Understanding Arthritis: Symptoms and Risks
This article explores arthritis's primary symptoms, risk factors, and the impact on daily life. It highlights the differences between common types like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and management for improved quality of life.
Sponsored
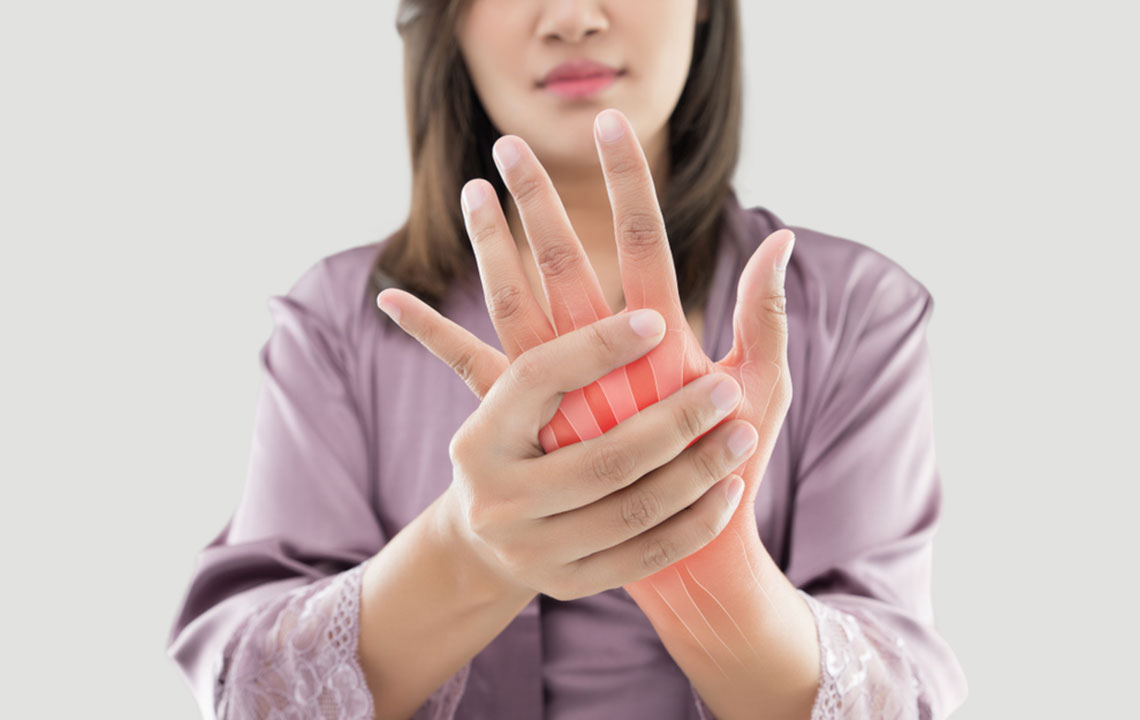
Arthritis is characterized by inflammation in one or multiple joints, leading to discomfort and stiffness. Common symptoms include joint pain, limited movement, swelling, and redness, which tend to intensify with age. Among various types, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most prevalent. Osteoarthritis involves cartilage deterioration, while rheumatoid arthritis results from immune system issues affecting joint linings. Factors like genetic predisposition, joint injuries, and obesity increase risk. Women are more susceptible, although both genders can be affected. Treatment typically targets symptom relief, as complete cures are rare.
Key symptoms encompass joint stiffness, tenderness, and reduced mobility. In some cases, arthritis impacts other organs, causing fever, fatigue, and gland swelling. Severe conditions can deform joints and impair daily activities, especially if weight-bearing joints are involved, affecting mobility and posture.