Effective Strategies for Managing Ankylosing Spondylitis
Learn about effective management strategies for ankylosing spondylitis, including medications, physical activity, diet, and alternative therapies. These approaches help alleviate symptoms, improve posture, and enhance quality of life for those affected by this chronic condition.
Sponsored

Managing Ankylosing Spondylitis: Common Approaches
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory disease primarily targeting the spinal joints, leading to bone fusion over time. This process can affect nearby structures, including the rib cage, causing abnormal bone connections. Symptoms often include persistent pain, stiffness, and inflammation from the neck down to the lower back. The condition may also impact ligaments and tendons, contributing to discomfort.
Breathing issues are frequent due to rib fusion limiting lung expansion. Persistent inflammation increases risks of flare-ups and may heighten the chance of cardiovascular complications.
Additional health concerns include eye inflammation (uveitis), gastrointestinal conditions, psoriasis, and fatigue. Consulting a specialist, such as an orthopedic surgeon or physical therapist, is essential for tailored treatment planning. Multiple therapies may be recommended.
Medications for Ankylosing Spondylitis
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs)
These drugs reduce inflammation-related pain and stiffness and are available over the counter. High doses, however, may cause gastrointestinal issues like stomach irritation, ulcers, or bleeding, although COX-2 inhibitors lessen these risks.
Corticosteroids
Injected directly into affected joints for quick relief, but long-term use can lead to side effects. Dosing and frequency should be managed by healthcare professionals.
TNF Alpha Inhibitors
Targeting inflammatory proteins, these inhibitors effectively reduce joint inflammation and slow disease progression, serving as primary treatment options for severe cases.
Physical Exercise in Ankylosing Spondylitis
Consistent movement helps maintain posture and reduce stiffness. Short, frequent exercises advised by physiotherapists can relieve vertebral compression. Combining posture correction with physical activity is vital, especially in advanced stages, to prevent hunching and improve quality of life. Regular check-ups help adapt exercise routines based on progress.
Diet and Nutritional Support
Proper nutrition assists in maintaining healthy bones and managing weight. Foods rich in calcium and vitamin D are recommended, with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains as dietary staples. Avoiding excess alcohol and saturated fats helps prevent osteoporosis, a risk heightened by spondylitis.
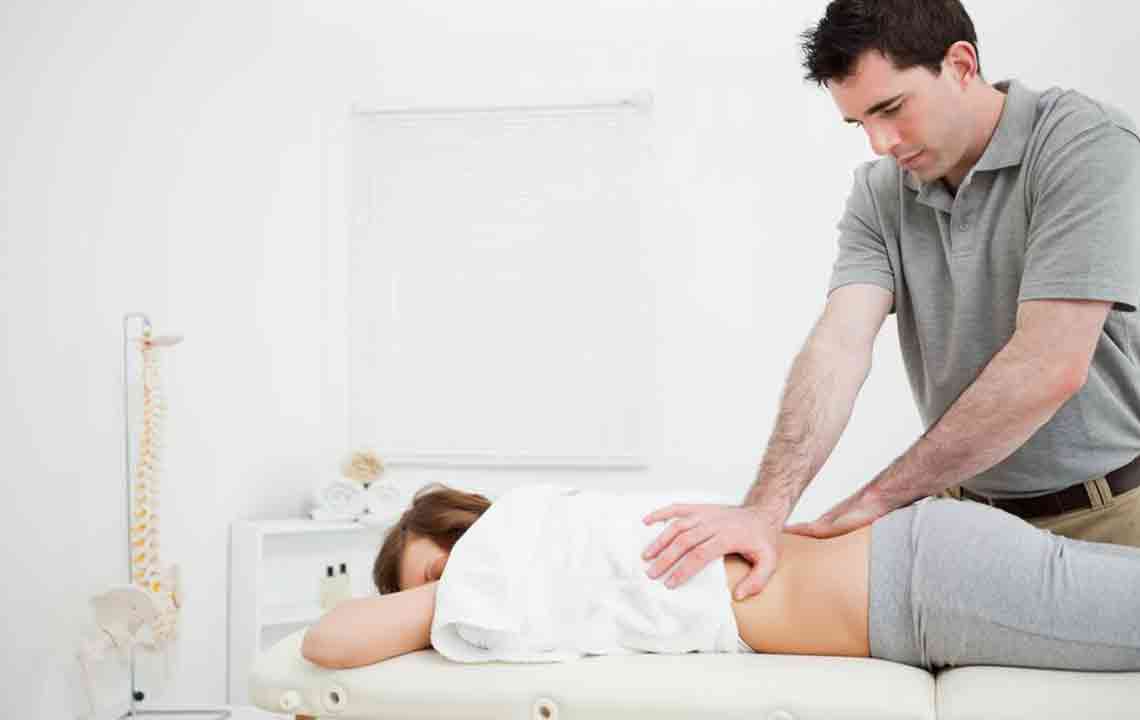
Complementary Therapies
Alternative treatments such as chiropractic care, acupuncture, yoga, massage, and TENS therapy can provide symptomatic relief. Acupuncture stimulates pressure points to ease pain, but must be performed by trained practitioners. Yoga and massage assist in relaxing muscles and improving flexibility, while TENS uses mild electric currents to reduce pain in severe cases. Since there is no cure, long-term management involving medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments is essential. Surgery is reserved for the most critical situations.