Integrative Approaches to Cancer Care: Nutrition and Innovative Therapies
This comprehensive overview highlights vital nutritional strategies and innovative treatment options for cancer management. Emphasizing foods rich in antioxidants and fibers, alongside advanced therapies like CAR T-cell and immunotherapy, the article offers vital insights into holistic cancer care. Embracing new medical developments, it underscores the importance of targeted treatments such as ripretinib and Pomalidomide, alongside ongoing clinical trials, to enhance patient outcomes. Proper diet and cutting-edge therapies together provide a balanced approach to improving quality of life for cancer patients.
Sponsored

Care Strategies for Cancer: Nutrition and Advanced Treatments
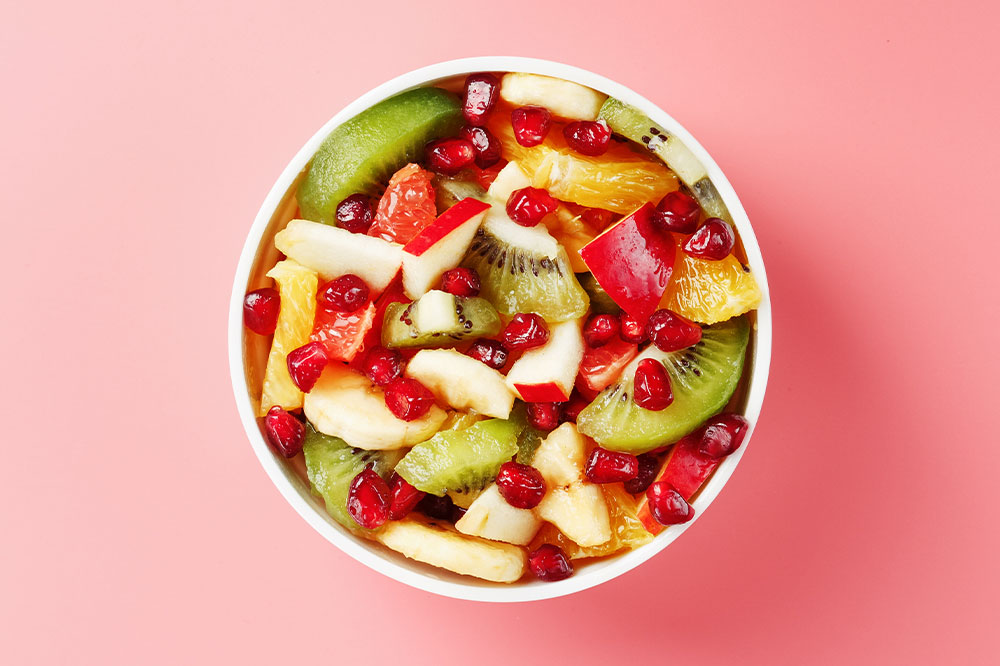
Proper nutrition is vital for overall health and can influence cancer outcomes. A balanced intake of vitamins, minerals, and nutrients from fresh foods supports the immune system and may lower cancer risks. Adjusting dietary habits during treatment can enhance well-being.
Consume more fruits and vegetables
Oxidative stress from free radicals exacerbates cancer progression. Eating antioxidant-rich foods like carrots, Brussels sprouts, squash, broccoli, spinach, and kale can provide protective benefits. Citrus fruits, tomatoes, berries, and foods high in lycopene help counteract oxidative damage. Allium vegetables such as garlic and onions contain compounds that reduce free radical activity and lower cancer risk.
Increase fiber intake
Dietary fiber aids digestion and alleviates constipation common during cancer treatments. Sources include beans, lentils, chickpeas, whole grains like oats, barley, and spelt, and nuts. Incorporating fiber-rich foods during breakfast is especially effective for digestive health.
Foods to limit or avoid
Reducing processed foods, saturated fats, trans fats, red meats, refined carbs, and added sugars can benefit cancer patients. Use less oil, salt, and spices during cooking to promote overall health.
Emerging cancer therapies
CAR T-cell therapy involves harvesting a patient’s T-cells, genetically modifying them to target cancer cells, and reintroducing them via transfusion. This approach offers promising results in specific cancer types. For gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), ripretinib has recently received FDA approval to help prevent tumor growth. Additionally, BTK inhibitors like ibrutinib are used for mantle cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, though they may cause side effects such as irregular heartbeat and fatigue.
Cancer immunotherapy
This biological approach uses substances derived from living organisms to fight cancer. Techniques include immune checkpoint inhibitors, which enhance immune cell efficacy, and monoclonal antibodies that target specific cancer cells. In advanced cases, treatments like Xofigo® (radium 223 dichloride) are used to manage symptoms of prostate cancer. For relapsed multiple myeloma, Pomalidomide (Pomalyst) is prescribed alongside dexamethasone, offering hope for resistant cases. Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to improve cancer treatment options, including novel immunotherapies targeting leukemia and multiple myeloma.