Top Strategies for Managing and Preventing Urinary Tract Infections
Discover effective methods to treat and prevent urinary tract infections, including diagnosis, medication, lifestyle changes, and hygiene practices. Learn how staying hydrated and avoiding irritants can accelerate recovery and reduce recurrence risks, with guidance from healthcare professionals. Implementing these strategies can help maintain urinary health and avoid complications.
Sponsored
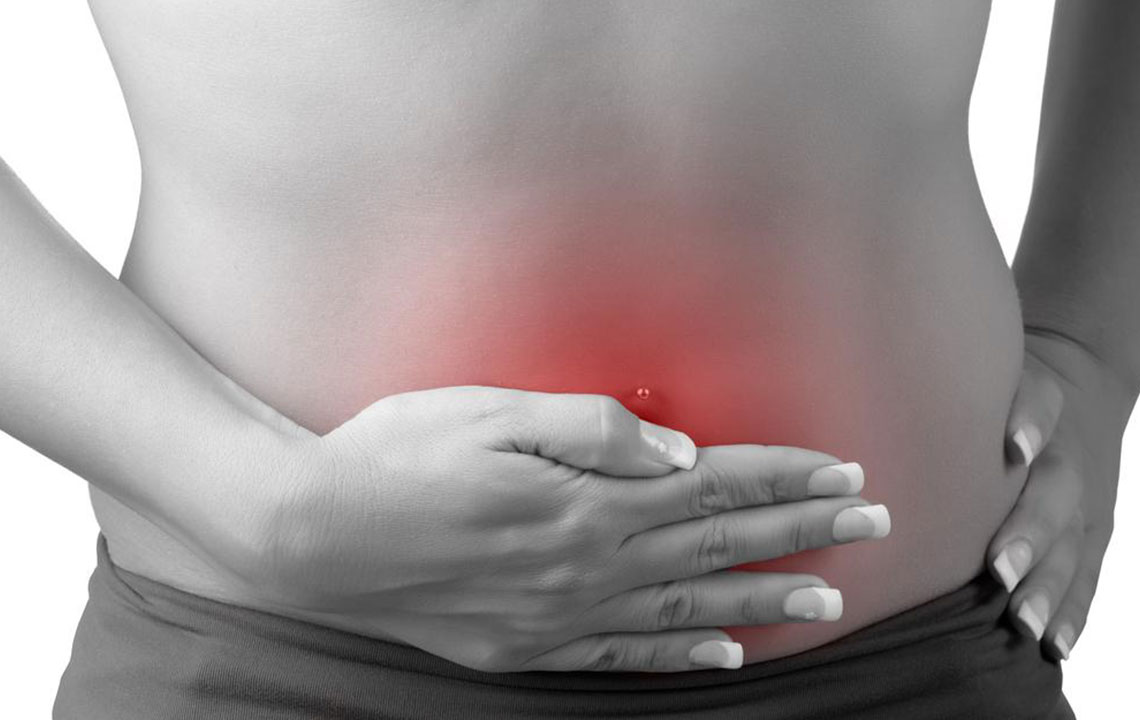
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), often called cystitis, are widespread, especially among women. Nearly 50% of women worldwide experience a UTI at some point.
UTIs develop when bacteria from the gastrointestinal or pelvic area invade the urinary system, causing bladder inflammation. While bacteria are common culprits, other factors like chemical irritants, fungi, kidney stones, and injuries can also trigger UTIs.
Recognizing UTI Symptoms
Common signs include:
Lower abdominal pain
Pain or a burning sensation during urination
Urgent and frequent need to urinate
Blood in urine or cloudy urine
Symptoms may vary with age. Infants may develop a fever, fussiness, or poor feeding, while older adults might experience fatigue, incontinence, or even cognitive decline.
UTI Treatment Approaches
Step 1: Confirm Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis is essential before treatment. Tests include:
Urinalysis: Checks for white blood cells and signs of infection. More than 5 WBCs per high power field suggest abnormality.
Dipstick Test: Detects Leukocyte Esterase and nitrites, indicating infection.
Urine Culture: The definitive test, identifying bacterial colonies over 100,000 CFU/ml for confirmed infection.
In cases where pus is present but bacteria are absent, sterile pyuria may indicate urethritis.
Step 2: Managing UTI
Antibiotic Therapy: Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to eliminate infection. Mild cases may be diagnosed and treated over the phone, but severe symptoms require face-to-face consultation.
Pain Management: Analgesics can alleviate discomfort in addition to antibiotics.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary system, aiding recovery.
Boost Vitamin C Intake: High doses of vitamin C increase urine acidity, discouraging bacterial growth.
Avoid Bladder Irritants: Cut back on caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, nicotine, and artificial sweeteners to promote healing.
Regular Urination: Empty the bladder frequently, especially after intercourse, to prevent bacterial buildup.
Practice Good Hygiene: Wipe from front to back to avoid spreading bacteria and prevent infection.
Consult your healthcare provider before starting any treatments to ensure safety and appropriateness.