Understanding Psoriasis: Symptoms and Types
This article explores the various symptoms and types of psoriasis, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis. It highlights common affected areas, differentiates psoriasis from eczema, and describes different psoriasis forms like plaque, guttate, inverse, and pustular. The piece also discusses associated health risks and urges consulting a dermatologist for effective management. Understanding these variations can aid in timely treatment and improve quality of life for those affected by this chronic skin condition.
Sponsored

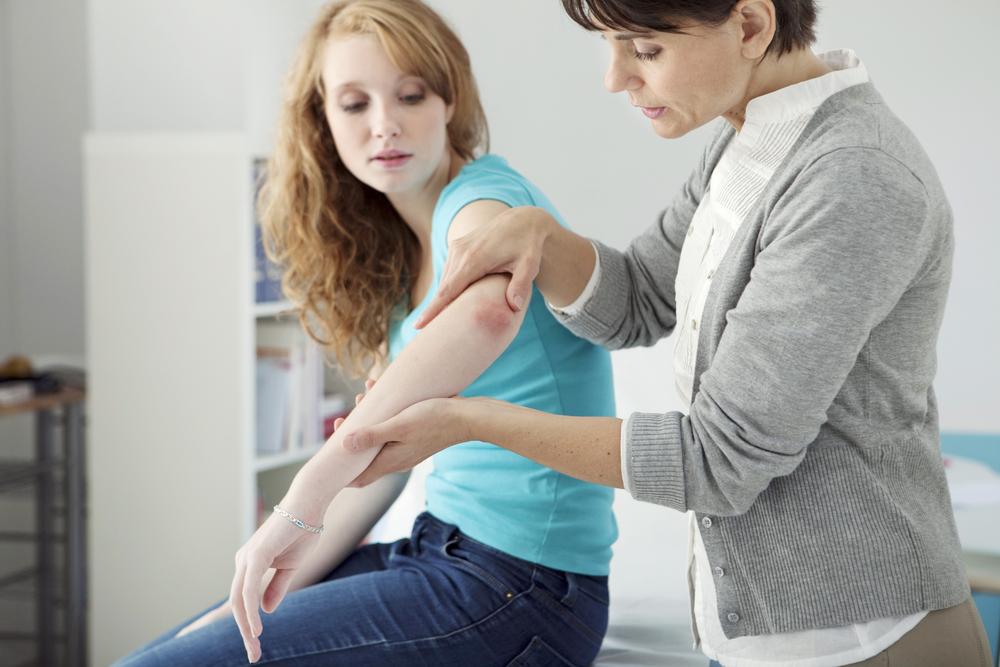
Recognizing Psoriasis Symptoms and Variations
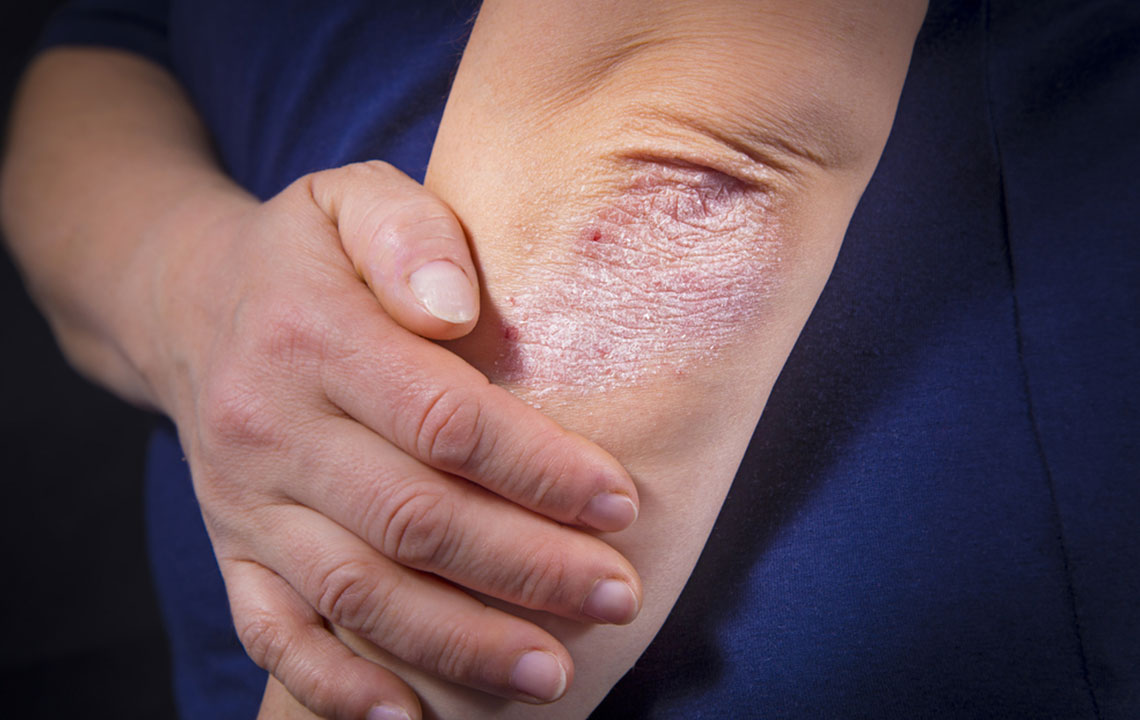
Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune skin disorder characterized by the development of thickened, scaly patches. This condition results from rapid skin cell turnover triggered by immune system chemicals produced by white blood cells known as T-lymphocytes. Commonly affecting areas like elbows, knees, and the scalp, psoriasis varies from small patches to widespread inflamed scales across the body. Though it impacts all genders and ages equally, it is most often diagnosed in early adulthood.
Research indicates that individuals with psoriasis have higher risks of diabetes, heart issues, and high cholesterol levels.
Distinguishing Psoriasis from Eczema
While eczema causes red, cracked, or blistered skin, psoriasis leads to thick, scaly patches with intense itching. Both involve skin inflammation, but their manifestations differ.
Types of Psoriasis and Their Symptoms
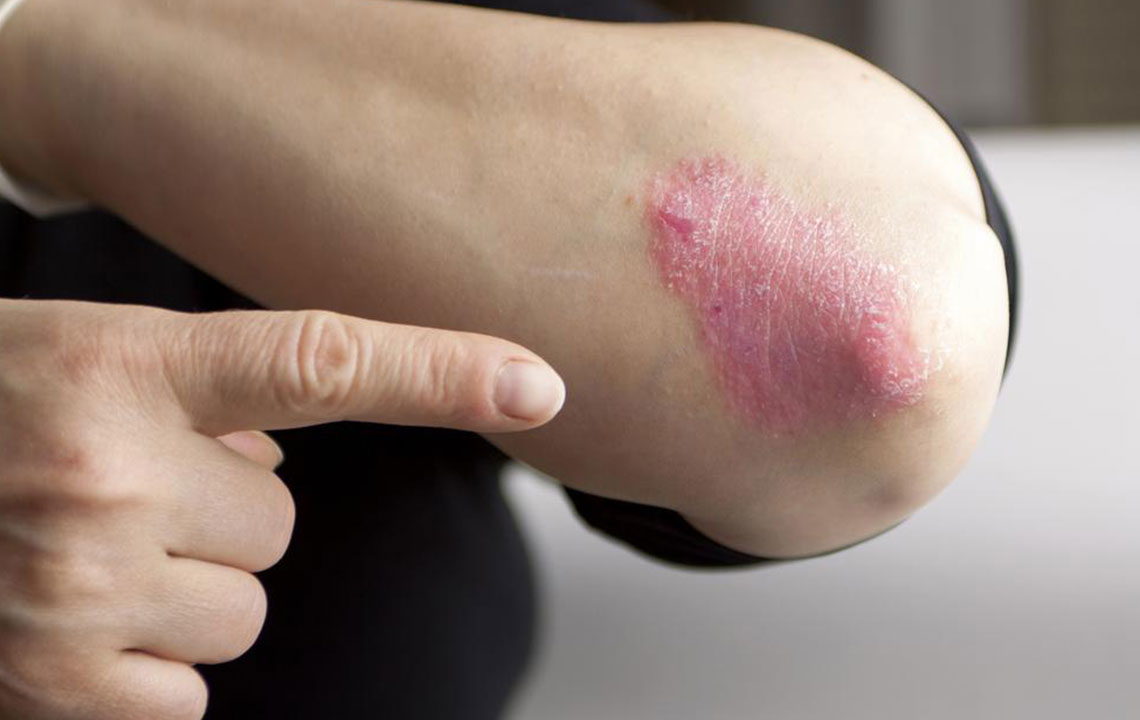
Plaque Psoriasis
Most common form, presenting as red, inflamed patches with silvery-white scales on elbows, scalp, and lower back.
Guttate Psoriasis
Appears as small, drop-shaped spots, often triggered by infections like tonsillitis or skin injuries, mainly affecting children and young adults.
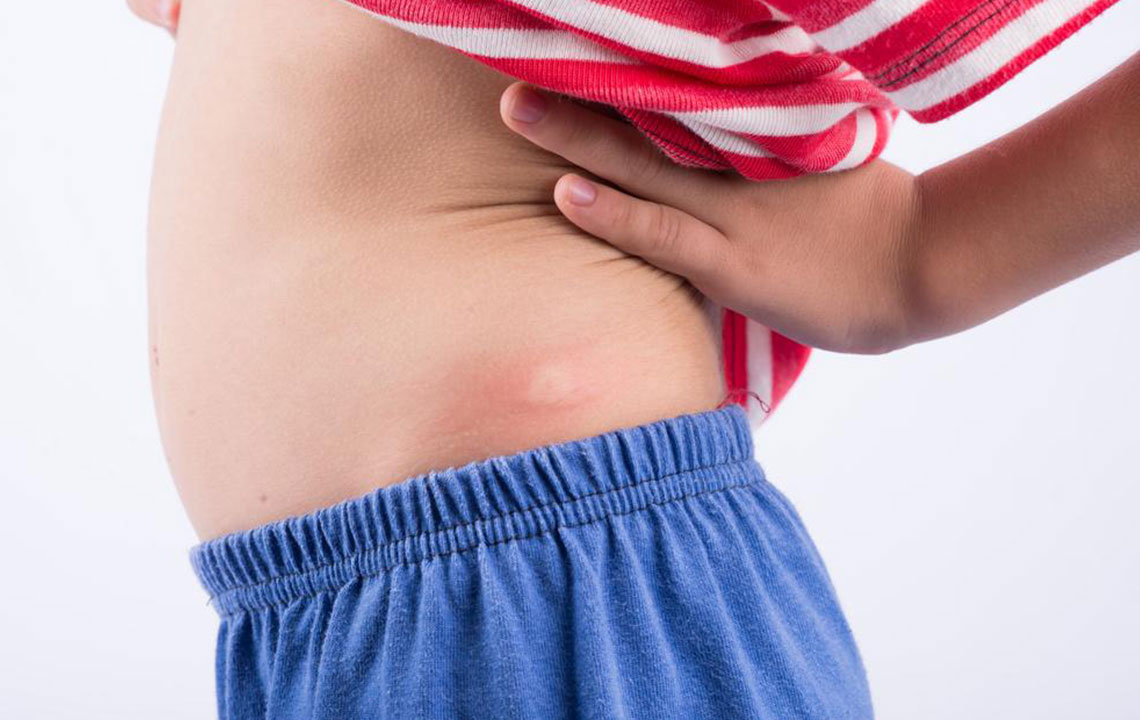
Inverse Psoriasis
Red, smooth, and shiny lesions appear in skin folds like underarms, groin, and navel.
Pustular Psoriasis
Yellowish pustules form on reddened skin, typically on hands and feet, often accompanied by scaling.
Palmoplantar Psoriasis
Thick, scaly patches develop on palms and soles.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Extensive redness covering large skin areas, risking fluid loss and heart issues. It requires urgent medical attention.
Nail and Scalp Psoriasis
Causes yellow pitted nails mistaken for fungal infections; scalp involvement may lead to hair loss and dandruff.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Occurs with joint inflammation, mainly affecting adults aged 30-50.
Consult with a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment options suitable for your psoriasis type and severity.