Comprehensive Guide to HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
This article provides an in-depth overview of HER2-positive breast cancer, including symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options such as chemotherapy, surgery, targeted therapy, and self-care strategies. It emphasizes early detection and personalized treatment plans for better outcomes.
Sponsored
HER2-positive breast cancer involves an overproduction of a specific protein receptor called HER2, also known as the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. This abnormal gene activity causes rapidly dividing cells, leading to tumor formation. Despite its aggressive nature, HER2-positive breast cancer is treatable with various medical approaches.
Common symptoms include lumps, breast swelling, skin dimpling, nipple pain, and changes in breast shape. Additional signs may be skin thickening or nipple discharge. Recognizing these early symptoms can facilitate prompt diagnosis.
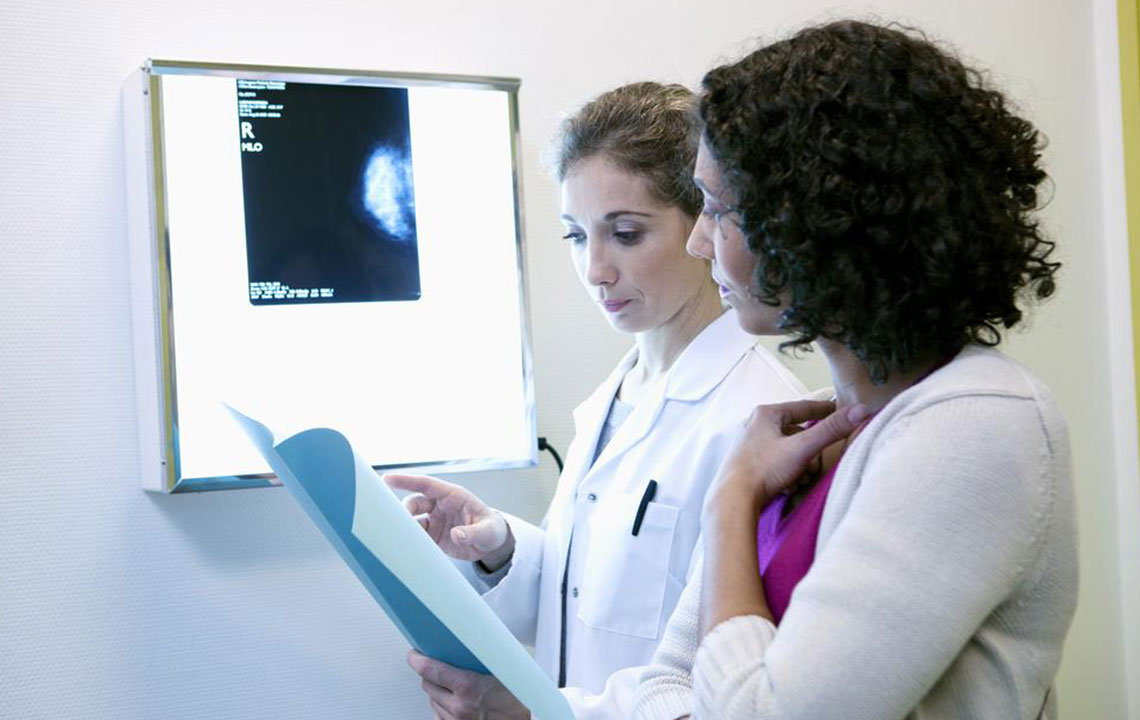
To confirm HER2 positivity, doctors perform several tests, including IHC, FISH, SPOT-Light HER2 CISH, and Inform HER2 Dual ISH. The IHC test detects HER2 proteins in tissue samples, while FISH maps genetic material to identify additional copies of the HER2 gene. The CISH and ISH tests involve visualizing and counting HER2 genes under a microscope.
Treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, participation in clinical trials, and self-care practices. Chemotherapy can be administered before or after surgery, often combined with other treatments to improve outcomes.
Radiation therapy, typically following surgery, helps prevent recurrence and target metastases. It includes external beam radiation and brachytherapy, where radioactive material is placed inside the body. Surgical procedures depend on the cancer stage, with options like lumpectomy or mastectomy. Lymph node removal procedures may also be performed to check disease spread.
Targeted therapy blocks HER2 receptors, hindering tumor growth, and is often recommended for over a year to reduce relapse risk. Hormone therapy is advised if the cancer is hormone receptor-positive, aiming to inhibit estrogen's effects. Clinical trials evaluate new treatments' safety and efficacy, offering additional options for patients willing to participate.
Self-care plays a vital role in managing breast cancer. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and seeking emotional support can significantly improve quality of life during treatment. Consulting healthcare providers ensures personalized care tailored to individual needs.






