Understanding Pneumonia: Key Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis Methods
This comprehensive overview explains pneumonia's symptoms, types, causes, risk factors, and diagnostic methods. Early detection and proper treatment are vital for recovery. The article highlights the importance of medical consultation and adherence to prescribed therapies to prevent complications.
Sponsored
Pneumonia requires prompt medical attention when symptoms appear, regardless of severity. Healthcare professionals will recommend suitable diagnostic tests to confirm the condition. Following the prescribed treatment and post-care advice is crucial for recovery.
Signs of Pneumonia
Symptoms vary from mild to severe, influenced by the pneumonia type, patient’s age, and overall health. Common symptoms include:
Cough
Persistent coughing often produces mucus that may be yellow, green, or contain blood.
Fever
Patients might experience fever, ranging from mild to high.
Chills and Shaking
Shivering episodes are common with pneumonia.
Difficulty Breathing
Shortness of breath may occur during physical activity or rest.
Chest Discomfort
Deep breaths or coughing can cause sharp chest pain.
Headaches
Headaches of varying intensities are frequent.
Excessive Sweating
Moist skin and profuse sweating are typical signs.
Reduced Appetite
Lack of desire to eat, fatigue, and decreased energy levels are common.
Confusion
Older adults may experience mental confusion alongside other symptoms.
Types of Pneumonia
Bacterial Pneumonia
Often accompanied by very high fever (up to 105°F), intense sweating, rapid heartbeat, and bluish lips or nail beds due to low oxygen levels. Confusion or delirium may also occur.
Viral Pneumonia
Resembles influenza, with symptoms like fever, headache, dry cough, body aches, and fatigue. Breathlessness and mucus production worsen over time, with lips possibly turning blue.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, mycoplasmas, or inhaled toxic substances. Viral infections may lead to bacterial pneumonia. Accurate identification guides effective treatment.
Risk Factors
Smoking
Increases vulnerability to lung infections, including pneumonia.
Recent Respiratory Infections
Cold, flu, or other viral illnesses elevate pneumonia risk.
Swallowing Difficulties
Conditions like stroke or neurological disorders may cause aspiration, leading to pneumonia.
Chronic Lung Conditions
Diseases like bronchiectasis or cystic fibrosis predispose individuals to pneumonia.
Certain Diseases
Heart disease, diabetes, or liver cirrhosis can increase risk.
Long-term Care Facilities
Living in nursing homes heightens exposure risk.
Neurological Impairments
Stroke or dementia impair the immune response, raising pneumonia chances.
Recent Surgery or Trauma
Recovery periods from surgeries or injuries are critical times for vulnerability.
Weakened Immunity
Illnesses, medications, or immune disorders reduce resistance to infections.
Diagnosis Methods
Physical Examination
Listening for crackling sounds during breathing can indicate pneumonia.
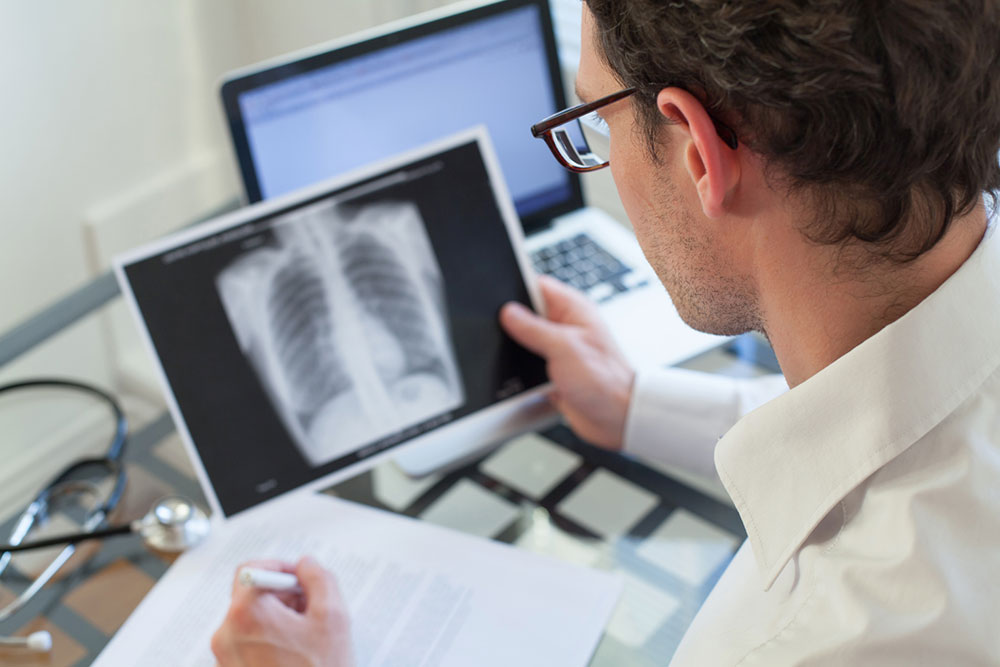
Chest X-ray
Confirms the presence of pneumonia and assesses extent.
Additional Tests
Blood tests, arterial gases, sputum analysis, chest CT, and other diagnostic procedures may be used to identify pneumonia and its cause.
Treatment Approaches
Rest, hydration, and medical supervision are essential. Prompt consultation for persistent cough or fever is recommended. Medications like antibiotics or antipyretics should be taken as prescribed to ensure full recovery.