Understanding Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Pneumonia is a significant lung infection affecting all age groups, especially vulnerable populations. Early detection, proper diagnosis, and targeted treatment using antibiotics or antivirals are essential to prevent complications. Recognizing symptoms such as cough, fever, and difficulty breathing can lead to prompt care. Preventive measures include good hygiene and avoiding exposure to infected individuals. Understanding the causes and risks helps in managing and reducing pneumonia-related health risks effectively.
Sponsored

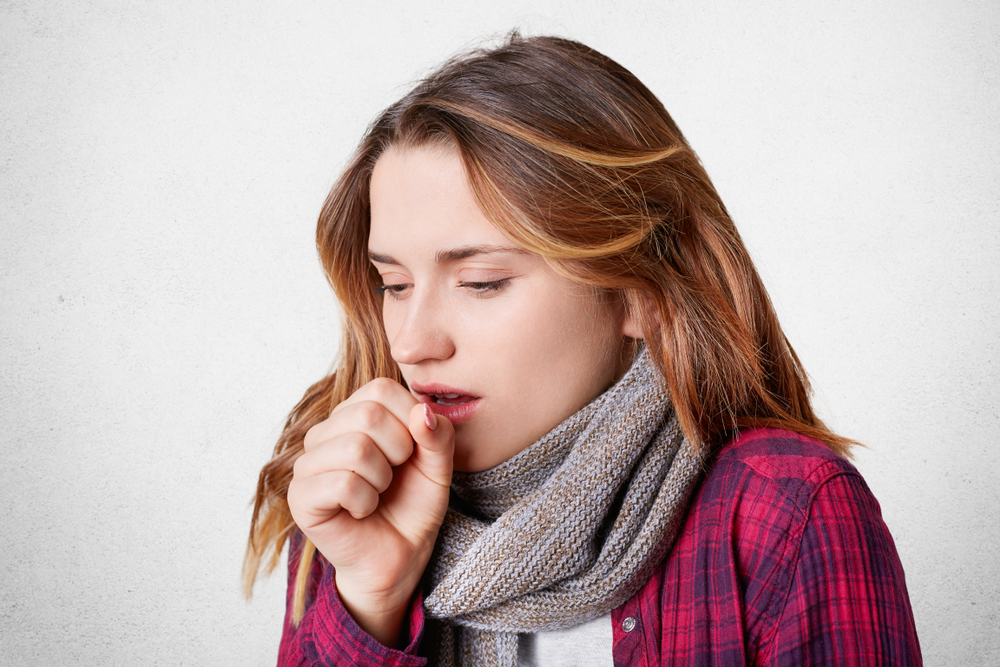
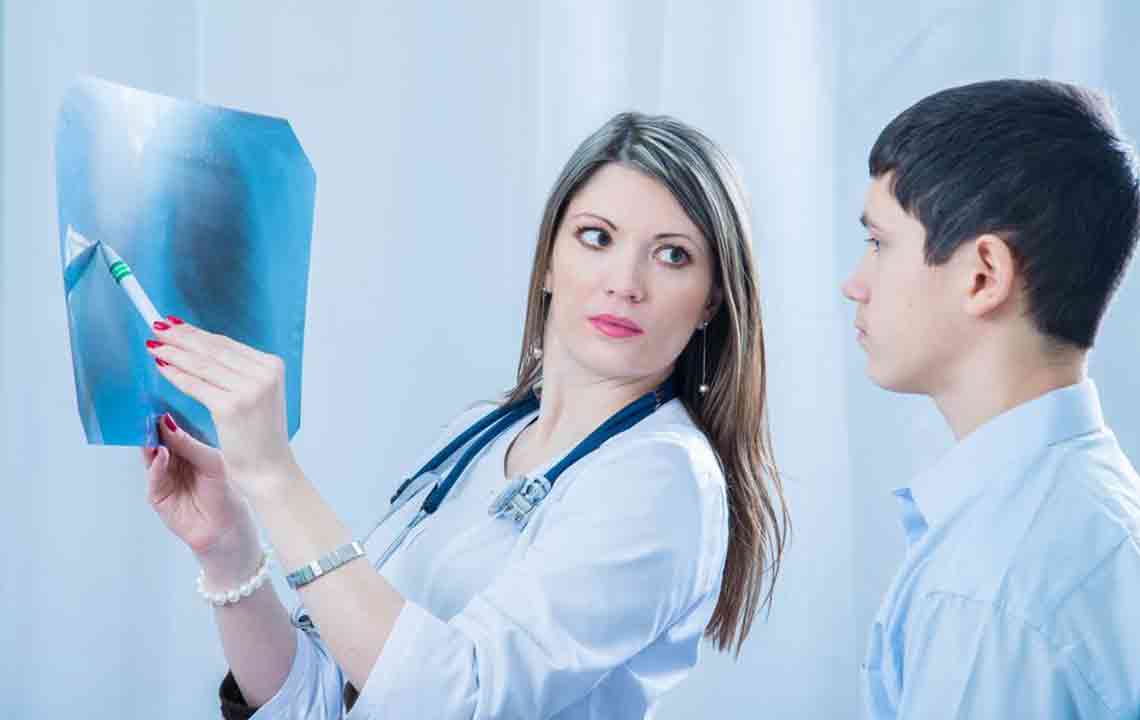
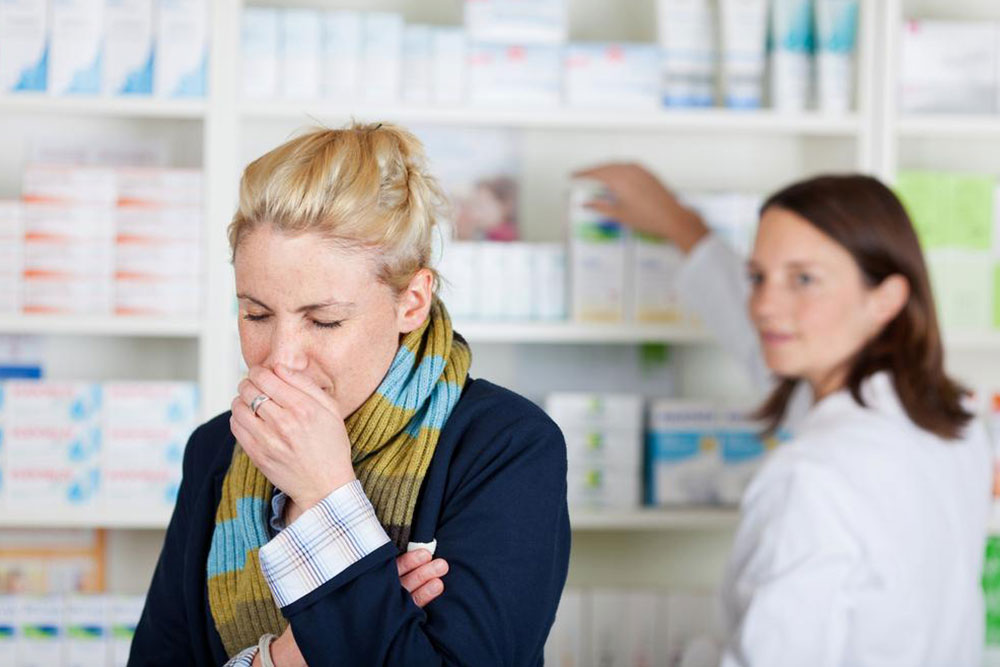
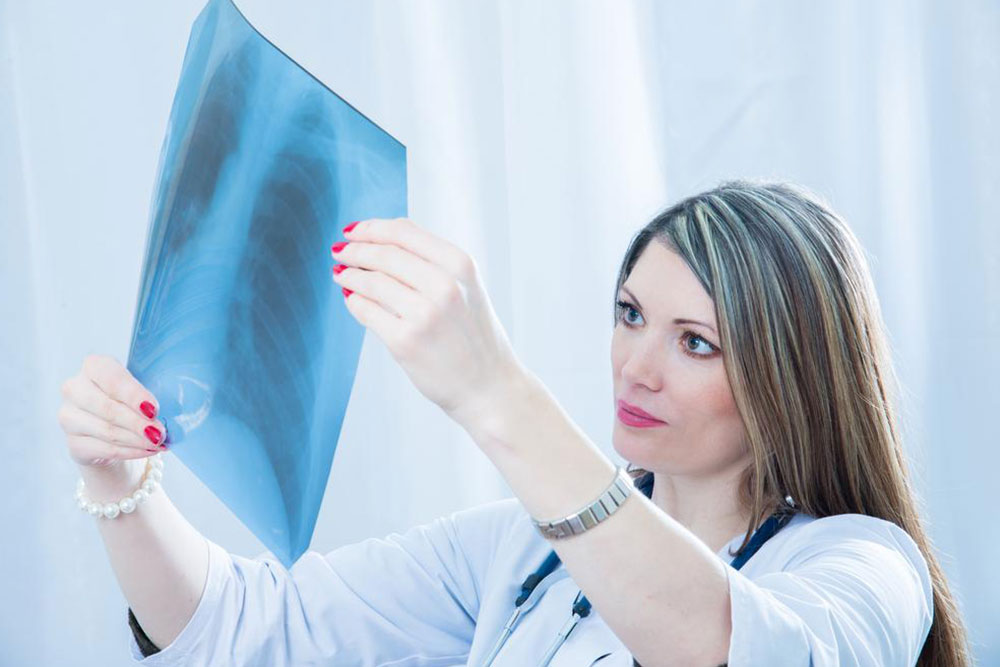
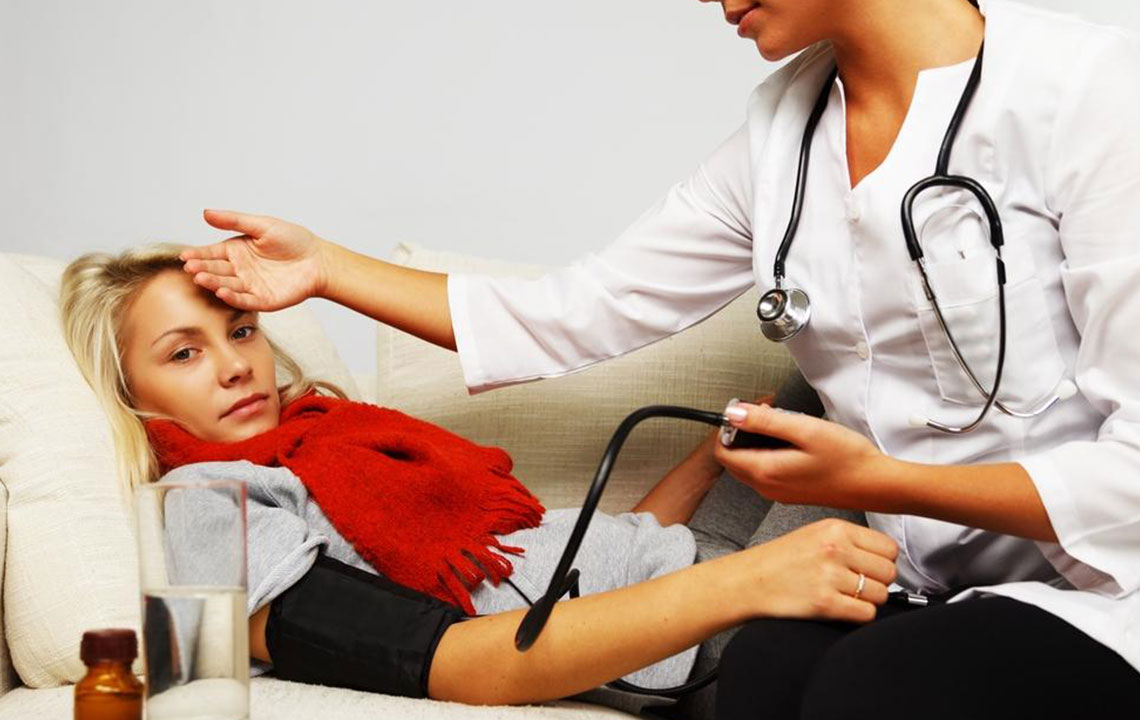
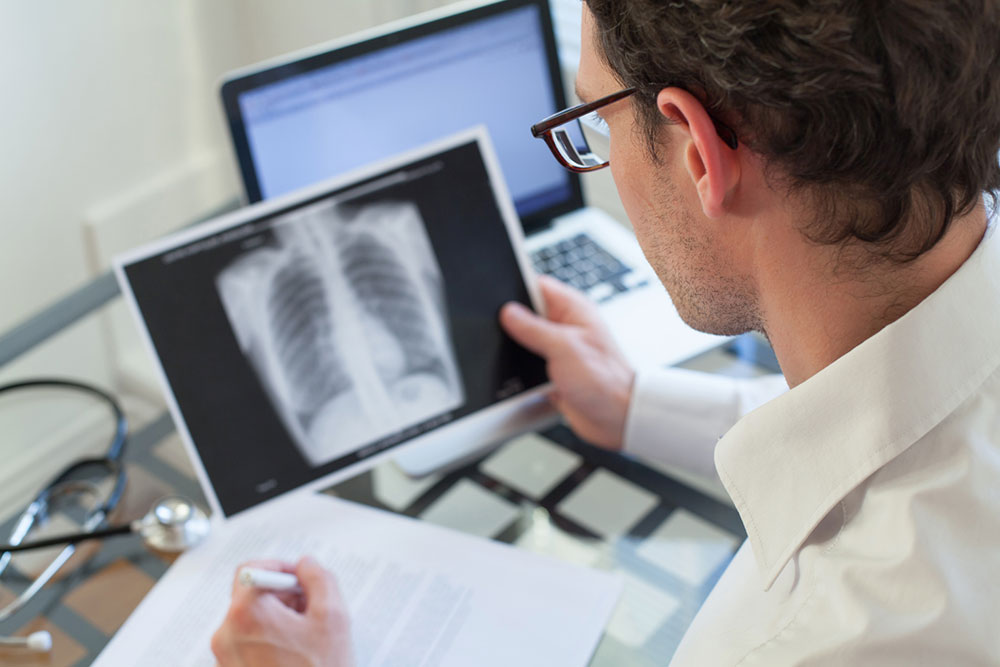
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can affect individuals of all ages, characterized by symptoms like sudden coughing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Commonly affecting children and those with weakened immunity, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications. Symptoms such as mucus cough, fever, chills, and fatigue vary depending on age and infection severity. Bacterial and viral pneumonia are primary causes, with bacteria often more severe. Transmission occurs through airborne droplets, making prevention important. Medical assessments including chest x-rays and tests facilitate accurate diagnosis. Treatment may involve antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungal medications, along with rest and fluid intake. Vulnerable groups include young children, the elderly, and individuals with chronic illnesses or compromised immunity.