Understanding Ovarian Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
This article provides a comprehensive overview of ovarian cancer, including causes, early symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early detection for better outcomes and discusses various surgical and medical therapies to manage the disease effectively, helping patients regain their health and confidence.
Sponsored
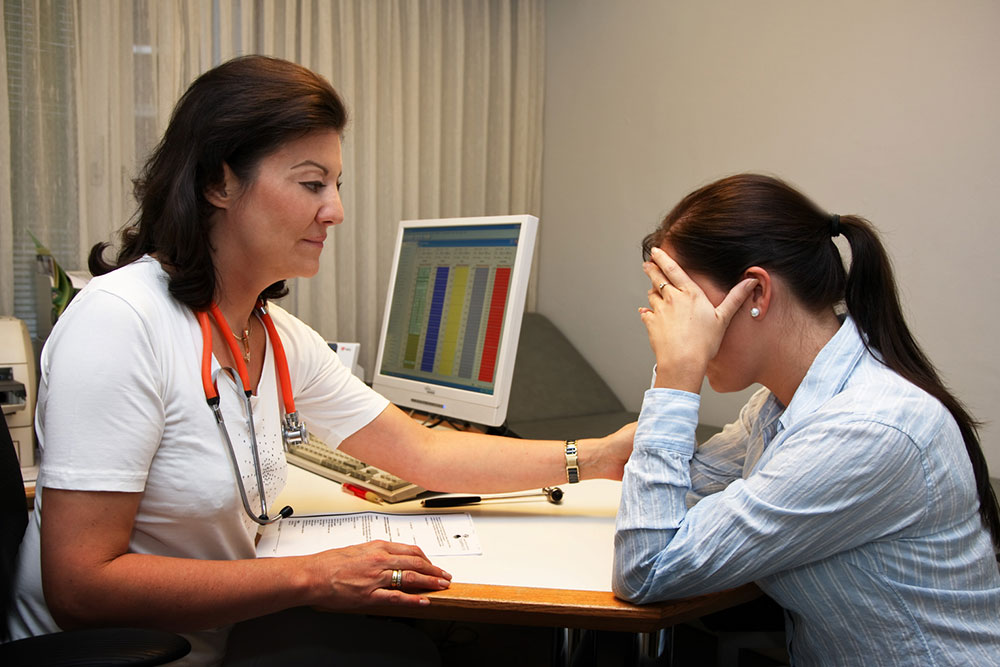

Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells within the ovary grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. This process is known as metastatic ovarian cancer. The ovaries, essential reproductive organs in women, produce eggs and vital hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. In 2017, over 22,000 women were diagnosed with ovarian cancer, with nearly 14,000 succumbing to the disease.
The early signs of ovarian cancer are often subtle and hard to detect, with only a small percentage diagnosed at an early stage. Recognizing risk factors and symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
While the exact cause remains unknown, several risk factors may increase susceptibility, including family history, personal history of breast or uterine cancers, obesity, use of hormone therapy, lack of pregnancy, and advancing age, especially post-menopause. However, ovarian cancer can develop even without these factors, and presence of risk factors doesn't guarantee disease onset.
Common early symptoms include lower abdominal or pelvic pain, back pain, indigestion, feeling full quickly during meals, frequent urination, discomfort during intimacy, and constipation. As the disease progresses, signs such as unexplained weight loss, loss of appetite, nausea, fatigue, and breathlessness may emerge.
Treatment options include surgical removal of tumors, which varies based on cancer stage, such as salpingo-oophorectomy (removing the fallopian tubes and ovaries), hysterectomy (removing the uterus), lymph node dissection, and cytoreductive surgery to excise cancer spread. Chemotherapy targets residual cancer cells, typically in multiple sessions, helping shrink tumors and prevent recurrence, but can cause side effects like hair loss, nausea, anemia, sores, diarrhea, and reduced appetite. Hormone therapy blocks estrogen’s effect on cancer cells, with side effects like weight gain, headaches, and fatigue. Radiation therapy is rarely used but may help in specific cases, with side effects including mouth sores, dry mouth, and jaw stiffness. Managing ovarian cancer depends on the stage, but early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and restore quality of life. Fighting the disease boosts confidence and hope for recovery.