Understanding Skin Abscesses: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
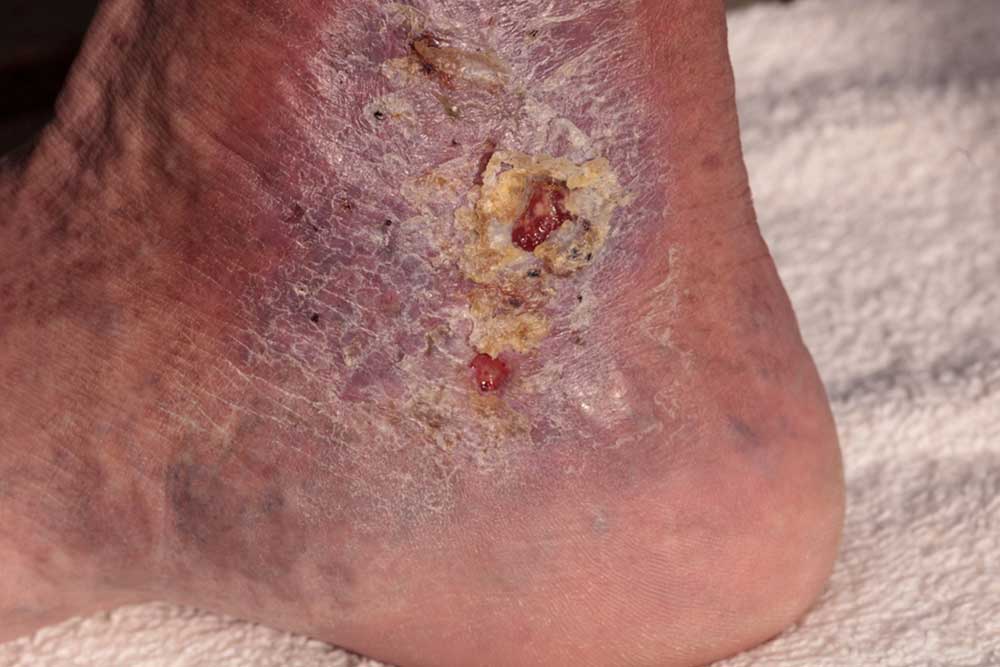
An abscess is a painful bacterial skin infection causing pus-filled swellings. It commonly appears in areas like the face, back, or buttocks, often due to bacteria entering through skin breaches. Treatment involves drainage and antibiotics, especially for larger or persistent abscesses. Good hygiene practices are vital to prevent infection. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely medical help ensures proper recovery. Preventative measures include keeping wounds clean, avoiding sharing personal items, and maintaining overall hygiene to reduce risk.
Sponsored

Overview of Skin Abscesses: Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
An abscess is a localized collection of pus caused by bacterial infection, typically forming a painful bump under the skin or on its surface. Common sites include the chest, back, buttocks, and face, with occasional occurrences in hairy regions like armpits. Symptoms often include warmth, tenderness, and swelling. Causes primarily involve bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus entering through cuts or bites. Proper hygiene and prompt treatment, including drainage and antibiotics, are essential for healing. Prevention focuses on maintaining good hygiene and avoiding shared personal items.
If an abscess persists beyond two weeks or grows larger, medical intervention is necessary for drainage and treatment. Those with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or underlying skin conditions are at higher risk. Symptoms include painful, swollen bumps with pus, fever, and chills. Small abscesses may be managed at home with warm compresses, but larger or multiple abscesses require professional care. Maintaining personal hygiene and proper wound care are key to prevention, along with avoiding sharing personal items.