Effective Strategies for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Discover effective management strategies for Type 2 diabetes, including medication, diet, and exercise. This guide outlines symptoms, risks, and lifestyle tips to help control blood sugar and prevent complications, ensuring better health and well-being for individuals with this common condition.
Sponsored
Diabetes is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, which primarily stems from the body's inability to manage glucose properly. Glucose, derived from food, serves as a vital energy source. The hormone insulin, produced by the pancreas, plays a key role in converting glucose into energy. When insulin production is insufficient or the body's cells become resistant, blood sugar rises, leading to diabetes. Proper management involves a combination of medication, diet, and regular physical activity to keep blood sugar levels in check.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes- In this form, the body fails to produce insulin due to immune system attacking insulin-producing cells. It typically develops in children and adults requiring daily insulin injections for management.
Type 2 Diabetes- This is the most common type, characterized by the body's inability to effectively use insulin. It can affect individuals of any age, including children. Managing type 2 diabetes involves a balanced diet, medications, and exercise routines to regulate blood sugar levels.
Signs of type 2 diabetes include:
Persistent hunger
Blurry vision
Non-healing cuts
Frequent urination
Excessive thirst
Weight gain may also be linked to this condition. Additionally, complications such as eye issues, foot problems, kidney disease, and bladder infections can occur if unmanaged.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Besides medication, adopting healthy habits is vital:
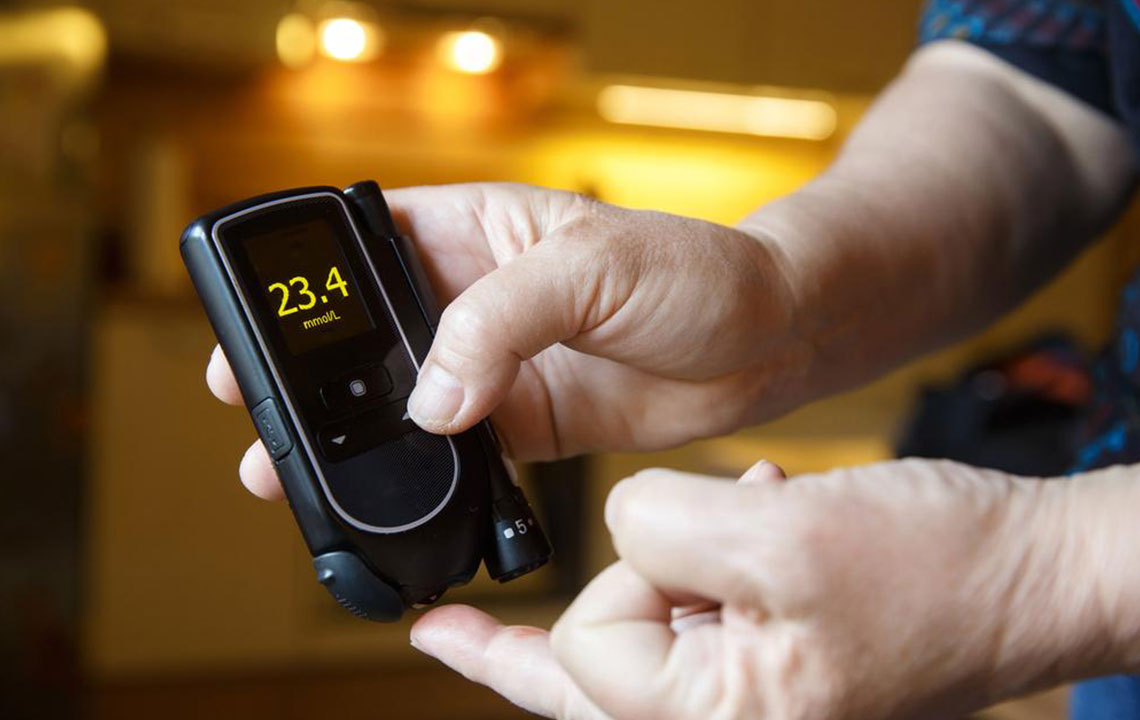
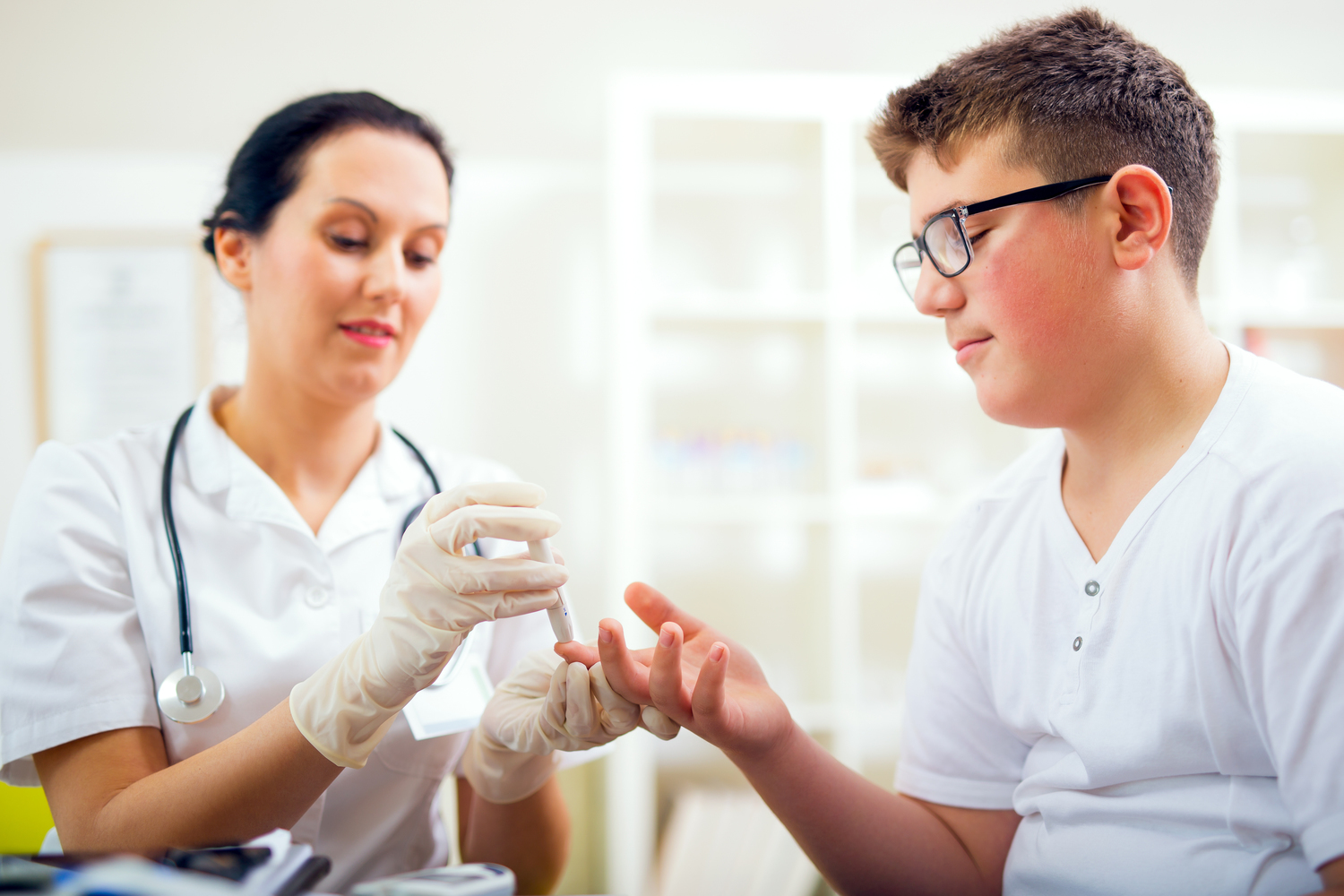
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Regular blood sugar testing helps track progress and adjust treatments effectively.
Diet & Exercise: Following a nutritious diet and exercising regularly assist in controlling blood sugar and improving insulin effectiveness. Consulting a dietitian can guide appropriate food choices.
Physical Activity: Engaging in physical activity aids in lowering blood sugar, enhances cell insulin sensitivity, and promotes overall health. Consistent exercise coupled with a proper diet can help maintain optimal blood glucose levels.
Medication: Doctors may prescribe specific medications to manage blood sugar levels. Combining medication with healthy lifestyle choices ensures better control and health outcomes.