Comprehensive Guide to Lung Infection and Its Indicators
This article offers an in-depth overview of pneumonia, covering causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, complications, and preventive measures. It emphasizes early detection and vaccination to reduce severity and improve outcomes for affected individuals, especially vulnerable populations like children and seniors.
Sponsored

Understanding Lung Infection and Recognizing Its Symptoms
Lung infection, commonly called pneumonia, affects one or both lungs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, with bacterial infections being most prevalent in adults. This condition involves inflammation of the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs, which become filled with pus, impairing breathing.
Risk Factors
While anyone can develop pneumonia, certain groups are more vulnerable. Infants under 2 and seniors over 65 are at higher risk. Individuals with stroke history, or chronic illnesses like asthma, diabetes, or heart conditions, also face increased susceptibility.
Complications from pneumonia may arise even with timely treatment, especially if the infection is severe. Risks include bacteria entering the bloodstream, leading to organ failure, or severe breathing difficulties. Hospitalization and ventilator support might be necessary until recovery.
Diagnosis Methods
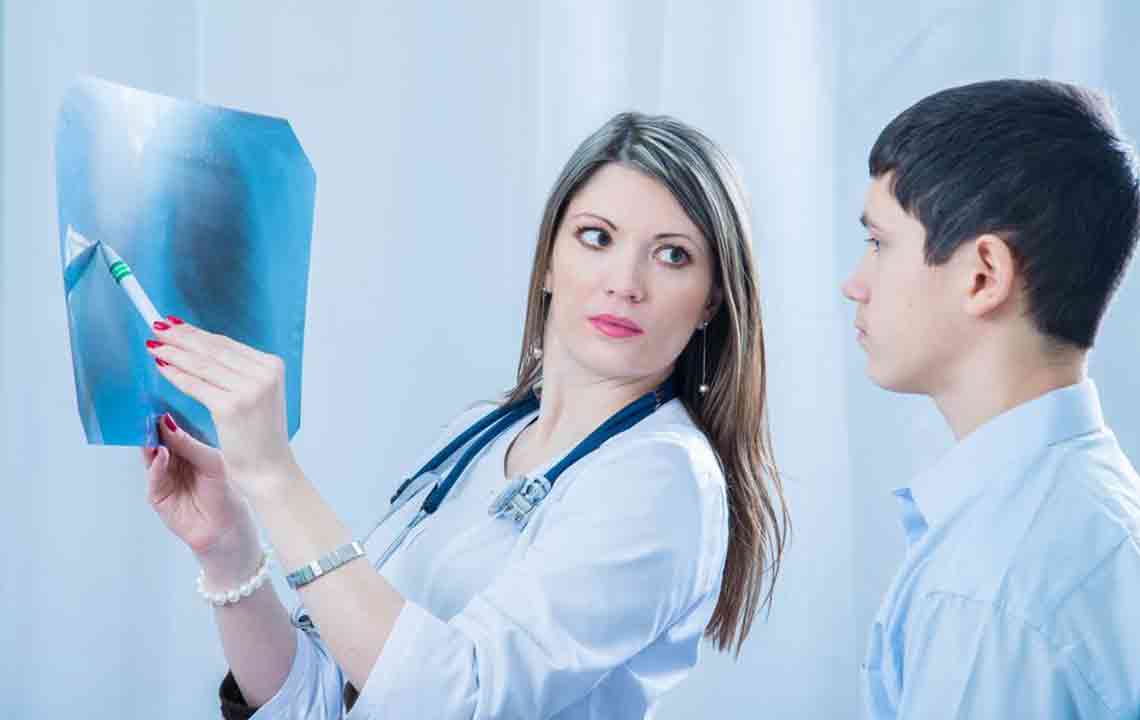
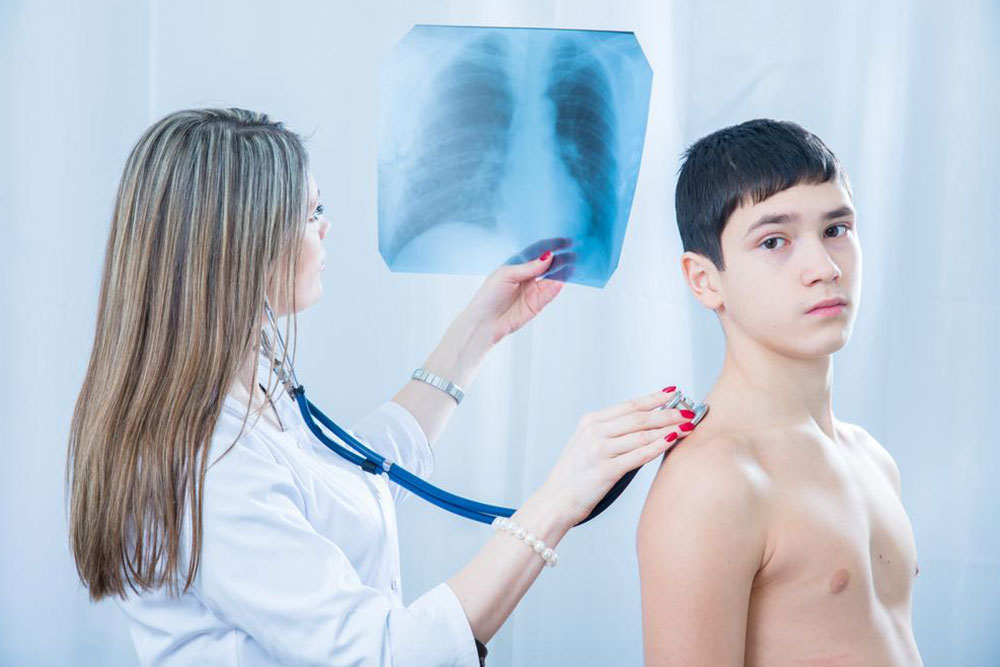
Doctors diagnose pneumonia by inquiring about symptoms and medical history. A physical exam is performed, followed by a chest X-ray to confirm the diagnosis. Additional tests like blood, sputum, urine, or CT scans may be recommended based on severity. In some cases, fluid samples or bronchoscopy are used to identify the cause precisely.
Blood Test - Confirms infection but doesn't specify the pathogen.
Sputum Analysis - Identifies the infectious agent from lung mucus.
Urine Test - Detects bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Legionella.
Imaging - CT scans provide detailed lung images for accurate diagnosis.
Fluid Sampling - Checks for fluid in the pleural space, aiding in cause identification.
Bronchoscopy - Visualizes airways with a camera, especially if symptoms are severe or unresponsive to treatment.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms vary from mild to severe, including cough with mucus, fever, chills, sweating, and shortness of breath. Chest pain may also occur in early stages. The presentation can differ by cause and age group. Viral pneumonia often starts with wheezing and high fever within hours, while bacterial cases may lead to blue lips, sweating, and confusion. In children under five, rapid breathing is common, and infants might vomit or have feeding issues.
Prevention Strategies
Getting vaccinated against pneumonia is the first line of defense. Since symptoms often mimic flu, annual flu shots help prevent confusion and ensure proper treatment. Taking precautions early can prevent life-threatening complications. With appropriate care and rest, most recover fully and resume normal routines.