Understanding Blood Glucose Monitoring and Charting
This article explores the importance of monitoring blood glucose levels, understanding glucose charts, and maintaining healthy levels through lifestyle and medical practices. It covers normal ranges, tracking tools, and lifestyle tips for both healthy individuals and diabetics to prevent complications and promote overall well-being.
Sponsored
Blood glucose levels reveal the amount of sugar present in an individual's bloodstream at a specific moment. This sugar is essential for providing energy to different body parts by being transported to the cells. Our bodies obtain glucose from various foods we consume.
The regulation of blood sugar is managed by body systems to ensure levels remain balanced. It’s important to note that blood sugar is specifically in the form of glucose, distinct from sucrose or common table sugar.
The glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day, typically lowest before breakfast and peaking after meals, then decreasing afterward. For healthy individuals, fasting blood glucose should be below 99 mg/dl. Diabetics often experience more variability. The goal is to keep pre-meal levels under 130 mg/dl and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dl.
What is a Blood Glucose Chart?
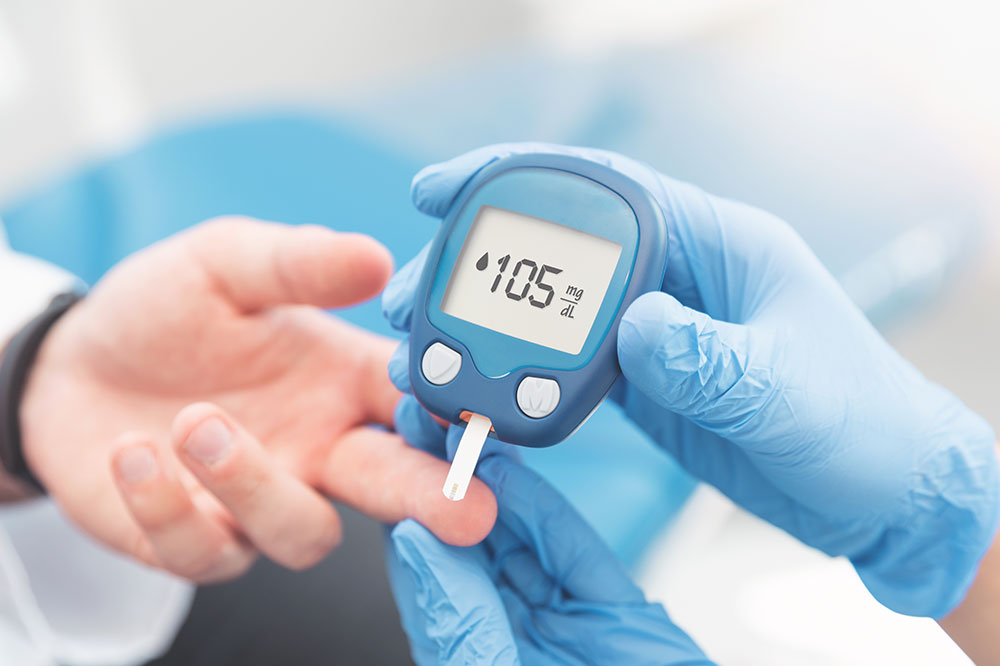
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and can be managed through diet, medication, and exercise. A blood glucose chart records these levels over time, offering insights into daily fluctuations. Since blood sugar varies throughout the day—lowest before meals and highest after—they serve as essential tools in diabetes management.
Significance of Tracking Blood Glucose and Maintaining Levels
Similar to blood pressure or cholesterol, tracking glucose levels helps assess overall health. Regular monitoring is vital for healthy individuals and especially for diabetics, as sudden changes can impact kidney function, vision, and heart health. Keeping a record helps prevent health complications by detecting irregularities early.
Tools, Components, and Tips for Blood Sugar Tracking
Various devices are available for measuring blood sugar, but it’s important to consult healthcare providers before use. For diabetics, key measurements include fasting glucose and post-meal levels. Comparing these figures with normal ranges guides treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Fasting levels should be under 100 mg/dl, and post-meal levels less than 140 mg/dl for healthy individuals.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle—balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol—is essential for maintaining optimal glucose levels. Activities like walking and jogging are effective, and managing stress is also critical to keep blood sugar within healthy limits.