Understanding the Root Causes of Joint Discomfort
This article explores various causes of joint pain, including arthritis, injuries, infections, and other medical conditions. Understanding these causes helps in effective management and treatment of joint discomfort, which can range from mild aches to severe agony affecting daily life. Early diagnosis and appropriate interventions are essential for maintaining joint health and mobility.
Sponsored

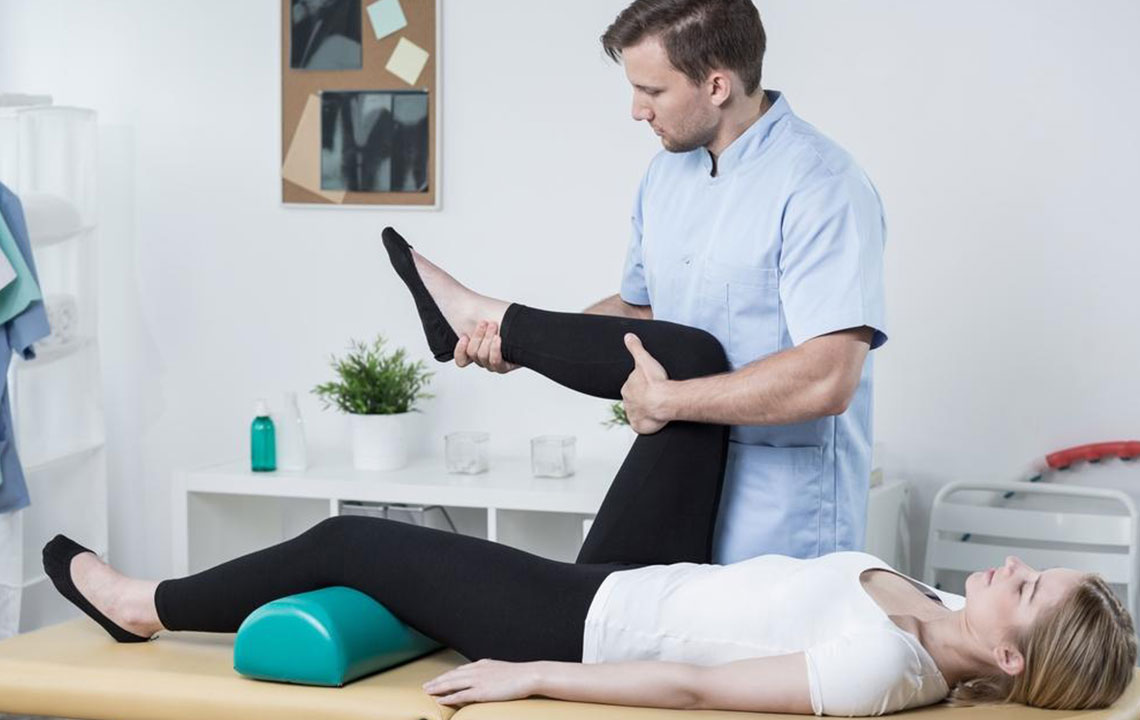
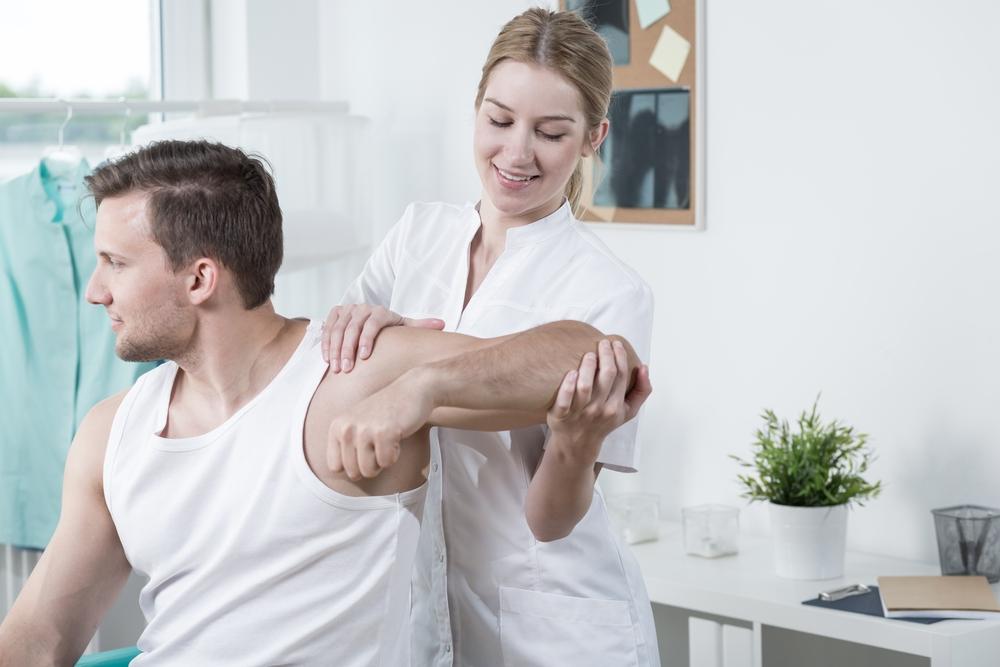
Joints are crucial parts of the skeletal framework where two bones connect, enabling movement. Common joints include shoulders, elbows, knees, and hips. Joint pain refers to soreness or aches in these areas and is a widespread issue affecting many individuals worldwide. Although not always urgent, persistent joint discomfort can significantly impact overall health. Arthritis is the leading cause of joint pain, but other factors can also contribute.
Joint pain can range from slight discomfort to intense agony. It may be temporary, resolving within weeks, or become chronic, lasting for months. Even fleeting swelling and pain can diminish quality of life. Effective management involves exercise, medication, physical therapy, and alternative treatments.
What causes joint pain?
Most often, arthritis is the culprit, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the primary types. The American College of Rheumatology reports that osteoarthritis is common among adults over 40.
Osteoarthritis develops gradually, affecting joints like the knees, hips, hands, and wrists, due to cartilage degeneration—the cushion that absorbs shocks in joints. Rheumatoid arthritis, affecting over 1.5 million Americans, is more prevalent in women. It causes joint deformation, pain, swelling, and inflammation as the immune system attacks joint linings.
Other causes include:
Inflammation of surrounding cushioning pads (bursitis)
Gout: sudden and severe joint pain with inflammation, affecting anyone
Tendinitis: inflammation of tendons and joint tissues, causing pain outside joints, often in wrists, knees, elbows, or shoulders
Psoriatic arthritis: joint stiffness and swelling in people with psoriasis
Cancer: bone cancers, mainly in long bones, can cause joint pain
Rickets: weakened bones in children from Vitamin D deficiency, leading to joint pain
Sarcoidosis: inflammatory granulomas forming in tissues like skin and lymph nodes due to immune response
Injuries such as sprains and strains affecting ligaments, muscles, and tendons
Pseudogout: crystal deposit-induced sudden joint pain and swelling
Blood cancers like leukemia affecting bone and joint health
Poor blood flow causing tissue death (avascular necrosis)
Infections like influenza or hepatitis impacting joints
Cartilage breakdown or conditions like chondromalacia
Trauma or overuse injuries
Osteoporosis or osteomalacia weakening bones
Identifying the root causes helps doctors develop effective treatment strategies to alleviate joint pain and improve mobility.