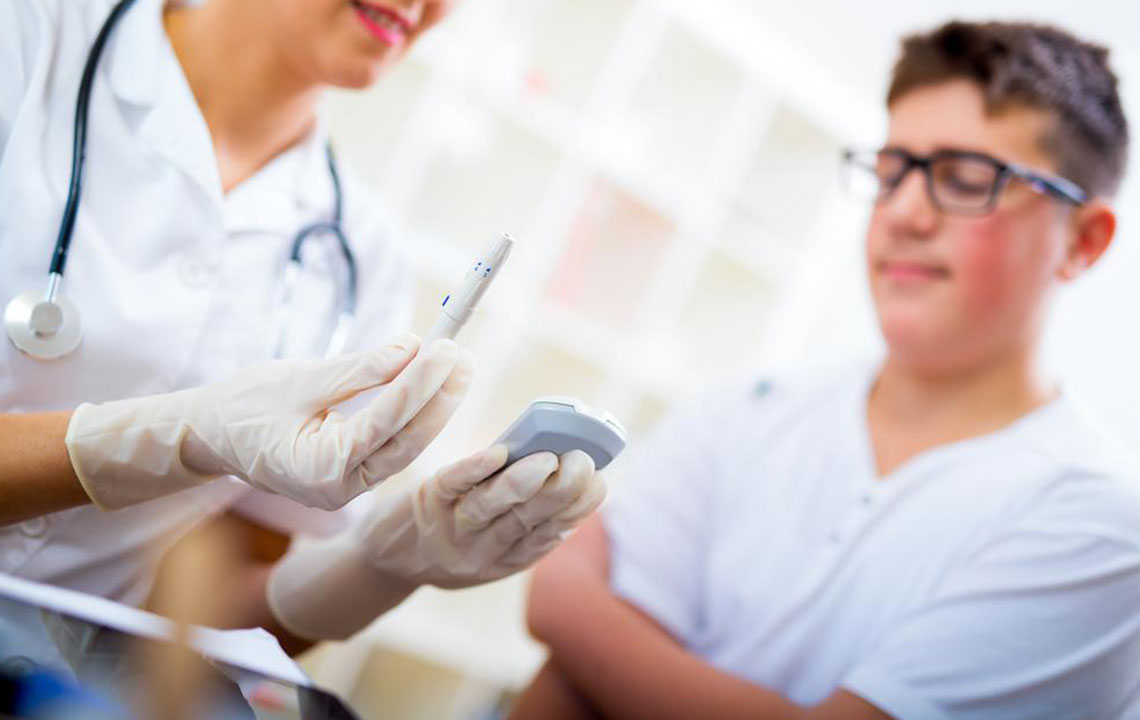
The ideal times for testing are determined by your healthcare provider, depending on the type and severity of diabetes.
For Type 1 diabetes, testing may be required multiple times daily — before meals, post-exercise, and occasionally overnight, especially during illness. For Type 2 diabetes managed with insulin, testing two to three times daily, often before and after meals, is common. If managed through lifestyle modifications alone, frequent testing may not be necessary.
Target Blood Glucose Levels
Target ranges vary based on individual health factors, age, duration of diabetes, pregnancy, and presence of complications.
Generally, optimal blood sugar levels are:
80 to 120 mg/dL for adults under 60 without other illnesses.
100 to 140 mg/dL for those aged 60 and above or with additional health issues like heart, kidney, or lung conditions.
Levels outside these ranges indicate the need for medical attention and stricter management to prevent complications.
How to Test Blood Sugar Levels
Using a glucose meter, individuals can measure blood sugar by pricking their fingertip to obtain a blood sample. The process involves cleaning hands, inserting a test strip into the meter, pricking the finger with a provided lancet, and applying a drop of blood to the strip. The meter displays the readings within moments.
If readings are consistently high or low, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. Regular calibration and correct technique ensure accurate results.
Effective blood glucose management is vital for preventing serious health issues, and timely testing supported by medical consultation makes a significant difference.