Root Causes and Solutions for Joint Discomfort
Understanding the diverse causes of joint pain helps in effective management. Factors like aging, obesity, injuries, and diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis play key roles. Treatments include medication, lifestyle changes, and surgical options. Proper diagnosis and early intervention are vital to restoring movement and reducing discomfort.
Sponsored

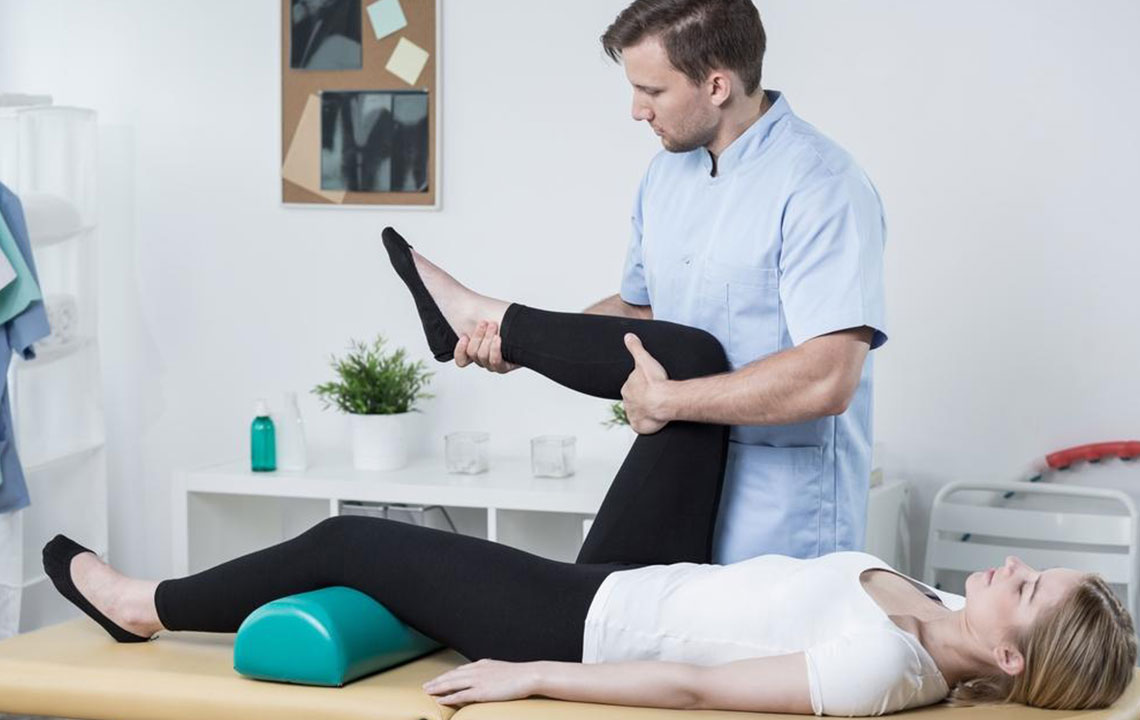
Joints are vital connectors of bones within the skeletal framework, enabling smooth limb movement. Some joints, like those in the knees, are highly mobile, while others, such as in the skull, allow minimal movement. A lubricating fluid between bones reduces friction, ensuring seamless motion. Joint pain arises when these structures weaken or become inflamed due to various factors. The intensity often correlates with the degree of inflammation and damage.
Activities like sports can cause temporary joint injuries such as strains and sprains, which typically heal quickly. However, conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and bursitis may persist long-term, impairing mobility and daily function. Managing joint pain involves addressing its root causes, which include:
Excess weight
Overweight individuals often face higher risks of developing arthritis due to added pressure on joints.
Age-related changes
Aging leads to fragile joints, reduced cartilage, and diminished synovial fluid, causing discomfort especially in knees and hips.
Trauma
Injuries such as sprains from overstretching further damage ligaments and tissues, resulting in swelling and pain.
Health conditions
Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis erode cartilage, causing stiffness and deformity.
Cancer
Bone cancers are rare but can cause joint pain; sometimes, joint pain signals metastatic tumors elsewhere.
Medication side effects
Certain drugs might trigger joint discomfort as a reaction.
Fibromyalgia
This condition amplifies pain signals in the brain, worsening joint ache without inflammation.
Joint pain divides into arthritis, characterized by inflammation, and arthralgia, which involves non-inflammatory joint injury. Common conditions include:
Gouty arthritis
Sudden, intense pain, often on toes, caused by uric acid crystals.
Rheumatoid arthritis
An autoimmune disorder leading to joint destruction, often inherited.
Osteoarthritis
Degenerative joint disease primarily affecting knees and hands, linked to obesity.
Lyme disease
An infection from tick bites can cause widespread joint pain.
Still’s disease
High fever, fatigue, and rashes contribute to joint discomfort.
Other causes include rheumatic fever, septic arthritis, trauma, and systemic diseases. Effective treatment targets the underlying issue through diagnostics, rest, therapies, medications, and sometimes surgical intervention like joint replacement.