Understanding Crohn’s Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
This comprehensive overview covers Crohn’s disease, detailing its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and various management options. It highlights the importance of early detection, tailored treatments, and lifestyle adjustments to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Sponsored
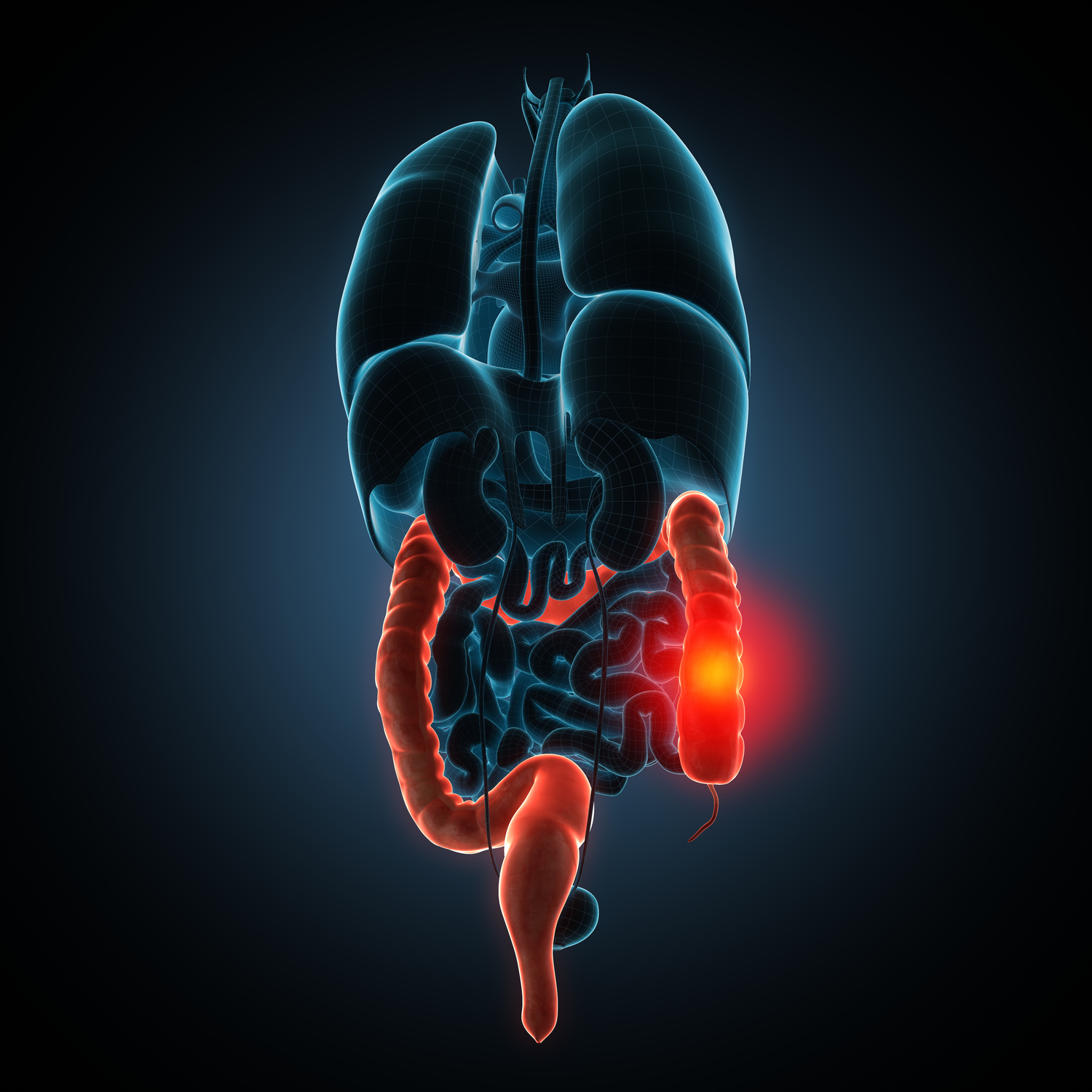
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that impacts the digestive tract, mainly targeting the small intestine and colon. The inflammation can disrupt normal digestion, causing pain and deep tissue damage, which may lead to severe complications.
Possible Causes of Crohn’s Disease
Although the exact cause remains unknown, research suggests autoimmune responses to gut bacteria, genetic predisposition, smoking, and age may contribute to its development.
Signs and Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
Symptoms may develop gradually or suddenly, and can become severe over time. Common indicators include:
Abdominal cramps
Diarrhea
Bloody stools
Fever
Urgent need for bowel movements
Fatigue
Advanced symptoms may involve:
Perianal fistulas
Ulcers between the mouth and anus
Anemia causing breathlessness
Joint and skin inflammation
Early detection of these symptoms can facilitate prompt treatment and prevent major health issues.
Diagnosis and Management
Doctors perform various tests to diagnose Crohn’s, as its exact cause remains elusive. Multiple assessments help determine tissue damage extent and activity. Diagnostic methods include:
Stool and blood tests to check inflammation and anemia
Capsule endoscopy to capture images of the small intestine
Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy to examine the colon
Imaging scans such as CT or MRI for detailed views of the intestines
While a cure is unavailable, treatment aims to lessen symptoms. Medications like anti-inflammatory and anti-diarrheal drugs are standard. Additional strategies include:
Diet Adjustments: Dietary consultation helps identify food triggers. Patients may log meals to optimize their nutrition intake while minimizing adverse effects.
Surgical Options: Surgery, often necessary for about 75% of patients, involves removing damaged intestinal sections and restoring function. It addresses tissue damage, scarring, or infection issues.
Depending on individual cases, treatment plans are tailored based on symptoms, disease history, and response to therapy. Other beneficial approaches include:
Probiotics: Live bacteria that restore gut flora balance and prevent harmful microorganisms from disrupting digestion.
Prebiotics: Foods like bananas, asparagus, artichokes, and leeks support healthy bacteria growth in the gut.
Omega-3 Fish Oil: Ongoing research explores its potential in managing inflammation associated with Crohn’s.
Aloe Vera: Known for anti-inflammatory properties, it may help soothe symptoms.
Dietary Tips for Symptom Management:
Reduce high-fiber foods during flare-ups
Limit fat and dairy intake
Stay well-hydrated
Consuming vitamin-rich foods
Supporting affected individuals involves listening, encouraging support group participation, and seeking psychological support if needed. Developing a personalized approach can improve quality of life for those with Crohn’s disease.