Understanding Lymphoma: Causes, Risk Factors, and Symptoms
Explore the key causes, risk factors, and symptoms of lymphoma, a cancer affecting the lymphatic system. Understand the differences between Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, their risk factors, and signs that require medical attention for early diagnosis and treatment.
Sponsored

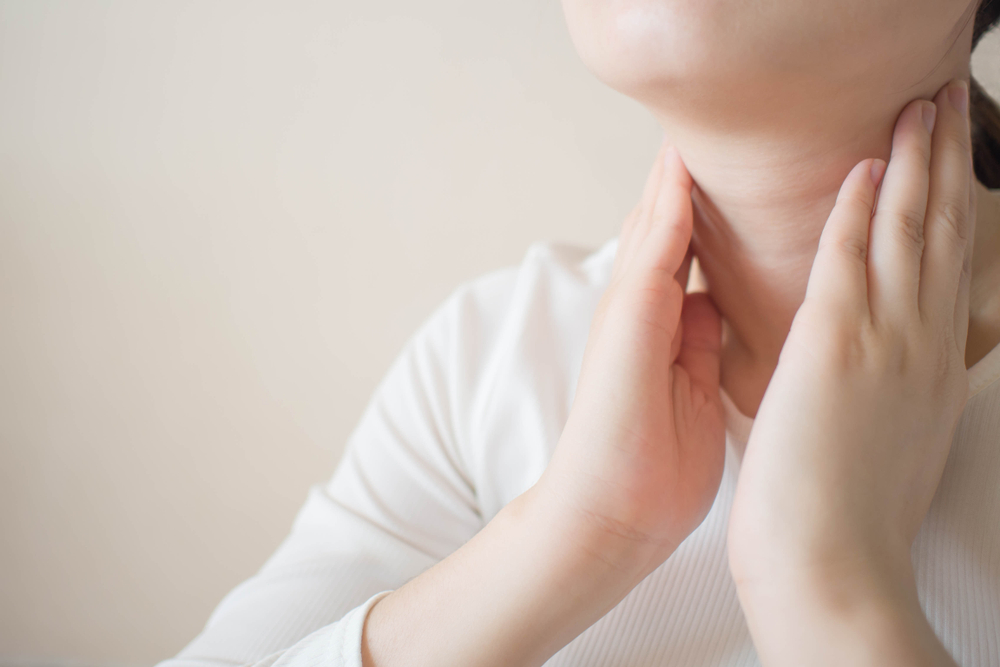
Lymphoma is a cancer that targets the lymphatic system, a key part of the immune defense. It involves the abnormal growth of lymphocytes, leading to uncontrolled cell division. The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes, bone marrow, thymus, and spleen, which are interconnected with vital organs. Both Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma types exist, each with distinct causes and risk factors. Hodgkin's often results from genetic changes linked to the Epstein–Barr virus and involves Reed-Sternberg cells. Non-Hodgkin's has various contributing factors such as genetic mutations, viral infections, and immune deficiencies. Symptoms include painless lumps, weight loss, fever, night sweats, and fatigue, signaling the need for medical evaluation. Recognizing these indicators early can improve treatment outcomes.