Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Crohn's Disease
Explore comprehensive insights into Crohn’s disease, including causes, symptoms, risk factors, and modern treatment options. Early diagnosis and management are key to living well with this chronic inflammatory bowel condition.
Sponsored

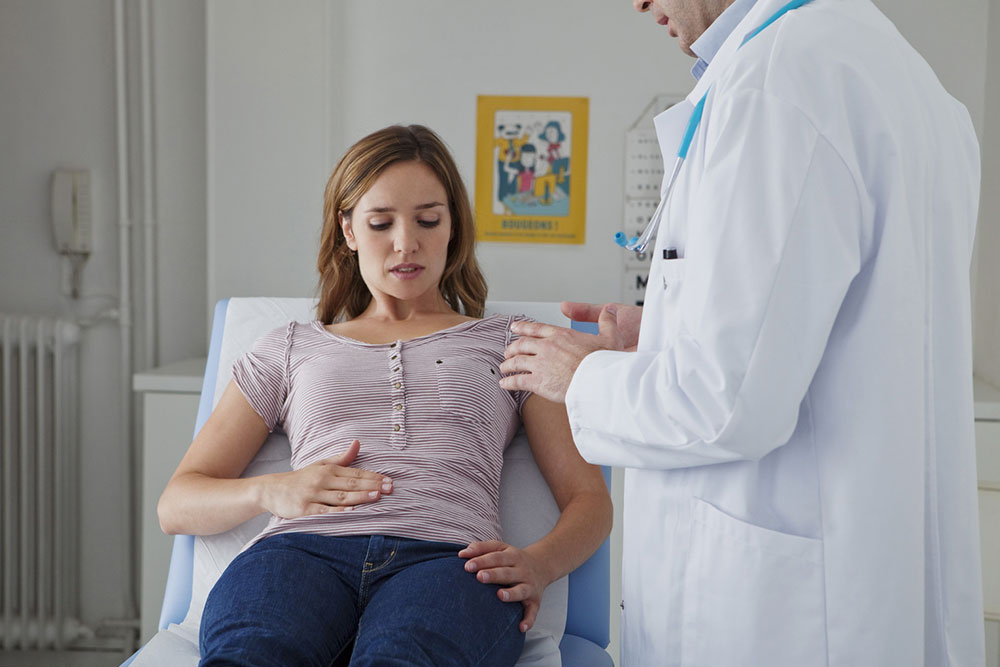
Every year, thousands are diagnosed with Crohn’s disease, a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the gastrointestinal tract. If not identified and managed early, it can lead to serious health complications. Recognizing the symptoms and getting proper diagnosis are crucial steps toward effective treatment and maintaining a normal lifestyle.
What is Crohn’s Disease? This ailment falls under inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). It causes inflammation in the digestive system, resulting in intense stomach pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and malnutrition. The inflammation can extend through various layers of the bowel wall, making it more severe than typical gastrointestinal issues.
The condition often leads to debilitating pain and disability. If untreated, it may result in life-threatening complications. The exact cause remains unknown, but factors like a weakened immune system, genetics, diet, and stress appear influential. People with a family history are more prone, although not all individuals with relatives affected develop the disease.
Risk factors include age, ethnicity, smoking habits, medication use, and living conditions. Crohn’s can manifest at any age but is most frequently diagnosed before age 30. Caucasians and those of Eastern European Jewish descent have higher susceptibility, though all ethnicities can be affected. Lifestyle factors such as smoking and environmental exposures also contribute.
Symptoms and Warning Signs Common symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, frequent diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. In some cases, only the terminal ileum or colon is affected, leading to varied symptoms. Severe cases may involve rectal bleeding, fever, night sweats, nausea, and joint pain. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, potentially causing significant health issues if untreated.
Complications include fistulas, fissures, intestinal obstructions, and nutritional deficiencies. Severe cases may lead to bowel perforation or systemic inflammation. Recognizing these symptoms early and consulting a healthcare provider is essential to prevent serious outcomes.
Despite the similarity to ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease impacts different areas of the gastrointestinal tract. Both conditions can have flare-ups and periods of remission, but diagnosis requires medical testing, including colonoscopy and biopsy, to distinguish between them.
Is There a Cure for Crohn’s Disease? Currently, there is no cure. However, early detection and appropriate treatment can significantly control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging, and endoscopic procedures to assess severity and location. Treatments focus on reducing inflammation, managing pain, and preventing complications. Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, antibiotics, and nutritional supplements are commonly used. Dietary modifications may also be recommended. In severe cases, surgery might be necessary to remove damaged portions of the intestine.
While Crohn’s disease is a lifelong condition, proper management allows many individuals to lead active, healthy lives with minimal discomfort.