Understanding Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by rapid skin cell shedding, causing red, scaly patches. Triggers like stress can activate immune responses, resulting in symptoms that vary from mild to severe. Treatments include topical creams, systemic drugs, and light therapy, tailored to individual needs. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help control flare-ups and improve quality of life.
Sponsored
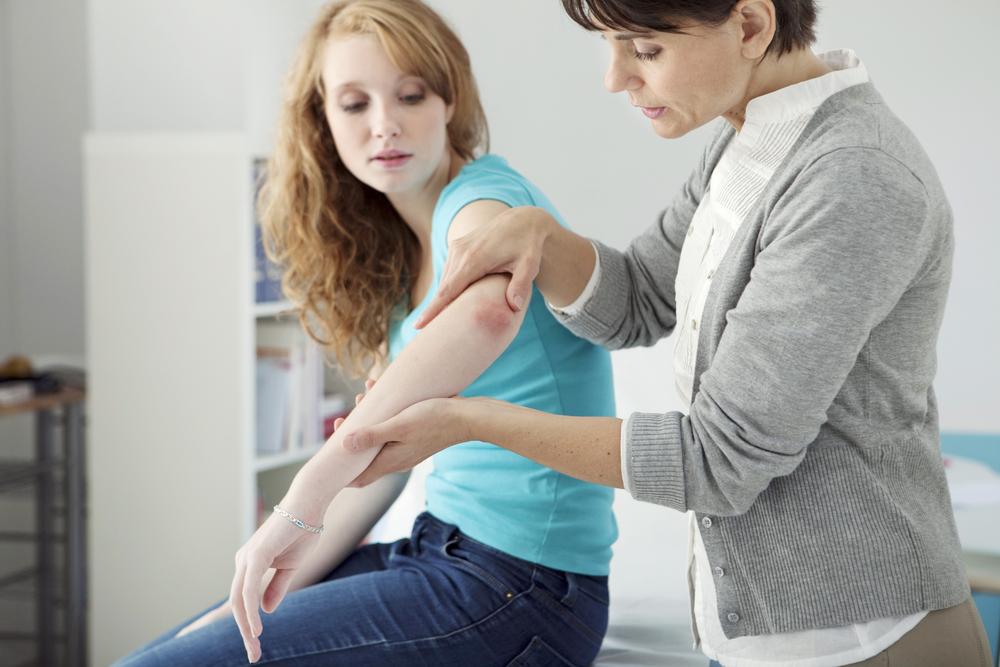

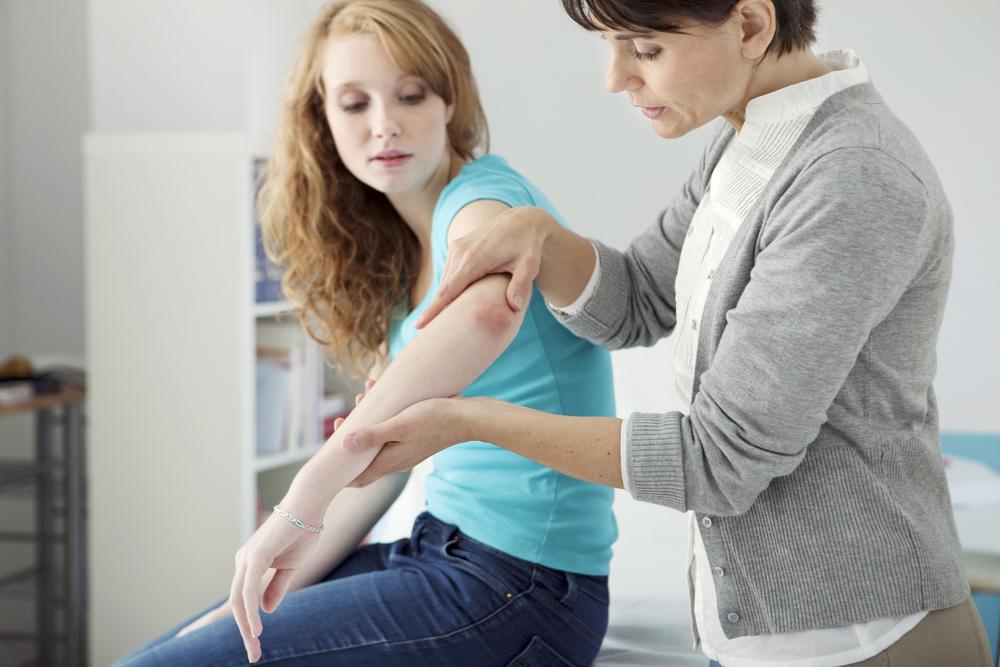
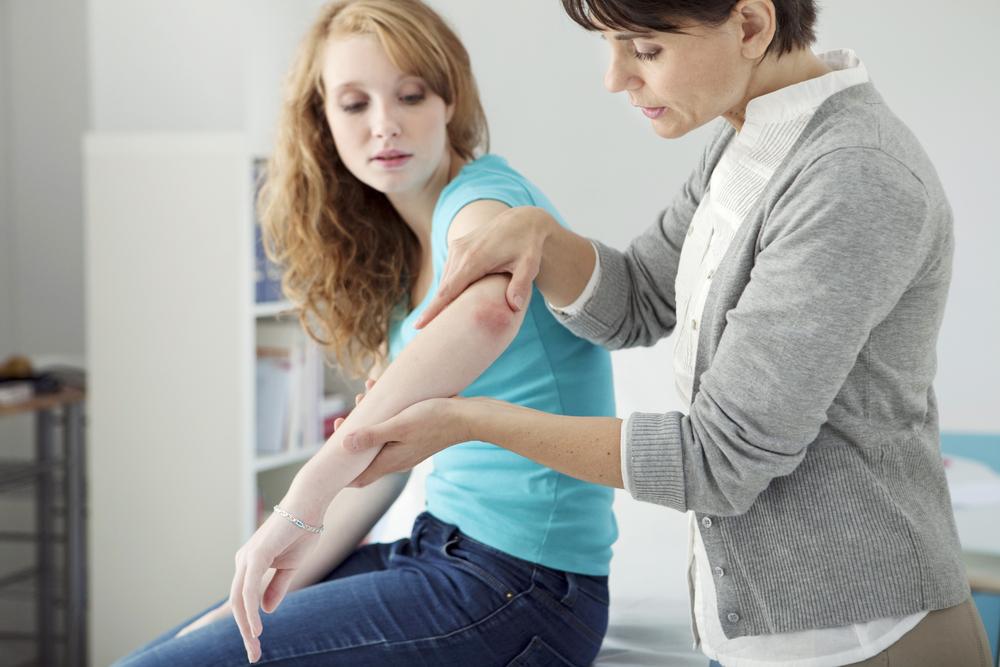
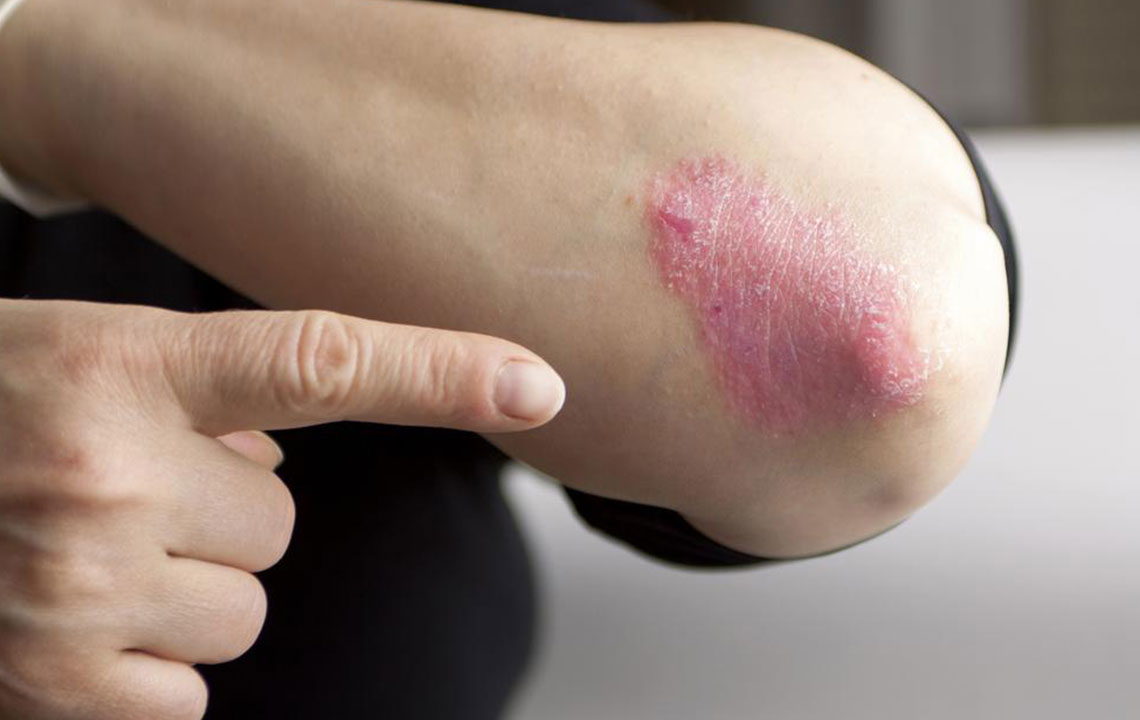
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition triggered by immune system irregularities. It manifests as red, flaky patches with silvery scales on the skin, which may come and go over time. Flare-ups can be triggered by stress, infections, or other factors.
Causes of psoriasis
The immune system's T cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, prompting inflammation and rapid skin cell production. Stress and anxiety are common triggers that activate these immune responses, leading to the characteristic symptoms.
In psoriasis, skin cells regenerate rapidly—within 2 to 6 days—compared to the normal 21 to 28 days, causing buildup on the surface. Globally, about 3% of the population is affected, with 7.5 million cases in our country. It affects both genders equally, typically developing between ages 15-35 and 50-60.
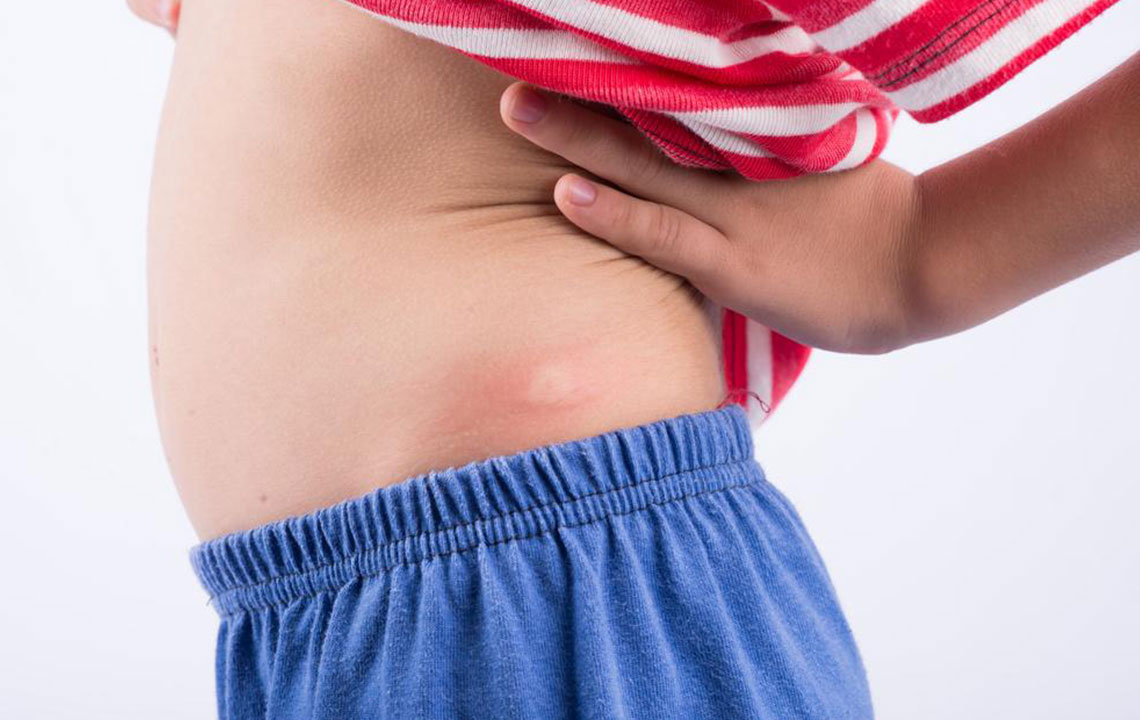
Signs of psoriasis include red patches with silvery scales, itching, and burning sensations. Severity ranges from mild to severe, affecting less than 3% to over 10% of the body. Commonly impacted areas include elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Treatment options include topical agents, systemic medications, and light therapy, personalized based on intensity. Consult a healthcare provider if persistent rashes don't improve with OTC remedies.