Comprehensive Guide to Bone Density Testing
Learn about bone density testing, its importance, procedures, and tips to maintain healthy bones. This comprehensive guide covers who should get tested, differences from bone scans, potential risks, and preventive measures. Regular testing can help detect osteoporosis early and guide effective treatment strategies for stronger bones and improved health.
Sponsored

Understanding Bone Density Assessments
Introduction to Bone Density Testing
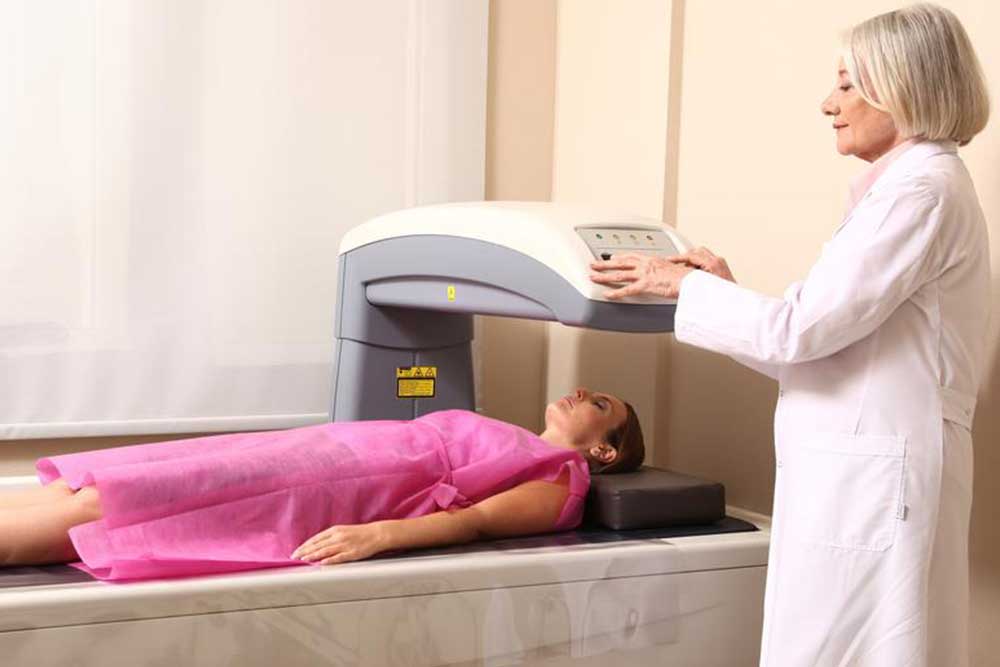
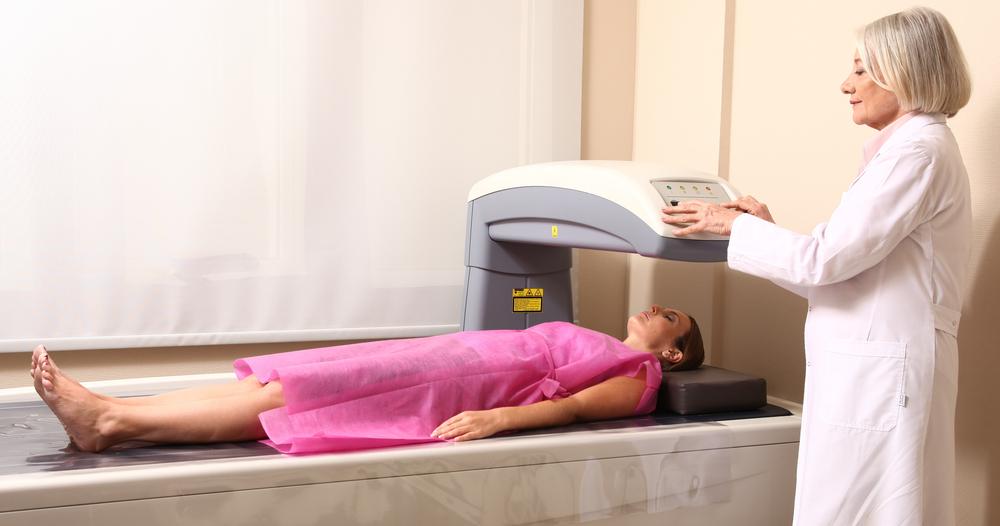
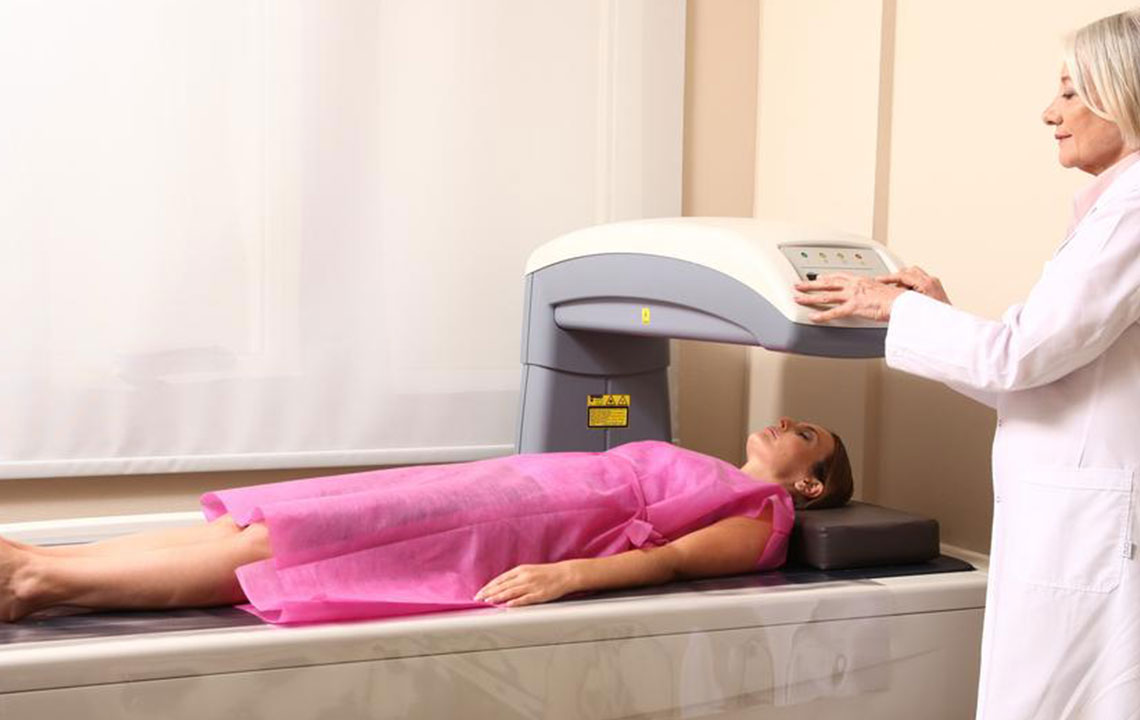
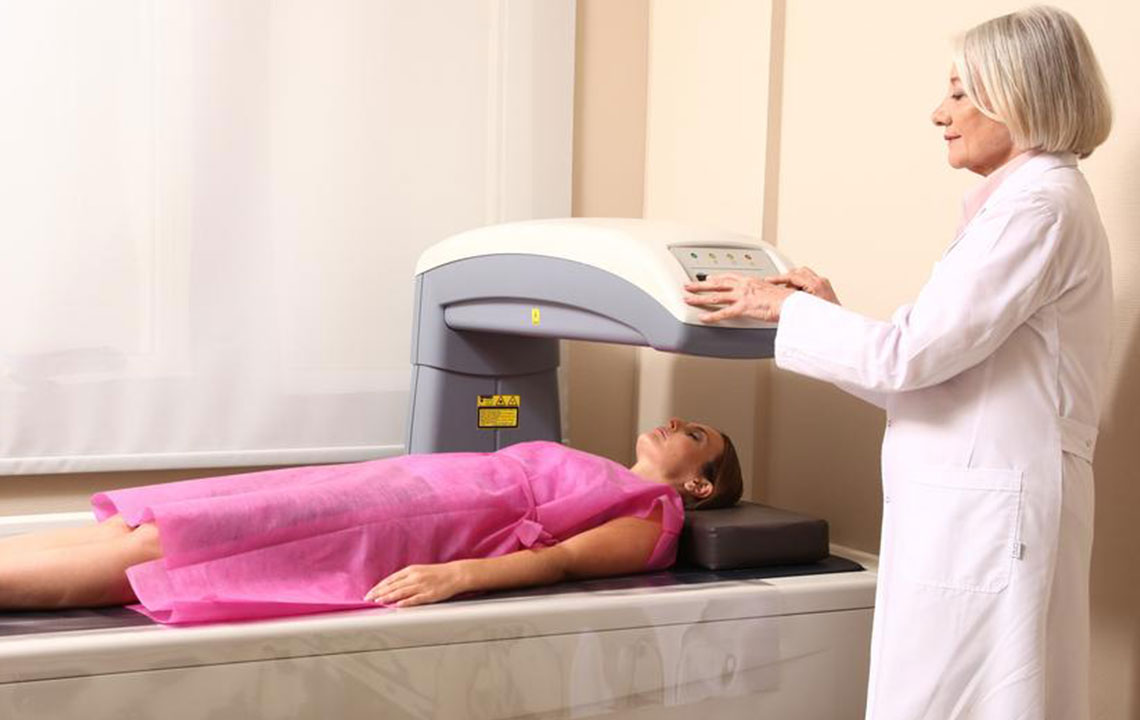
Bone density testing is an essential procedure to evaluate bone strength and detect osteoporosis risk. The common method used is the DEXA scan, an X-ray-based test that measures the mineral content in bones. This helps determine how healthy the bones are by assessing calcium levels and other minerals. Typically, the hips, spine, and forearms are examined to gauge bone health accurately.
Why Is a Bone Density Test Important?
Periodic bone density testing is recommended for several reasons:
To monitor bone strength and take preventive measures against fractures.
To evaluate fracture risk factors.
To assist in diagnosing osteoporosis and tracking treatment progress.
Who Should Consider a Bone Density Test?
People experiencing height loss, often caused by spinal fractures from osteoporosis.
Individuals who suffer fractures from minimal trauma, such as sneezing or coughing.
Patients on long-term medications that affect bone health.
Those who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplants, which increase osteoporosis risk.
Persons experiencing hormonal imbalances or drops.
Bone Density Test vs. Bone Scan
A bone scan identifies specific bone issues, such as tumors or infections, using nuclear imaging.
This involves a radioactive substance injected into the bloodstream.
Bone scans detect conditions like fractures, arthritis, or cancer.
In contrast, bone density tests focus solely on measuring mineral content to assess bone strength.
Who Should Get Tested? Individuals aged 50 to 69 with risk factors like low weight, alcohol use, smoking, previous fractures, corticosteroid use, or osteoporosis-related conditions should consider screening.
Potential Drawbacks
Radiation exposure, though minimal, may impact health.
Multiple testing devices can increase costs, and insurance coverage may be limited.
Results indicate bone health but do not specify causes for low density.
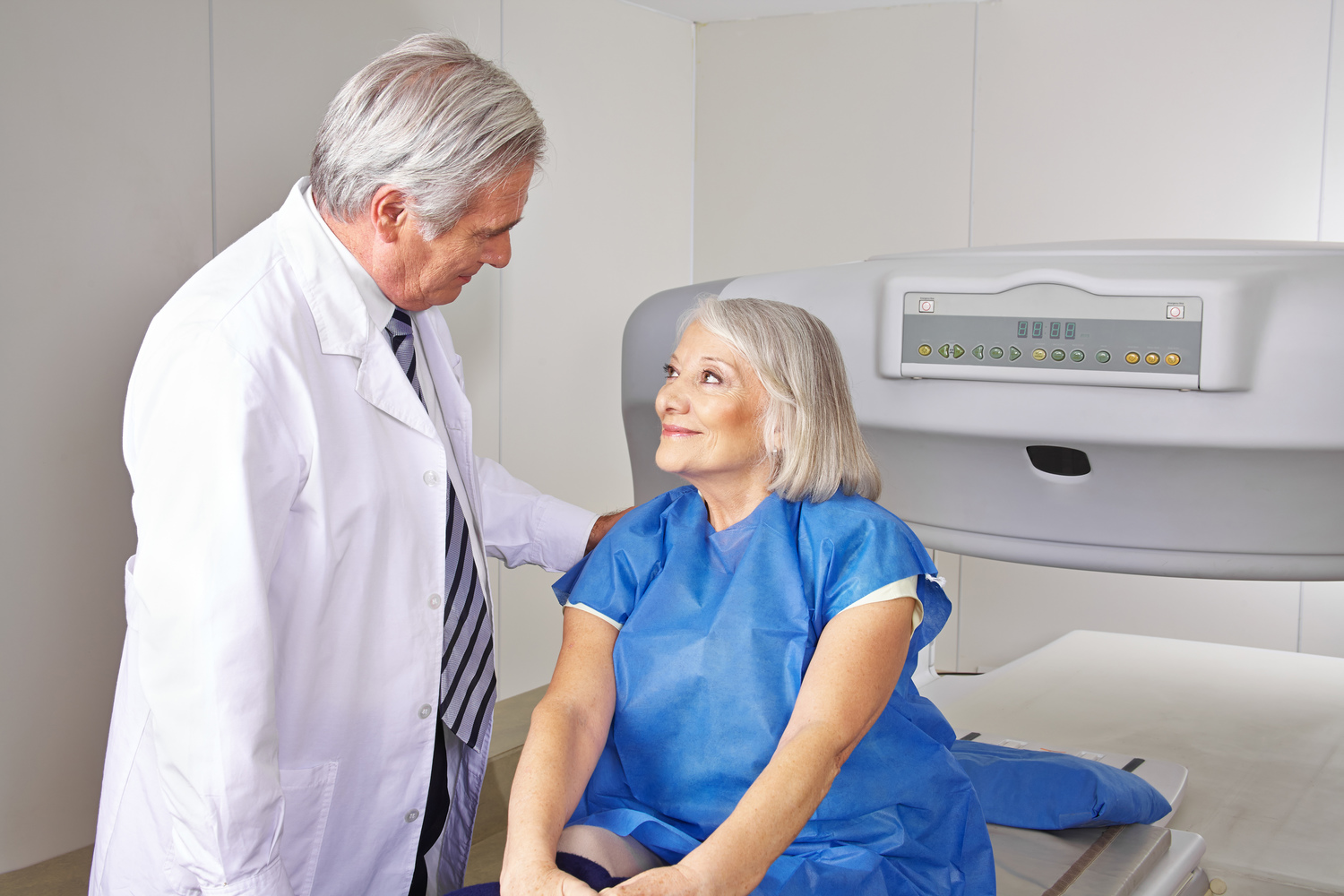
Preparing for a Bone Density Test
The procedure is painless, quick, and requires no special preparation.
Inform your doctor about any health issues beforehand.
Tips for Maintaining Strong Bones
Engage in weight-bearing exercises like walking or lifting weights daily.
Consume calcium-rich foods such as leafy greens and dairy products.
Increase vitamin D intake through sunlight exposure.
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Consult your healthcare provider before using medications that may weaken bones.
If you are at risk or experiencing symptoms, schedule a bone density test to safeguard your bone health and overall well-being.