Understanding Digestive Gas and Abdominal Discomfort
This comprehensive overview explains what causes digestive gas and bloating, highlights typical symptoms like belching and abdominal pain, and recommends when to seek medical advice. It offers insights into diet adjustments and underlying health conditions contributing to persistent gas problems, ensuring better management and relief strategies.
Sponsored

Insights into Digestive Gas and Related Discomfort
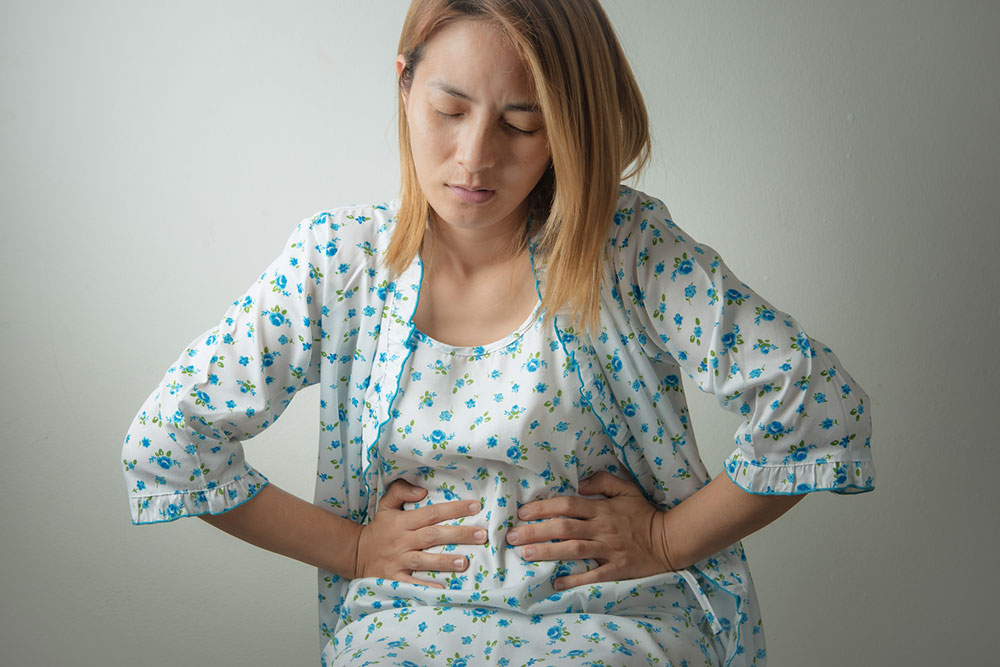
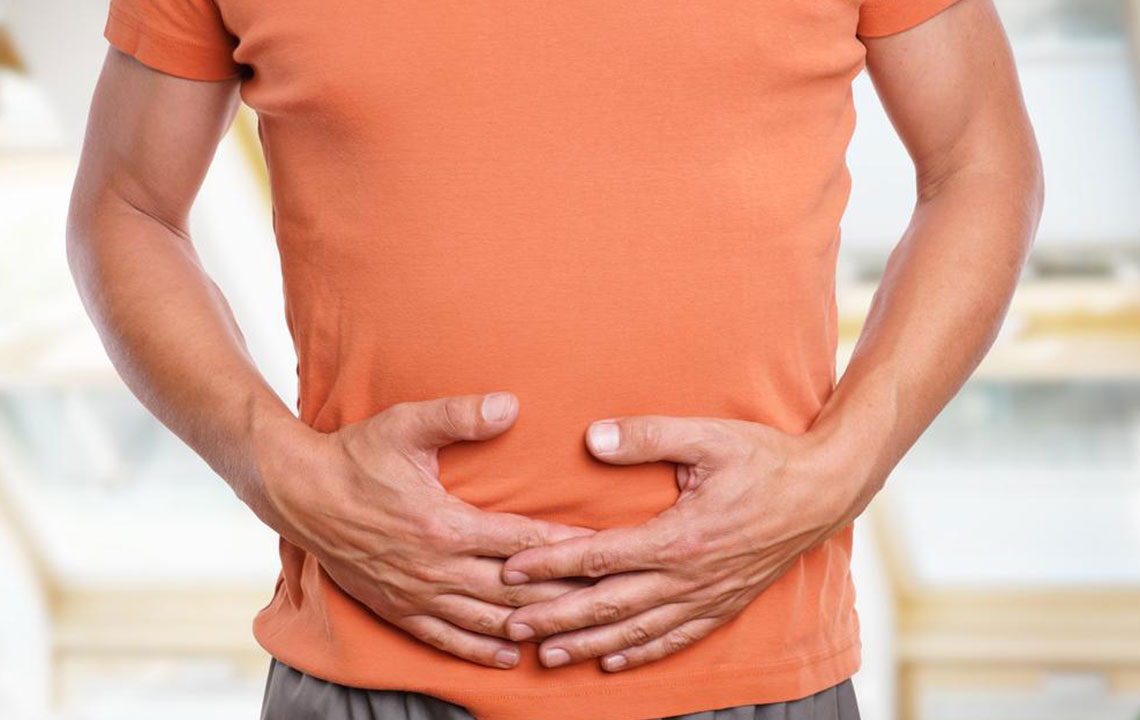
After meals, many experience a swollen stomach, feeling as if a heavy weight resides inside. This sensation, along with frequent burping or passing gas, can be socially awkward. Bloating, gas, and distention occur from time to time, but persistent symptoms can disrupt daily life. Fortunately, various remedies—home treatments or medical consultation—can provide relief. Common causes include consuming carbonated drinks, gas-producing foods like legumes and cruciferous vegetables, or fermentation processes in the intestines.
Recognizing the signs and understanding triggers is vital. Simple diet modifications, such as reducing gas-inducing foods, can alleviate symptoms. If gas symptoms are frequent or severe, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. Causes include swallowing excess air, certain foods, or digestive irregularities.
Common symptoms include belching, passing gas, bloating, and abdominal discomfort. Belching often occurs when air is swallowed during eating, while passing gas is normal up to 20 times daily. Bloating involves a swollen, full feeling, especially after meals. If symptoms persist or worsen, or are accompanied by blood in stools, weight loss, or severe pain, medical attention should be sought promptly. Underlying conditions like Crohn’s disease, constipation, bacterial overgrowth, or food intolerances may contribute to excessive gas and warrant diagnosis and treatment.