Effective Strategies to Combat Urinary Tract Infections
Learn about effective treatments for urinary tract infections, including hydration, antibiotics, pain relief, and home remedies. Early intervention is crucial to prevent serious complications. Women are more affected by UTIs, but proper care can ensure quick recovery and prevent long-term effects.
Sponsored

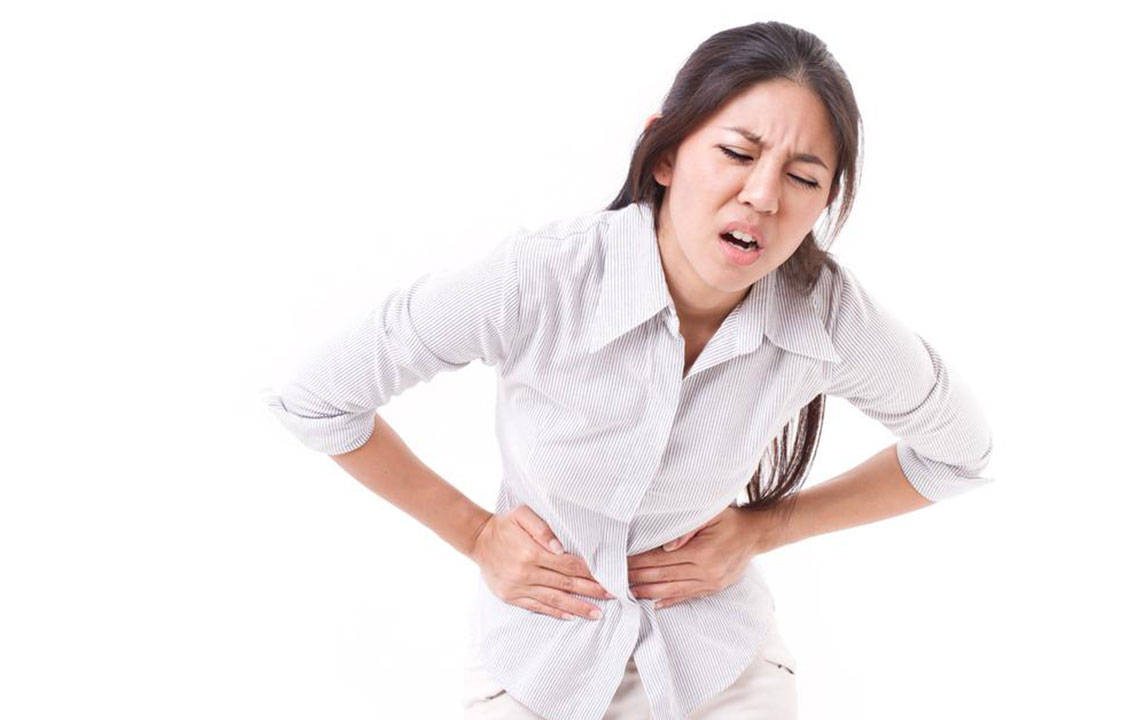
The urinary or renal system in the human body is responsible for removing toxins and waste. It includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Infections occurring anywhere within this system are classified as urinary tract infections (UTIs). These can involve the bladder (cystitis), ureters, or kidneys (pyelonephritis). One common cause of UTIs is the bacteria E. coli. Other factors such as frequent sexual activity, multiple partners, diabetes, poor hygiene, menopause, or kidney stones can increase UTI risk. Public restrooms may also pose infection risks. Symptoms include frequent urges to urinate and pain during urination. Left untreated, kidney infections can become severe and lifelong, emphasizing early intervention.
Managing UTIs involves understanding treatment options. Women are more prone to UTIs, but effective treatments are available. Hydration is key—drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the bladder, making urination lighter and reducing discomfort. In persistent cases, antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional are vital to eliminate infection and prevent complications like kidney involvement. Over-the-counter painkillers such as ibuprofen can ease cramps and discomfort temporarily. Applying heat with a heating pad offers additional relief, though it doesn’t cure the infection. Home remedies, including increased vitamin C intake and lifestyle adjustments like quitting smoking and improving hygiene, may also help reduce UTI risk.